Daily Current Affairs Quiz
9 January, 2025
International Affairs
1. MAGA (Make America Great Again)
Context:
There is a big battle brewing between Trump and his advisor Elon Musk, who support H-1B visas, and the MAGA (Make America Great Again) group that wants jobs to go to Americans.
What is H1B Visa?
Make America Great Again (MAGA)
“Make America Great Again,” abbreviated as MAGA, is an American political slogan officially popularized by Donald Trump during his presidential campaigns in 2016 and 2024. It refers to Trump’s political base and generated widespread clamor as a pop culture phenomenon. Originally used in the 1980 campaign of Ronald Reagan, the slogan has been denounced as racist and dog-whistle politics.
2. Greenland
Context:
President-elect Donald Trump has reignited interest in Greenland, proposing it as a valuable strategic addition to the U.S. territory. While the idea may sound audacious, it has sparked discussions about the island’s value, strategic significance, and feasibility of such a purchase.
Greenland
Greenland is an autonomous territory of Denmark, the largest of two within the Kingdom. It is one of the Overseas Countries and Territories of the European Union, and its citizens are European Union citizens. The capital is Nuuk, and it lies between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans. Greenland is the world’s largest island, and the location of the northernmost point of land, Kaffeklubben Island off the northern coast.
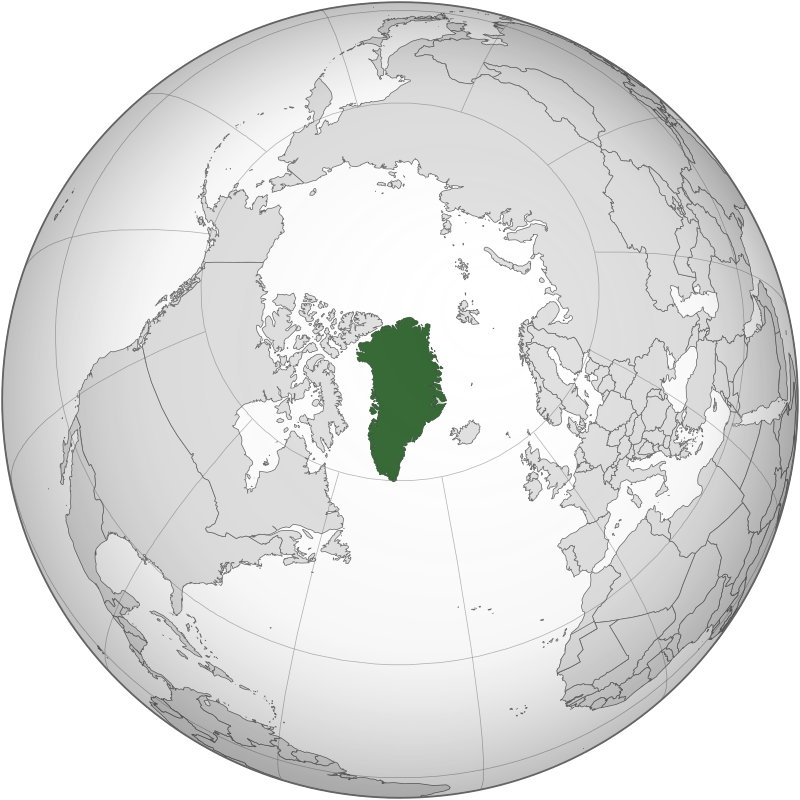
Greenland is a significant geographical feature for a number of reasons, including its size, location, and natural resources:
- Size:
- Greenland is the world’s largest island, covering 2.175 million square kilometers. It is even larger than the combined areas of France, Germany, Spain, the United Kingdom, Italy, Greece, Switzerland, and Belgium.
- Location:
- Greenland is located between the Atlantic and Arctic Oceans, which makes it Geopolitically positioned between Europe, North America, and the Arctic zone.
- Natural resources:
- Greenland has most probably potential oil, gas, and rare earth mineral reserves. Global warming is melting the ice, which has increased access to these resources.
- Ice cap:
- Over 80% of Greenland is covered with a permanent ice cap that’s 4 kilometers thick in some places.
- The melting of this ice due to global warming has increased the possibility of new trade routes opening in the Arctic.
- Coastline:
- Greenland’s coastline is jagged and made up of fjords and icebergs.
- National park:
- Northeast Greenland National Park is the world’s largest national park.
Greenland is an autonomous Danish dependent territory with having self-government and its own parliament. It is technically part of North America, but has been politically and culturally associated with Europe since the 9th century.
3. Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV)
Context:
The World Health Organization is in contact with Chinese health officials and has not received any reports of unusual outbreak patterns, its latest disease outbreak report on Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) said.
National Affairs
1. Digital Personal Data Protection Rules
Context:
Union Minister of Electronics and Information Technology Ashwini Vaishnaw is planning to finalize and notify the draft Digital Personal Data Protection Rules by mid-year.
The Draft Digital Personal Data Protection Rules 2025
2. Joint Parliamentary Committee
Context:
At the first meeting of the Joint Parliamentary Committee on two Bills on conducting simultaneous polls.
Joint Parliamentary Committee
A joint parliamentary committee is formed in case a motion is adopted in one house and then supported or agreed upon by another house. It can also form a joint parliamentary committee by making a joint representation to the presiding chiefs of both houses where they can correspond with each other and form such a committee.
What is a motion?
A motion in Parliament is a proposal put forth by a member of Parliament with the intent of discussing or changing the course of the law. Parliamentary proceedings and motions are the very roots of a practice allowing legislators to debate all the topics of great public concern.
ONE NATION ONE ELECTION
3. Battery Energy Storage System (BESS)
Context:
India’s first commercial utility-scale battery energy storage system (BESS) will be launched in Delhi.
Key Highlights:
- Battery Cluster
- A 20 MW/40 MWh battery cluster will provide power for four hours in a day.
Battery Energy Storage System (BESS)
A battery energy storage system (BESS) is a collection of batteries that stores energy from a power plant or grid, integrating renewable energy sources like solar and wind, stabilizing the grid, reducing carbon emissions, and providing backup power during blackouts.
4. National Green Hydrogen Mission
Context:
“The country launched the National Green Hydrogen Mission in 2023. Our aim is to make 5 million metric tons of green hydrogen production annually by 2030. As a first step, two green hydrogen hubs will be set up, out of which one is in Visakhapatnam,” PM said.
The National Green Hydrogen Mission
The National Green Hydrogen Mission is a program that the Government of India launched on January 4, 2023.
- Objectives
- Accelerate the use of green hydrogen as a clean energy source
- Make India a global hub for the production, use, and export of green hydrogen
- Reduce India’s reliance on fossil fuels
- Contribute to India’s goal of becoming self-reliant
- Inspire the global transition to clean energy
- Targets
- Annual output of 5 million metric tonnes of green hydrogen by 2030
- Total investment of over ₹8 lakh crore by 2030
- Reduce fossil fuel imports by ₹1 lakh crore by 2030
Green hydrogen can be produced using renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydropower. It can replace fossil fuels in transportation and industry, and provide a reliable source of energy.
Other Initiatives Related to Renewable Energy
Green Ammonia
- Ammonia is a chemical used in nitrogenous fertilisers and engine running.
- Renewable Energy
- Green ammonia production is 100% renewable and carbon-free.
- Process
- Process involves hydrogen from water electrolysis and nitrogen separated from the air, powered by sustainable electricity.
- Uses
- Uses include energy storage, zero-carbon fuel, and marine industry.
- Green ammonia is crucial for producing carbon-neutral fertiliser products and decarbonizing the food value chain.
- It could also be a future climate-neutral shipping fuel.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles produce one of the following as “exhaust” (2010)
(a) NH3
(b) CH4
(c) H2O
(d) H2O2
Ans: (c)
5. Dam Safety Act, 2021
Context:
A three Supreme Court judge Bench headed by Justice Surya Kant said the Dam Safety Act, 2021, was “existing on paper” after the State of Kerala argued that “nothing has been done”, including the constitution of a National Committee on Dam Safety.
Dam Safety Act, 2021: Need and Features
- Need for Dam Safety:
- India is the third-largest dam builder in the world, with approximately 1,100 dams over 50 years old.
- The shelf life of medium and minor dams is lower, and the structural vulnerability of dams is a major concern.
- Flooding is increasing in frequency and intensity, which can exceed the design limits of the dam.
- Large dams are classified under “high hazard” infrastructure based on the risks of loss of lives, livelihood, and destruction.
The Salient features of the Dam Safety Act:
- Objective
- Provide for surveillance, inspection, operation, and maintenance of all the specified dams situated in the whole country.
- Institutional Mechanism
- Two National Level Bodies: National Committee on Dam Safety (NCDS) and National Dam Safety Authority (NDSA) providing policy guidelines as well as technical support to the State Dam Safety Organisations.
- State Level Bodies
- The SDSOs shall be in charge of inspection and surveillance of dams, and the State Committee on Dam Safety will oversee the state dam rehabilitation activities.
- Liability of Dam Owners
- Dam owners are liable for safe construction, operation, maintenance, and supervision of a dam.
- Offenses and Penalties
- Obstruction of a person or failure to comply with a direction may amount to imprisonment for one year or imprisonment for two years if the loss of life has ensued.
Problems with the Act:
- Jurisdiction of Parliament to Frame a Law on Intra-State River Dams
- The Act is applicable to all the dams specified in the country, but Parliament may regulate and develop inter-state river valleys if required.
- Schemes
- Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs approved the Dam Rehabilitation and Improvement Project (DRIP) Phase II and Phase III in 2020.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. On which one of the following rivers is the Tehri Hydropower Complex located? (2008)
(a) Alaknanda
(b) Bhagirathi
(c) Dhauliganga
(d) Mandakini
Ans: (b)
Exp:
- The Tehri Hydropower Complex (Tehri HPC) is located on the Bhagirathi River in the State of Uttarakhand in India. Hence, option (b) is correct.
Mains
Q. Suppose the Government of India is thinking of constructing a dam in a mountain valley bound by forests and inhabited by ethnic communities. What rational policy should it resort to in dealing with unforeseen contingencies? (2018)
Q. What do you understand by Run-of-river hydroelectricity project? How is it different from any other hydroelectricity project? (2013)
6. Ken-Betwa River Link Project
Context:
Ken-Betwa River Link Project, which aims to solve the water scarcity in the Bundelkhand region that covers parts of Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh. The project also includes the construction of a dam located within the Panna Tiger Reserve, raising concerns about its submergence.
Ken-Betwa River Link Project
7. The Right to Information Act 2005
The Right to Information (RTI) Act, 2005 provides rights to people with regard to receiving information from a public authority. The RTI Act came into force on June 15, 2005.
The Right to Information (Amendment) Act, 2019 is Act No. 24 of 2019. It was enacted by Parliament on August 1, 2019. The Act amended the Right to Information Act, 2005.
- The main amendment was to Section 13 of the Right to Information Act, 2005, which sets the term of the central Chief Information Commissioner and Information Commissioners.
- Objectives
- To ensure transparency in public service system Enable citizens of having access to the information by a public authority.
- Time Limit
- A few other salient provisions under the RTI Act include the strict following of time limit for delivering the information.
- Public authorities are entitled to pay response within 30 days of a request, or within 48 hours for matters related to life or liberty.
- Penalties
- There are penalties for failure to provide information on time, or for providing incorrect or incomplete information.
- Appeals
- Citizens can appeal decisions made by Public Information Officers (PIOs) if their requests are denied or not addressed properly.
- Fees
- Applicants below the poverty line (BPL) do not have to pay any fee, but they must submit proof.
- Exemptions
- A PIO can deny providing information if it would:
- Infringe on someone else’s copyright
- Cause disproportionate diversion of resources of the public authority
- Be detrimental to the safety or preservation of records
- A PIO can deny providing information if it would:
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. The Right to Information Act is not all about citizens’ empowerment alone, it essentially redefines the concept of accountability.” Discuss. (2018)
8. Public Distribution System (PDS)
Public Distribution System (PDS): A government-owned system that delivers food and other essentials to the poor at a subsidized rate. The PDS is operated by the Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution. Procurement, storage, and transportation of food grains are the Central Government’s responsibilities, while operational aspects are those of the State Governments.
Public Distribution System (PDS) Problems & Solutions
- Core Problems
- Public Distribution System exclusion from PDS rolls:
- Families in Bihar and Jharkhand are left without food entitlements.
- Lack of good ration supply by FPS dealers along with corruption:
- They issue short rations while the quality “Usna” rice is extremely poor.
- Public Distribution System exclusion from PDS rolls:
- Unnecessary Documentation
- Applicants are often asked for caste, income, and residence certificates, which are not required under the National Food Security Act (NFSA) or PDS control order.
- Middlemen Exploitation
- The Musahars, as well as other marginalized communities, are being exploited by middlemen who are charging up to ₹3,000 to process ration card applications.
- Delay in Ration Card Issuance
- Applications take months to be processed, denying people access to essential food items.
- The state knows what is wrong but still hasn’t come with systemic changes, it continues to bear the suffering of the worst-off communities.
- Digital Exclusion
- With the push for e-governance and a move toward digitalization of services, many people in rural areas, especially cannot access the system simply because they don’t have the resources or digital literacy to navigate the system.
- Possible Solutions
- System Reform Change
- Streamline the PDS application process and remove unnecessary documentation.
- Transparency and Accountability
- Reinforce oversight mechanisms against corruption in PDS.
- Digital Literacy and Access
- Invest in digital literacy programs that assist the underprivileged to better operate the e-governance platform.
- Ration Cards within the Specified Time
- The time for processing applications for ration cards must not exceed 30 days.
- Local-Level Support Mechanisms
- Ensure support systems are available at local levels for those applying under PDS.
- System Reform Change
Public Distribution System (PDS)
10. State Revenues and Fiscal Health
Main Priorities:
- Increased Reliance on Central Transfers:
- From FY16 to FY25, the share of central transfers in state revenue is expected to range between 23% to 30%.
- Declining Own Tax Revenue:
- For over a decade, the own tax revenue of states has remained stagnant below 50% of their total revenue.
- Emergence of SGST:
- The State Goods and Services Tax (SGST) has become a major revenue contributor, rising from 15% of total revenue in FY18 to 22% currently.
- Decreasing Non-Tax Revenue:
- Non-tax revenue is expected to fall below 24% of total state revenue in FY25, marking a 25-year low.
- Increasing Central Grants:
- Over the last 10 years, the share of Central grants in states’ non-tax revenue has risen to 65-70%.
State Tax Collection Efforts:
- Ineffectiveness in Tax Collection:
- States have struggled to fully utilize channels to enhance their own tax revenues.
- Falling Revenue-to-GSDP Ratios:
- States have witnessed a decline in their own tax revenue as a percentage of Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP) from FY13-15 to FY22-24.
Prominent Findings and Conclusions:
- Prolonged Dependence on the Centre:
- States are increasingly dependent on the Centre for financing, as central transfers and grants continue to grow as a proportion of their total revenue.
- Erosion of Fiscal Independence:
- Declining or stagnating own tax revenues are undermining the fiscal autonomy of states, limiting their ability to implement independent fiscal policies.
- Restricting Policy Flexibility:
- The inability of states to effectively mobilize their own tax revenues limits their policy space for implementing countercyclical fiscal measures.
- Focus on Tax Mobilization:
- States must enhance tax collection efficiency, broaden their revenue base, and reduce dependence on the Centre.
9. Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act
- Aim
- UAPA was passed in 1967.
- Seeks to prevent unlawful activities in India.
- Features
- Unlawful activity is defined as any action that disrupts the territorial integrity of India.
- Absolute power is assigned to the central government.
- Punishment
- The highest punishments include death penalty and life imprisonment.
- Applicability
- Applicable to both Indian and foreign nationals, even on foreign land.
- Time Period
- Charges can be filed within 180 days of arrests.
- Amendments
- 2004 amendment added “terrorist act” to offenses, banned 34 outfits.
- Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Amendment Bill, 2019
- In August 2019, Parliament cleared the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Amendment Bill, 2019 to designate people as terrorists.
- Act gives powers to the Director General of National Investigation Agency (NIA) to sanction seizure or attachment of property.
- The Act also permits officers of NIA to probe terrorism cases.
10. POCSO Act
Context:
In March 2024, the Sadashivanagar police booked Mr. Yediyurappa under POCSO Act for allegedly sexually assaulting a 17-year-old girl on February 2, 2024, at his residence. The case was later transferred to the Criminal Investigation Department (CID), which chargesheeted Mr. Yediyurappa.
The POCSO Act
The POCSO Act was enacted on 14th November 2012, addressing offenses of sexual exploitation and abuse of children in India.
- Definition
- The Act defines a child as any person below the age of 18 years and provides punishment based on the gravity of the offense.
- Ammendment
- This Act was read and amended in 2019 to introduce higher punishment, the death penalty to be precise to crimes of sexual violations against children.
- The government of India notified the POCSO Rules of 2020.
- Features
- There are some highlighted features, the Gender Neutrality, Easy cases reporting, Strict definition of all terms, also the support provider for the child.
- Under the POCSO Rules 2020, the Special Court can also pass an order for interim compensation for the child’s relief or rehabilitation needs pertaining to the period from the filing of the FIR.
- Courts Status
- On May 31, 2023, a total of 758 FTSCs with 412 e-POCSO Courts are operational across the country in 29 States/UTs.
Problems and Challenges under the POCSO Act:
- Investigation Issue:
- There is a very low percentage of women in the police force, lapses in the investigation, no examination by judicial magistrates, issue of age determination, delays in the filing of charges, and no conditions to prove recent intercourse.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Examine the main provisions of the National Child Policy and throw light on the status of its implementation. (2016)
11. The Venus Orbiter Mission
Context:
ISRO’s to-do list includes the Chandrayaan-4 moon mission, the development of the space station, Bharatiya Antariksha Station, a second mission to Mars, and the maiden Venus Orbiter Mission.
The Venus Orbiter Mission
The Venus Orbiter Mission, also known as Shukrayaan, is a mission by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) to study the planet Venus:
- Objectives
- The mission will study the surface, atmosphere, and interaction of the planet with the sun. It will also test aerobraking and thermal management techniques in the Venusian environment.
- Payloads
- The mission will carry 16 Indian payloads, two Indian and international collaborative payloads, and one international payload.
- These payloads include the Venus Ionospheric and Solar Wind Particle AnalySer (VISWAS), Radio Anatomy of Venus Ionosphere (RAVI), and VIRAL (Venus InfraRed Atmospheric gases Linker).
- Launch
- The mission is scheduled for launch in March 2028. The LVM-3 launch vehicle is expected to place the spacecraft in an elliptical parking orbit around Venus.
- Collaboration
- The mission will include Indian industries, academic institutions, and students at different stages of the project.
- Significance
- Scientists can learn about climate change, atmospheric dynamics, and the evolution of a planet by studying Venus.
- This knowledge might help scientists know more about Earth’s potential future and what makes a planet habitable.
12. PM E-Drive Scheme
‘PM Electric Drive Revolution in Innovative Vehicle Enhancement (PM E-DRIVE)’ Scheme, approved by Cabinet recently with a financial outlay of Rs.10,900 crore, has come into effect from October 1, 2024, and will remain in force until March 31, 2026.
- Ministry
- Ministry of Heavy Industries (MHI) of the Government of India
Key Features
- Features
- Offers 80% maximum subsidy for all charging points installation across the country.
- Provision of ₹2,000 crore for establishing the fast-charging points in a total of 72,300 points, which will include 48,400 for electric two and three wheelers, 22,100 for electric cars, and 1,800 for electric buses and trucks.
- Focus
- It will mainly focus on upgrading the present 1,300 charging points in India, especially in 40 identified cities and 40 highway corridors.
- Charging Infrastructure
- On the general note, it also emphasizes India’s underdeveloped charging infrastructure, with Evs supposedly having a market share of about 7.5% by 2025.
- Subsidy
- Points out the significance of the effectiveness of the subsidy-disbursal mechanism for the success of the scheme.
- Public Transportation
- Stimulates the using of electric buses and trucks to mitigate environmental as well as logistic challenges posed by diesel-powered vehicles.
- Major Drawback
- Digs into the problem on the part of the deficiency of charging stations, an important hurdle in the EV market development.
Banking/Finance
1. Laxmi Dental sets IPO price band
Context:
Laxmi Dental Ltd. will tap the capital market with an initial public offering (IPO) in the price band of ₹407 to ₹428 per equity share of face value of ₹2 each.
How a Company Decides its IPO Price?
- The past financial performance of the company
- The peers of the company in the industry
- The potential growth of the company
- Industry outlook:
- General view of the industry
- The most significant method of valuing a company is through discounted cash flow, which works as the net present value of the company’s future expected cash flows.
- There are two types of IPOs: fixed price and book building
- Fixed Price:
- The price of the shares is fixed on the first day of listing.
- Fixed Price:
- Book Building:
- The price is determined after aggregating the demand from bids. In this process, the company sets a price range, and investors place their bids within that range.
Initial Public Offering (IPO)
3. Supervisory Restrictions by RBI
Context:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) lifted the supervisory restrictions imposed on Chennai-based Asirvad Micro Finance Ltd., and Delhi-based DMI Finance Private Ltd. with immediate effect.
- Reason for Lifting Restrictions:
- The RBI was satisfied with the changes implemented by the companies to ensure fairness in loan pricing.
- Background:
- The restrictions were initially imposed in October due to concerns over excessive interest rates charged to borrowers, specifically linked to the weighted average lending rate (WALR) and interest spread over the companies’ cost of funds, which were deemed too high.
- The weighted average lending rate (WALR) is the average lending rate for a group of loans.
- As of the end of November 2024, the WALR on fresh rupee loans from commercial banks was 9.40%, down from 9.54% in October 2024.
- The restrictions were initially imposed in October due to concerns over excessive interest rates charged to borrowers, specifically linked to the weighted average lending rate (WALR) and interest spread over the companies’ cost of funds, which were deemed too high.
The Reserve Bank of India has the following supervisory restrictions imposed on banks:
- Prompt Corrective Action (PCA) Framework
- This framework puts a restriction on lending by the banks that have financial difficulties and watches them until the financial position is improved.
- PCA Framework includes restrictions in the form of dividend distribution, branch expansion, and management compensation.
- Capital-related actions
- Making the banks review capital planning at the board level
- Compelling banks to file plans to raise additional capital
- Compelling banks to raise their reserves through retained profits
- Limiting investment in subsidiaries and associates
- Limiting the expansion of high risk-weighted assets
- Reducing exposure to high risk sectors
- Limiting increasing stake in subsidiaries and other group companies
- Supervisory returns
- The RBI has standardized the filing of supervisory returns by banks.
- For instance, state-run banks are required to submit half-yearly and quarterly reviews of accounts within 21 days.
- Other supervisory initiatives
- Quarterly monitoring visits to banks
- Appointment of monitoring officers
- Direct monitoring of certain problem areas
- Monitoring cases of frauds perpetrated in banks
4. SEBI Warns Ola!
SEBI, the markets regulator in India has warned Ola Electric for announcing information about its firm on social media before making a disclosure to investors.
What are SEBI norms on Social Media Content?
- Unregistered financial influencers
- SEBI, India’s securities and commodity market regulator, has suggested the end of unregistered financial influencers’ social media content.
- SEBI identifies these influencers as practices to persuade the public into investing in the stock market.
- SEBI, India’s securities and commodity market regulator, has suggested the end of unregistered financial influencers’ social media content.
- Draft Circular for Specified Digital Platforms (SDP Circular)
- The SEBI published a Consultation Paper on the Draft Circular for Specified Digital Platforms (SDP Circular) on 22 October 2024 to safeguard the public from financial and securities advertisements by unregistered individuals.
SEBI Introduces Fixed Price Process for Delisting Shares
- SEBI introduces a fixed price process for delisting frequently traded shares and a delisting framework for Investment and Holding Companies (IHC).
- The move comes amid concerns over potential risks associated with unregulated finfluencers offering biased or misleading advice.
Understanding Financial Influencers
- Financial influencers provide information and advice on financial topics, primarily on social media platforms.
- Income sources include advertisements, collaborations to promote financial products, and affiliate partnerships.
Rise of Finfluencers
- Finfluencers help educate and create awareness among new investors because of India’s low financial literacy rate.
- Increased retail investment and the pandemic have increased demand for financial advice.
- Technological advancements and affordable smartphones have enabled finfluencers to reach through social media platforms.
Problems from Rise of Finfluencers
- Lack of regulation makes it hard to evaluate the expertise and qualification of the finfluencer.
- Company manipulation of markets can lead to losses.
- Some high-risk investment products may be presented without adequate disclosures of risks involved.
- Quality and reliability of the financial advice tend to be compromised due to content-first approach.
- Social influence may be diluted by promoting the stocks in favor of personal gain.
Regulatory Action Previously Taken for Finfluencers:
- SEBI Regulations 2013 frames the guidelines of financial advice providers.
- ASCI revised guidelines require SEBI registration for influencers.
5. RBI’s Regulations on Asset Qualification Norms
Context:
Representatives of microfinance institutions (MFIs) raised concerns with Ministry of Finance officials regarding the Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI’s) regulations on asset qualification norms, which have been increased from 75 per cent to 85 per cent of total assets.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) regulates asset qualification norms for banks, microfinance institutions (MFIs), small finance banks (SFBs), and non-banking financial companies (NBFCs):
- Asset Classification
- Banks have to classify assets into four categories: Standard, Sub-standard, Doubtful, and Loss.
- This classification is based on the credit exposure’s realizability and the duration of non-performance.
- Provisioning norms
- Banks will need to keep a portion of their money in provisions to mitigate losses on non-performing assets.
- Asset qualifying norms for MFIs
- Applicants for the NBFC-MFI license have to, as minimum, dedicate at least 75 percent of the assets towards microfinance.
- Asset qualifying norms for NBFCs
- The minimum eligibility requirement for the NBFC is now fixed at 25 percent.
- NPAs
- An account shall be classified as an NPA if:
- Interest and/or principal installment are more than 90 days past due The account remains “out of order” The bill is more than 90 days past due SMA accounts Special mentioned.
- SMA Accounts (SMAs) are accounts that indicate stress in the borrower’s repayment behavior.
- An account shall be classified as an NPA if:
6. LIC’s Bima Sakhi Scheme
Context:
More than 52,000 registrations in a month since launch, an indicator of good demand and early success.
7. SEBI’s Amended Rules for Independent Advisers and Research Analysts
Context:
SEBI has made rules for independent advisers and research analysts more transparent and investor-friendly.
Independent advisers
Independent advisers are professionals who provide financial guidance and services without being affiliated with a large financial institution. They are also known as independent financial advisers (IFAs).
A research analyst
A research analyst is a professional who collects, analyzes, and interprets data to help businesses make informed decisions. They are often quantitative, analytical, and logical, and are good at managing numbers and data.
Key Features:
- Deposit Requirement
- Deposit requirement is linked with the maximum number of clients served in the previous financial year. independent advisers (IAs): 30 June, Research Analysts (RAs): 30 April.
- Registration flexibility
- RAs are allowed to be certified as IAs, ensuring separation between advisory and research functions.
- Scope of Advice
- IAs can give investment advice that is Sebi-regulated in securities. They are allowed to provide holistic financial planning for non-Sebi products.
- Implementation deadline
- 30 April.
- Revised Fee Structure
- IAs can change the mode of fee charging at any time, without the previous 12-month waiting period.
- AUA fees are capped at 2.5% per annum per family across all services.
- The maximum charge under the fixed fee is now raised to ₹1,51,000 per family per year against ₹1,25,000 till now.
Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI)
Economy
1. Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy (CMIE)
Context:
According to data from the Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy (CMIE), unlisted firms recorded sales growth of 8.34 per cent in the financial year 202324, compared to just 1.69 per cent for listed companies.
An Unlisted Public Company
An unlisted public company, also known as an unquoted public company, it is a public company that is not listed on any stock exchange. This enables it to raise finance by the issuing and sale of shares to the public, such as through advertising, but without listing on an exchange.
The Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy
The Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy is an independent private limited company, which is at the same time an economic think-tank and a business information company. CMIE research group has developed databases on the Indian economy and private companies. CMIE offers this information in the form of databases and research reports through a subscription-based business model.
- Founded
- 13 April 1976
- Founder
- Narottam Shah
- Headquarter
- Mumbai
2. Basic Terms of Economy
Context:
Achieving the aspirational target of increasing per capita income to attain developed country status by 2047 requires the economy to grow at an average rate of more than 8 per cent per year over the next 23 years.
Per capita income (PCI)
Per capita income (PCI) is a measure of the average income earned per person in a specific area over a given period of time:
- Calculation
- PCI is calculated by dividing a country’s national income by its population.
- Purpose
- PCI is used to evaluate the standard of living and quality of life for a population or area.
Purchasing power parity (PPP)
- PPPs are currency conversion rates that eliminate price level differences between countries. They are calculated for individual goods and services, product groups, and other levels of aggregation, including GDP.
- Example
- If a hamburger costs £2 in London and $4 in New York, the PPP exchange rate would be 1 pound to 2 U.S. dollars.
Inclusive growth
Inclusive growth is a concept that aims to create a society that is free, equal, and wealthy, while also reducing poverty and preserving economic freedoms.
Capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system where private individuals or organizations own the means of production, and prices are determined by supply and demand in a free market. The main characteristics of capitalism include:
- Private ownership: Private individuals and organizations own the means of production.
Crony Capitalism
Crony capitalism is a term used to describe an economic system where businesses are able to profit due to their close ties with the government.
Idea of National Income
3. Gold Googly Bamboozles Import Data
Context:
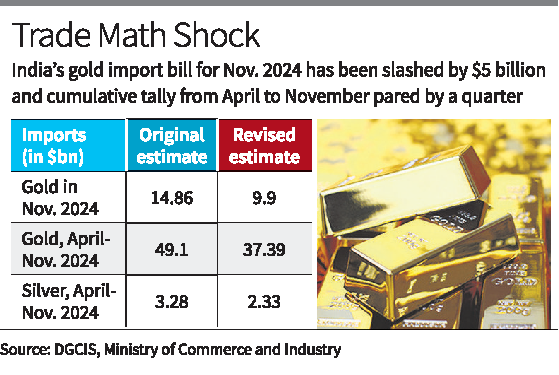
India’s overall import bill for the first eight months of 2024-25, reckoned to have grown 8.35% at $486.73 bn, has been pared by almost 3% to $472.5 bn, as per DGCIS data; the dramatic revisions alarm economists and one calls it ‘statistical harakiri’
Gold Reserve in Central Bank
The World Gold Council
Agriculture
1. Reforms in ICAR
Context:
P K Mishra, Principal Secretary in the Prime Minister’s Office said that there was a need for reforms in ICAR to have better outcomes and optimum resource use.
Key Suggestion:
- Financial Support to ICAR
- RS Paroda, founder chairman of Trust for Advancement of Agricultural Sciences demanded increased financial support to ICAR’s agriculture research and development.
- Hybrid Technology adoption
- Mishra said that this hybrid technology, especially for pulses and oilseeds should be accelerated.
- Issues in Hybrid Seed Adoption
- Mishra admitted that farmers face a challenge in adopting hybrid technologies, including the problem of annual seed purchases for hybrid crops.
- Hybrid seeds are seeds that are created by crossing two different varieties of the same plant species
- Mishra admitted that farmers face a challenge in adopting hybrid technologies, including the problem of annual seed purchases for hybrid crops.
- Potential of Hybrid Technology
- Though hybrid technology has proven potential to enhance productivity and climate resilience, their adoption is not uniform across different crops.
Genetically Modified (GM) Crops
The Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR)
2. ITC’s Medicinal and Aromatic Plants Initiative
The Aroma Mission is a CSIR initiative that aims to increase the cultivation of aromatic crops and improve farmers’ income.
Context:
ITC Limited is focusing on medicinal and aromatic plants, diversifying beyond traditional crops like wheat and rice.
- 101-acre Organic-Certified Farm:
- ITC runs a demonstration and training center for 27 medicinal plant varieties in Sehore, Madhya Pradesh.
- MAPS Programme:
- ITC is driving the MAPS Programme, focusing on raw herbs and value-added products.
- Modern Agriculture Platform (MAP)
- A program that aims to help farmers sustainably grow high-quality crops. MAP uses digital agriculture systems and a quality control system to connect the agricultural and food value chains.
- Agro-MAPS
- A web-based information system that provides statistics on primary food crops. The data is presented on a map background and can be selected by country, crop, and year.
- Precision agriculture mapping
- A subset of GIS (geographic information systems) that uses satellite and aerial imagery to map agricultural features. Farmers can use this information to determine where to apply water, fertilizer, and pesticides, and to assess soil conditions.
- Farmer Support:
- Trains and guides medicinal plant cultivation across 14 districts in Madhya Pradesh.
- Growth in Income:
- Farm families growing medicinal plants earns 26% to 35% more than the other crops they grow.
- Value-added Support Post-Harvest:
- Grading, sorting, marketing, and a buy-back.
- NextGen Agriculture Strategy:
- The effort is aligned with the strategy of scaling up the portfolio of Value-Added Agri Products.
Schemes for Welfare of Farmers
3. Large Area Multipurpose Co-Operative Society (LAMPS)
Facts To Remember
1. SIP Inflows Cross Rs 26,000 Crore Mark For 1st Time In December
- AMFI The inflow into systematic investment plans (SIPs) crossed the 26,000 crore rupee mark for the first time, reaching 26,459 crore rupees in December, compared to 25,320 crore rupees in November.
2. 2nd shipment of 27,000 tons of rice from India to arrive in Bangladesh
In Bangladesh, under the government’s open tender agreement, the second shipment of 27,000 tons of rice is scheduled to arrive tomorrow at Chattogram port from Kakinada port of Andhra Pradesh, India
3. Indian diaspora serves as nation’s ‘ambassadors to the world’
- PM Modi Prime Minister Narendra Modi today emphasized the crucial role of the Indian diaspora in transforming the country into a developed nation by 2047.
4. India, Afghanistan discuss bilateral ties, development projects & humanitarian assistance
- Foreign Secretary Vikram Misri and Acting Foreign Minister of Afghanistan, Mawlawi Amir Khan Muttaqi, discussed various issues pertaining to bilateral relations as well as regional developments in Dubai yesterday.
5. Union Minister Shivraj Singh Chouhan discusses budget with FM Sitharaman
- Union Minister for Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare, Shivraj Singh Chouhan met Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman in New Delhi and discussed several issues given the upcoming union budget.
6.ISRO again postpones docking experiment of 2 SpaDex satellites
- Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has postponed the docking experiment of its two satellites rotating in low Earth orbit under the SpaDex mission.
7. Malaysia open 2025: Indian shuttler HS Prannoy losses in Men’s Singles pre-quarterfinals In Malaysia
- Open Badminton, Indian shuttler HS Prannoy lost to China’s Li Shifeng 8-21, 21-15, 21-23 in Men’s Singles pre-quarterfinals in Kuala Lumpur today.
8. NZ cricketer Martin Guptill announces retirement from international cricket
- New Zealand Cricketer, Martin Guptill announced his retirement from international cricket at the age of 38. Guptill’s career spanned around 14 years during which he scored over 14 thousand runs in 367 matches and smashed 23 international hundreds. Guptill played 198 ODI, 122 T20Is and 47 Tests.
9. Filmmaker and poet Pritish Nandy passes away at 73
- Poet, painter, film producer and former parliamentarian Pritish Nandy passed away at 73 on Wednesday. Actor Anupam Kher paid tribute in a post on X, calling Mr. Nandy a fearless artist and a source of strength during his struggling years.
10. India’s Misri meets Taliban’s Foreign Minister in Dubai
- Marking the highest outreach with Afghanistan’s Taliban regime, Foreign Secretary Vikram Misri on Wednesday met with the Taliban’s Foreign Minister Mawlawi Amir Khan Muttaqi, in the UAE.
















