SEBI Phase II Main English Descriptive Previous Year Questions and Model Answer 2024
| Section | Details |
|---|---|
| Year | SEBI 2024 |
| Essay (30 Marks) | – Word Limit: 250-270 words |
| – SEBI Asked in 2024: | |
| 1. How can environmental social governance norms help in global business prospects (Economy/CA)? | |
| 2. How can organisations and management nurture organisational culture? (Management) | |
| 3. What role can banks play in pushing social healthcare expenditure? (ESI) | |
| 4. One machine can replace 5 average humans, but 5 machines cannot replace 1 smart human. Elaborate. | |
| Precis (30 Marks) | – Word Limit: 140-160 words 1. Dawn of social influencers |
| Reading Comprehension | – Marks: 40 |
| – Questions: 5 (70-80 words each) | |
| – Previous Year Asked Passages 2024: | |
| 1. Evolution of gaming industry since 2000s | |
| Exam Pattern | – Mode: Online (Typed using keyboard) |
| – Paper: General English (33.33%) | |
| – Type of Paper: Descriptive | |
| – No. of Questions: 3 | |
| – Duration: 60 minutes | |
| Previous Year Cutoff | To be updated based on available data |
Model Answer, word limit, pattern and Previous Year cutoff for SEBI Phase II English descriptive question
01. Pattern of Exam
| Exam | Mode | Paper | Type of Paper | No. of Questions | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paper 2 | Online (typed using keyboard) | General English (33.33%) | Descriptive | 3 | 60 minutes |
02. Word Limit for SEBI Grade A English descriptive online paper phase II
| Section | Word Limit | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Essay | 250-270 words | Write a detailed essay on the given topic. |
| Reading Comprehension | 5 questions, 70-80 words each | Answer questions based on a given passage. |
| Precis | 140-160 words | Summarize the given passage concisely while retaining its essence. |
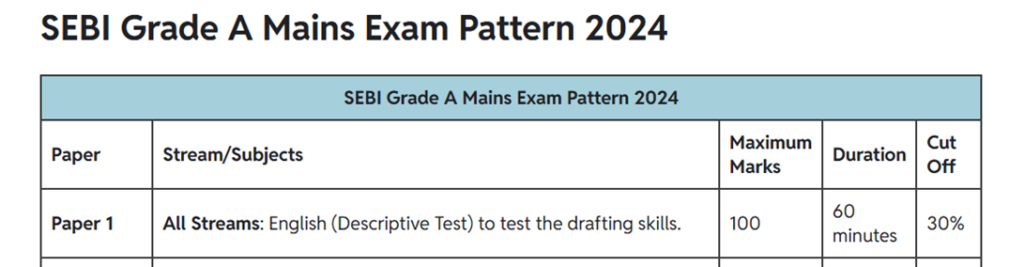
03. Cutoff of SEBI English descriptive paper phase II – Paper -2
04. Model Answers
The length of model answers are more with more number of points which will help you to have better idea for the topic and write accordingly as per your need
- How can environmental social governance norms help in global business prospects?
(Economy/ C A) - How can organisations and management nurture organisational culture? (Management)
- What role can bank play in pushing social healthcare expenditure (ESI)
- One machine can replace 5 average humans but 5 machines cannot replace 1 smart human. Elaborate. (Static)
SEBI Previous Year Question Section
01. How can environmental social governance norms help in global business prospects?
Introduction
Environmental, social and governance (ESG) is a framework used to assess an organization’s business practices and performance on various sustainability and ethical issues. It also provides a way to measure business risks and opportunities in those areas. In capital markets, some investors use ESG criteria to evaluate companies and determine their investment plans, a practice known as ESG investing. In the face of increasing environmental challenges and societal expectations, businesses worldwide are embracing environmental and social norms to align with sustainability and ethical practices. These norms, rooted in addressing climate change, promoting social equity, and ensuring responsible corporate behaviour, are instrumental in shaping global business prospects. By integrating these norms into their strategies, companies are not only contributing to global well-being but also unlocking significant business opportunities.
ESG’s three core principles
As the number of ESG funds for managing investments increases, business and IT leaders are increasingly paying attention to ESG as a functional approach to doing business. Each aspect of ESG plays an important role in the effort to increase a company’s focus on sustainable and ethical practices. The following are details on common ESG criteria companies and investors use.
Environmental
Environmental factors involve considerations of an organization’s overall effect on the environment and the potential risks and opportunities it faces because of environmental issues, such as climate change and measures to protect natural resources.
Examples include Energy consumption and efficiency, Carbon footprint including greenhouse gas emissions, Waste management, Air and water pollution, Biodiversity loss, Deforestation, Natural resource depletion.
Social
Social factors address how a company treats different groups of people and its social impact, including employees, suppliers, customers and community members.
Examples include Fair pay for employees including a living wage, Diversity, equity and inclusion programs, Employee experience and engagement, Workplace health and safety, Data protection and privacy policies, Fair treatment of customers and suppliers, Customer satisfaction levels, Community relations including the organization’s connection to and impact on the local communities in which it operates, Funding of projects or institutions that help poor and underserved communities and Support for human rights and labour standards.
Governance
Governance factors examine how a company polices itself, focusing on internal controls and practices to maintain compliance with regulations, industry best practices and corporate policies. Examples include Company leadership and management, Board composition, including its diversity and structure, Executive compensation policies, financial transparency and business integrity, Regulatory compliance and risk management initiatives, Ethical business practices.
Rules on corruption, bribery, conflicts of interest, and political donations and lobbying.
ESG norms to promote global business prospects
- Driving Consumer Trust and Brand Value according to SASB Standards.
Consumers are increasingly favouring businesses that prioritize environmental and social responsibility. According to a 2023 Nielsen report, 73% of global consumers are willing to pay more for products and services from companies that demonstrate sustainability. Brands such as IKEA and Unilever have leveraged environmental norms by focusing on sustainable sourcing and reducing carbon emissions, which has led to increased customer loyalty and expanded market share.- Governments have also introduced initiatives to support businesses adopting environmental norms. For example, the European Union’s Green Deal promotes sustainable production and consumption, creating opportunities for companies to align with consumer preferences while accessing incentives like green subsidies.
- Attracting Investments through ESG Integration
Environmental and social norms are central to Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria, which many investors now prioritize. A 2022 report by Morningstar revealed that ESG-focused funds attracted $649 billion globally, a testament to the growing importance of sustainability in investment decisions. Businesses that adhere to these norms are perceived as lower-risk, future-ready, and aligned with long-term growth, attracting substantial capital.- Governments worldwide are fostering this shift. For instance, India launched the Sovereign Green Bond Framework in 2023 to finance projects addressing climate change. Such initiatives signal clear opportunities for businesses integrating environmental and social standards.
- Regulatory Compliance and Competitive Advantage
Adherence to environmental and social norms ensures regulatory compliance, safeguarding companies from penalties and market exclusions. For instance, the European Union’s Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) mandates companies to disclose their ESG practices, fostering transparency and accountability. Non-compliance with such regulations can lead to hefty fines, loss of reputation, or restricted access to international markets.
China’s 14th Five-Year Plan (2021-2025) includes stringent targets for reducing carbon intensity and improving energy efficiency. Companies that align with these goals can benefit from government incentives, tax breaks, and increased trade opportunities. - Promoting Innovation and Cost Efficiency
Environmental norms drive innovation, as companies invest in renewable energy, waste reduction, and sustainable technologies to meet global standards. For example, renewable energy adoption saved businesses approximately $4.7 billion globally in energy costs in 2022, according to a report by the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA).- Governments are also facilitating this transition. The United States’ Inflation Reduction Act (2022) offers $369 billion in climate and clean energy incentives, encouraging businesses to innovate in renewable energy and carbon capture technologies. By adopting such measures, businesses not only reduce operational costs but also gain a competitive edge in global markets.
- Expanding Market Access and Partnerships
Environmental and social norms open doors to new markets and partnerships. Many countries require businesses to meet sustainability criteria to access their markets. For instance, the African Continental Free Trade Area (AFCFTA) prioritizes green trade, creating opportunities for businesses adopting sustainable practices.- Moreover, global initiatives like the Paris Agreement have fostered cross-border collaboration, with governments encouraging sustainable development. Businesses that align with these norms can partner with international organizations, governments, and NGOs to access funding and new markets.
- Fostering Resilience Against Global Risks
Adopting environmental and social norms helps businesses prepare for and mitigate risks associated with climate change, resource scarcity, and social instability. For example, a 2022 report by Deloitte found that companies with strong ESG frameworks were 63% more likely to recover from supply chain disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic.- Governments are actively supporting risk mitigation efforts. Japan’s Green Growth Strategy, introduced in 2021, aims to develop resilient industries that address environmental risks while fostering economic growth. Businesses that align with such strategies can build resilience and ensure long-term viability.
Conclusion
Environmental and social norms are no longer peripheral considerations but central to global business success. By aligning with these norms, businesses can enhance consumer trust, attract investments, ensure regulatory compliance, drive innovation, and expand market access. Supported by government initiatives such as the EU Green Deal, India’s green bond framework, and the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act, these norms offer a pathway to sustainable growth. As the global economy transitions toward sustainability, businesses that embrace environmental and social norms will not only contribute to a better world but also secure their place in the competitive global market
02. How can organisations and management nurture organisational culture?
“Positive culture comes from being mindful and respecting your co-workers, and being empathetic” Biz Stone
A strong company culture encourages teamwork and collaboration, which binds employees with trust and support for each other. This unity helps break down silos which result in better communication, innovation, and effective problem-solving among employees. The work culture is a product of its history, traditions, values and vision.
Importance of work culture in the success of an organisation
Transparency, innovation and discipline: Healthy work culture promotes transparency, innovation and discipline in an organisation.
Reduced Conflicts: Good work culture promotes effective communication and helps in reducing conflicts among individuals/team during work.
Increases Productivity and Quality: Transparency, responsibility, unbiased are underpinnings of good work culture. These will enable individuals and teams to become self-organized which in turn improves quality and productivity.
Sustainable Work: Good work culture includes peer respect, recognition of hard work, and freedom to bring new ideas (innovation). These will help in long term prospects of the organization.
Effective Communication: Healthy work culture provides a platform for effective communication among the verticals and horizontals of the organisation which helps in getting work done effectively.
Steps to improve organizational culture
Improving organizational culture is essential for fostering a positive, productive workplace where employees feel valued and motivated. Here are some key strategies to achieve this
- Connect employee work to a purpose: Help employees see how their work contributes to the organization’s mission and vision. When employees understand the impact of their efforts, they are more likely to feel engaged and aligned with the company’s objectives and key results (OKRs).
- Create positive employee experiences: Focus on crafting moments that matter throughout the employee lifecycle, from onboarding to offboarding. Positive experiences, like a warm onboarding process or celebrations of milestones and tools like pulse surveys and workplace chatbots, which allow employees to share their thoughts in real time contribute to an environment where employees feel supported and appreciated.
- Be transparent and authentic: Open communication builds trust. Share successes, challenges, and organizational updates openly with employees. Authenticity in leadership fosters a culture where people feel safe to voice opinions and ideas, creating a collaborative and honest workplace.
- Schedule regular and meaningful 1:1s: One-on-one meetings and team building activities between managers and employees offer an opportunity to address challenges, provide constructive feedback, and discuss career aspirations. When done regularly, these conversations build stronger relationships and demonstrate that the organization cares about professional growth and are effective ways to bring your team together and promote communication
- Encourage frequent employee recognition: Recognition is a powerful motivator. Celebrate achievements, both big and small, to create a culture of appreciation. Employee recognition platforms make it easy to implement a consistent and engaging recognition program, ensuring employees feel seen and valued for their contributions. Publicly celebrating these efforts reinforces that your values are more than just words — they’re guiding principles that drive your organization forward
- Make your leaders culture advocates
Building a strong workplace culture starts with team leaders and managers. Their actions set the tone for the entire organization, making it crucial that they consistently model the values your culture prioritizes.
To cultivate the right culture, leaders must make it a priority in every aspect of their work. This means consistently demonstrating the organization’s values, fostering open discussions about culture, and integrating employee feedback into their cultural initiatives. When leaders align their actions with the stated culture and advocate for it authentically, employees are more likely to follow suit. A leadership team that champions culture inspires employees to live those values daily, driving long-term success. - Live by your company values
Your company’s values are the foundation of its culture. While crafting a mission statement is a great start, living by company values means weaving them into every aspect of your business. This includes support terms, HR policies, benefits programs, and even out-of-office initiatives like volunteering. Your employees, partners, and customers will recognize and appreciate that your organization puts its values into practice every day. You can also recognize employees for actions that exemplify your values to show that they’re more than just words and incentivize employees to build the value-based culture you want to see. - Forge connections between team members
Building a workplace culture that can handle adversity requires establishing strong connections between team members, but with increasingly remote and tense communication, creating those bonds can be challenging.
These connections improve communication, spark creativity, and help resolve conflicts more effectively, especially among those from different generations that might otherwise have a difficult time relating to each other. This can create new pathways for understanding and empathy that are vital to improving communication, creativity, and even conflict resolution. - Focus on encouraging continuous learning and development
Organising work in a way that includes training programs, mentorship opportunities, and upskilling initiatives nurtures a learning-oriented culture. Great workplace cultures are shaped by employees who are continually learning and companies that prioritize staff development. Training initiatives, coaching, and offering new responsibilities are all effective ways to demonstrate that you are invested in your team’s growth.
By fostering a culture of continuous learning, companies can ensure long-term success while building an engaged and high-performing workforce and they are more likely to stay engaged, loyal and motivated. - Personalize the employee experience
As modern consumers, your employees expect personalized experiences, so you need to focus on ways to help each team member identify with your culture.
Additionally, incorporating personalized recognition and rewards into your workplace culture reinforces these efforts. Recognizing employees in ways that reflect their individual contributions and preferences fosters a sense of belonging. When employees feel seen and valued for who they are, they are more likely to engage, perform at their best, and contribute to a thriving culture. Personalization strengthens connections and promotes a positive work environment that drives success. - Prioritize mental health and well-being
Prioritizing mental health and well-being is essential to building a high-performing organizational culture. When employees feel supported in their mental health, they are more focused, engaged, and productive. Employees who feel mentally and emotionally supported are more likely to contribute creatively, collaborate effectively, and take on new challenges, all of which are crucial for driving performance leading to higher job satisfaction and lower turnover rates.
By offering resources such as counselling, mental health days, or stress management programs, companies show a genuine commitment to their employees’ overall well-being. A mentally healthy workforce is not only more resilient but also more aligned with the organization’s goals, ultimately contributing to long-term success. - Recognize and celebrate diversity
Recognizing and celebrating diversity, equity, inclusion, and belonging (DEIB) is key to building a strong and vibrant organizational culture. When individuals from different cultural, ethnic, and personal backgrounds come together, they bring unique viewpoints that can spark creativity and innovation. This diverse mix helps to challenge conventional thinking and encourage new solutions to problems.
A culture that values diversity also fosters a sense of belonging, where employees are empowered to be their authentic selves without fear of discrimination or exclusion. Celebrating diversity ultimately strengthens the organization and leads to improved performance, creativity, and employee satisfaction.
Conclusion
Work organisation is a fundamental tool for nurturing organisational culture. By aligning processes with core values, promoting collaboration, empowering employees, and fostering continuous learning, organisations create an environment that reflects and sustains their cultural ideals. Ultimately, a well-organised workplace not only drives operational success but also strengthens the shared values that bind employees together, creating a thriving organisational culture.
03. What role can bank play in pushing social healthcare expenditure?
Healthcare is a critical sector for social and economic development. However, financing healthcare effectively remains a challenge for many countries, especially in developing and emerging economies. In this context, banks can play a pivotal role in increasing social healthcare expenditure by serving as facilitators, financiers, and innovators. This essay explores the multifaceted role banks can play in driving healthcare investments and improving access to healthcare services.
- Facilitating Public and Private Investments in Healthcare
Banks are essential intermediaries in mobilizing funds for healthcare. By providing loans and credit facilities to governments, private entities, and non-governmental organizations (NGOs), banks enable the construction of hospitals, clinics, and other healthcare infrastructure. For instance, banks can collaborate with governments to offer long-term financing for public healthcare projects, ensuring the availability of modern medical equipment and technology in underserved regions.- Additionally, banks can encourage private-sector participation in healthcare through public-private partnerships (PPPs). These partnerships can help finance large-scale healthcare projects, such as specialty hospitals and rural health centres, by sharing risks and resources between public and private entities. For example, many banks globally have supported PPP models to build cost-effective primary healthcare facilities in rural areas.
- Promoting Inclusive Healthcare Financing
Banks have the potential to expand access to affordable healthcare by offering innovative financial products. For example, banks can introduce low-interest medical loans and health insurance schemes targeting low-income individuals. Microfinance initiatives can also empower marginalized communities by providing small loans for medical emergencies or preventive healthcare measures.
Moreover, banks can work with insurance companies to develop affordable health insurance plans and ensure their widespread availability. For instance, subsidized insurance policies facilitated through banks can provide coverage for critical illnesses and maternity care, reducing out-of-pocket expenses for vulnerable populations. - Supporting Technological Innovations in Healthcare
The banking sector can drive technological advancements in healthcare by investing in startups and companies developing innovative solutions. For example, banks can provide venture capital to firms working on telemedicine platforms, AI-powered diagnostics, and mobile healthcare applications. These technologies can bridge the gap between rural and urban healthcare facilities, offering affordable and accessible services to remote communities.
In addition, banks can leverage digital payment platforms to streamline healthcare financing. By promoting cashless transactions, banks can enable seamless payment for medical services, thereby enhancing efficiency and transparency in healthcare expenditure. - Creating Awareness and Financial Literacy
Banks can play an indirect but significant role in increasing social healthcare expenditure by promoting financial literacy and awareness. Through educational campaigns, banks can encourage individuals and families to prioritize healthcare savings and insurance. For example, financial literacy workshops can teach people how to set aside funds for health emergencies, thereby reducing the financial burden during crises. - Sustainable and Socially Responsible Investments
Many banks have adopted environmental, social, and governance (ESG) principles, prioritizing investments that generate positive social impacts. By channelling funds toward sustainable healthcare projects, such as green hospitals and renewable energy-powered clinics, banks can contribute to both healthcare improvements and environmental sustainability. Additionally, social bonds issued by banks can directly fund healthcare initiatives, such as vaccination drives and maternal health programs. - Role in Public Health Crises
During public health emergencies, such as pandemics, banks can play a crucial role in mobilizing resources quickly. For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, many banks partnered with governments to provide financial aid, support vaccination efforts, and ensure liquidity in the healthcare sector. Banks can establish special funds or emergency credit lines to support healthcare systems in times of crisis.
Conclusion
Banks are uniquely positioned to drive social healthcare expenditure by acting as enablers of financial resources and innovation. By financing healthcare infrastructure, promoting inclusive healthcare solutions, and investing in technological advancements, banks can bridge the gap between healthcare needs and resources. Moreover, their focus on financial literacy, sustainable investments, and crisis management ensures that they contribute to both immediate and long-term improvements in the healthcare sector.
As healthcare challenges evolve, the banking sector must continue to innovate and collaborate with stakeholders to ensure equitable access to healthcare services for all segments of society. By doing so, banks not only fulfil their social responsibility but also contribute to building healthier and more resilient communities.
04. One machine can replace 5 average humans but 5 machines cannot replace 1 smart human. Elaborate
Machines can’t replace human beings” means that while technology can automate many tasks, it lacks the essential human qualities like creativity, empathy, emotional intelligence, and complex decision-making abilities that are crucial for many aspects of life, making it impossible for machines to fully replicate the human experience and fulfill all the roles humans play in society.
The human brain is the ultimate source of creativity and it is man who created machines.
Teaching:
While a machine can deliver educational content, it cannot provide the emotional support, mentorship, and personalized guidance that a human teacher can.
Healthcare:
Although AI can assist in diagnosis, a doctor’s ability to empathize with patients and make complex medical decisions based on experience and intuition is crucial.
It is true that technology cannot replace manpower but it is also true that technology can reduce the requirement of manpower in any job. The famous example of this is US based Tesla motors, a leading electric car manufacturing company. Tesla motor uses cutting edge technologies in its manufacturing plant but assembly of cars occur manually. It is known fact that only 6 people are capable there who can assemble the engine of a category of car at Tesla motors which limits its production to maximum 250 cars per year. There is no such area extending from neurological surgery to cutting of grass which is fully automated. Everywhere requires human intervention.
There is a well- known robot hotel in Japan, where all activities starting from welcoming, taking order, serving food to cooking recipes are performed by robots only. There is also laboratory in Japan where research work performs by robots. But still there requires the human interface for maintenance and supervision of the activities of this human robot.
Technology can reduce effort, time, and fuel, shorten manpower requirement in every field but complete replacement of manpower is not possible. This is because machines can often perform such tasks faster, more consistently, and without fatigue. Thus, a single machine can “replace” the effort of multiple humans in such roles.
Man has created and developed the technology hence no technology shall be above the human being. Of course, there will be some instances when technology would appear dominant and society shall feel that requirement of manpower is reducing. Today every sector is having ample development in the field of technology but man power requirement has not been reducing significantly. Following are some of the reasons why technology can’t replace manpower completely.
- Technology has limitation in its field. This limitation is imposed by the developer itself. But human being has no limitation and it is evolving day by day.
- Every technology becomes absolute after some time and requires up gradation. Here manpower becomes essential component in area of research and development. While a machine can process resumes, a smart HR professional understands how to assess potential, cultural fit, and human motivations.
- At the time of European Industrial evolution, it was envisaged by many economists that rapid industrialization would result in unemployment but result is opposite. This has created high employment and played crucial role in economic empowerment of rural as well as urban areas.
- Development in IT sector has provided platform to new entrepreneurs, who are giving breakthrough in every aspect of human life. This has not replaced manpower but had generated greater opportunities where manpower can engage.
Smart humans, however, bring unique qualities that machines lack:
Creativity: Smart humans innovate, design, and think outside the box. Machines follow programmed instructions and lack the ability to independently create new ideas.
Problem-solving: When faced with ambiguous or complex challenges, smart humans can analyse the situation, learn from it, and adapt. Machines struggle without pre-defined rules.
Emotional Intelligence: Machines do not understand human emotions or cultural nuances. Smart humans excel at leadership, persuasion, and empathy—skills essential for managing people and driving progress.
Advantages and disadvantages of technological development run side by side. A perfect collaboration between both the sides is required.
Technology is dependent on human interference. No technology can replace manpower completely until unless a self-sustained, self-controlled; mutually interconnected computer program is designed, as occurs in science fiction movies which automatically controls the whole world.
This statement emphasizes the difference between repetitive, mechanical tasks and tasks requiring creativity, critical thinking, and emotional intelligence. Let’s break it down:
Conclusion
Machines are excellent tools for efficiency, but they lack the depth, adaptability, and human insight that “smart humans” bring. In fact, smart humans are often the ones designing and improving machines, ensuring they work better. This symbiotic relationship highlights that machines are complements, not replacements, for human intelligent.
Precis
Questions asked in NABARD PHASE -2 Paper 1 English descriptive online exam
Paragraph based on evolution of gaming industry since 2000s
Model answer to be updated soon
Reading Comprehension asked in SEBI English descriptive phase 2 online exam 2024
5 Questions on Passage on Dawn of social influencers
70-80 Words answer was to be written for each Question
Model answer to be updated soon
Burning topics for Essay Writing
1. Financial and Economic Topics
- The Role of SEBI in Regulating India’s Financial Markets
- Impact of Digital Currency on Financial Stability
- Importance of Financial Literacy in India
- Pros and Cons of Privatization of Public Sector Banks
- India’s Path Towards a $5 Trillion Economy
- ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) Investing: Trends and Challenges
- Startups and Unicorns: Their Role in India’s Economy
- Impact of Inflation on Investment Behaviour
- Financial Inclusion and the Role of FinTech Companies
02. Technology and Innovation
- Artificial Intelligence in Financial Regulation
- Role of Blockchain in Transforming Capital Markets
- Cybersecurity in Financial Institutions: Challenges and Solutions
- Impact of Digital Transformation on the Banking Sector
- RegTech: The Future of Regulatory Compliance
03. Social and Environmental Issues
- Climate Change and Its Impact on Financial Markets
- Sustainable Finance: The Way Forward
- Role of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) in Modern Businesses
- Gender Diversity in Leadership: Need for Change
- Impact of Urbanization on Real Estate Markets
04. Governance and Policy
- Role of SEBI in Investor Protection
- Corporate Governance in Indian Companies: Trends and Challenges
- Effectiveness of Monetary Policy in Combating Recession
- Impact of Recent SEBI Amendments on Corporate Compliance
- Data Privacy Laws and Their Implications for Financial Markets
05. General and Current Affairs
- Role of Media in Shaping Investor Sentiment
- Evolving Role of Women in Finance
- Influence of Global Recession on Indian Markets
- India’s Digital Economy: Growth and Challenges
- Ethical Investing: Balancing Profit with Purpose
















