
Origin
The Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC) was established in 1997. The organization was created to promote economic and social development among its member countries.
About
- Headquarter:
- Dhaka, Bangladesh
- Ministry:
- Ministry of External Affairs
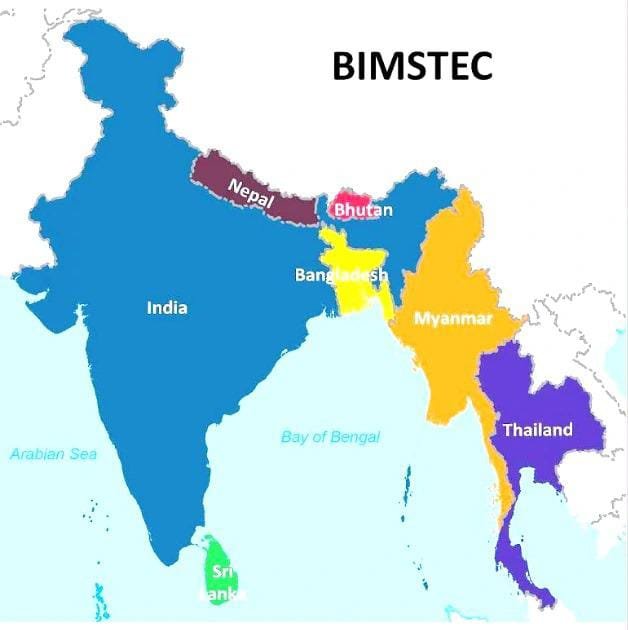
- BIMSTEC, which stands for the Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation, is a regional organization comprising seven countries:
- Bangladesh
- India
- Myanmar
- Sri Lanka
- Thailand
- Nepal
- Bhutan
- It was established in 1997 with the aim of fostering cooperation among these countries in various sectors such as trade, technology, energy, environment, and tourism, while promoting regional integration and development.
What is BIMSTEC?
BIMSTEC was established in 1997 and consists of seven member states that are located around the Bay of Bengal. These countries are:
- India
- Bangladesh
- Myanmar
- Sri Lanka
- Thailand
- Nepal
- Bhutan
- The primary objective of BIMSTEC is to foster cooperation across multiple sectors, focusing on economic and technical development, trade, connectivity, and regional security.
- The organization aims to enhance regional integration among its member countries, which are geographically significant and have cultural, historical, and economic ties.
Key Objectives of BIMSTEC
- Economic Cooperation:
- Enhancing economic connectivity and trade relations between member countries through reduction of trade barriers, tariffs, and improving infrastructure.
- Regional Security:
- Promoting peace and security in the region through collaboration in combating terrorism, transnational crime, and addressing maritime security concerns.
- Cultural and People-to-People Connectivity:
- Encouraging cultural exchanges, tourism, and collaboration in education to foster closer ties among the people of member nations.
- Technology and Knowledge Sharing:
- Strengthening collaboration in sectors like information technology, agriculture, energy, and education through sharing of technical expertise and resources.
- Environmental Cooperation:
- Working together on climate change, natural resource management, and disaster response in the region, which is highly prone to natural disasters like cyclones and floods.
BIMSTEC’s Structure and Mechanisms
BIMSTEC is structured around several key working groups and mechanisms that ensure its objectives are met. These include:
BIMSTEC Secretariat
- Location:
- Dhaka, Bangladesh
- The Secretariat functions as the administrative and coordinating body of BIMSTEC. It ensures the implementation of decisions made during summits and ministerial meetings and works towards fostering cooperation among member states.
- Leadership:
- The Secretariat is headed by an Executive Director, who is appointed from one of the member states on a rotating basis.
Summit and Ministerial Meetings
- Summits:
- Held every two to three years, BIMSTEC Summits bring together the heads of state/government from member countries to review and advance cooperation in key areas.
- Ministerial Meetings:
- These occur more frequently, typically annually, involving foreign ministers or ministers from other relevant departments. They address the progress of cooperation, approve the annual action plan, and review issues related to regional and global challenges.
Sectoral Working Groups (SWGs)
These are the core mechanisms through which BIMSTEC’s goals are implemented. Each SWG focuses on specific sectors, including:
- Trade and Investment:
- Led by the Economic and Trade Division, this group works on promoting intra-regional trade, enhancing investment opportunities, and addressing trade barriers.
- Technology and Innovation:
- Works on fostering research and development (R&D) collaboration, as well as technology transfer, particularly in areas like ICT, biotechnology, and agriculture.
- Energy:
- This group promotes the development of energy infrastructure, focusing on renewable energy and cross-border energy trade, such as the India-Bangladesh energy cooperation.
- Environment:
- Works to improve environmental governance, tackle regional challenges like climate change, and collaborate on disaster management.
- Agriculture and Food Security:
- Focuses on ensuring food security and sustainable agricultural practices.
- Transport and Connectivity:
- Aims to enhance regional connectivity through infrastructure development, such as roads, ports, railways, and aviation, along with regional transport agreements.
- Tourism:
- Encourages cross-border tourism initiatives and joint marketing of the BIMSTEC region as a travel destination.
Regional Cooperation Agreement (RCA)
- The BIMSTEC Regional Cooperation Agreement lays out the specific framework under which member states work together. This includes cooperation in sectors like trade, disaster management, technology, and environment.
BIMSTEC and India’s Strategic Interests
- India’s involvement in BIMSTEC is driven by both regional and global strategic interests. The Bay of Bengal region is increasingly becoming an important geopolitical space, especially as global power dynamics evolve. India has several reasons for prioritizing BIMSTEC as a key pillar of its foreign policy.
- Strengthening Neighborhood First Policy:
- As part of its Neighborhood First policy, India seeks to deepen its ties with its immediate neighbors in South Asia and Southeast Asia. BIMSTEC is a natural platform for India to build stronger relations with countries like Bangladesh, Bhutan, Nepal, and Myanmar.
- Countering China’s Influence:
- One of India’s key objectives in BIMSTEC is to counterbalance China’s growing influence in the region. China’s involvement in the Indian Ocean Region, particularly through the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), has raised concerns in India.
- BIMSTEC offers an alternative regional cooperation platform, ensuring that the countries in the Bay of Bengal region can develop without being overly reliant on China. India’s role within BIMSTEC, thus, serves as a counterweight to China’s strategic presence.
- Promoting Regional Connectivity:
- India’s emphasis on connectivity projects within BIMSTEC serves not only to enhance trade and commerce but also to strengthen regional ties. Projects like the Asian Highway Network and the Mekong-Ganga Cooperation are central to India’s approach to enhancing connectivity in the Bay of Bengal.
- Economic Growth and Trade Opportunities:
- India views BIMSTEC as a platform to improve trade relations with countries that are strategically positioned in the Indo-Pacific region. Access to new markets and trade opportunities, especially with countries like Thailand and Bangladesh, provides India with a significant economic advantage.
- Peace and Stability in the Region:
- The Bay of Bengal region is vital to India’s maritime security. Strengthening regional cooperation through BIMSTEC helps India ensure peace and stability in its immediate neighborhood. By fostering closer ties with regional partners, India aims to mitigate security risks and promote a rules-based order in the region.
Key Initiatives

BIMSTEC Free Trade Area (FTA)
The BIMSTEC FTA aims to reduce tariffs and barriers to trade between member countries, thereby increasing intra-regional trade and reducing dependency on outside regions. It is currently under negotiation, with specific focus on:
- Goods Trade:
- Tariff reduction and non-tariff barrier removal.
- Services and Investment:
- Moving towards liberalizing services trade and cross-border investments.
Connectivity and Infrastructure Development
- Transport Connectivity:
- BIMSTEC emphasizes the development of multimodal transport networks (road, rail, sea, and air) to improve the movement of goods and people.
- Energy Connectivity:
- Focus is placed on creating cross-border energy corridors to facilitate energy trade and ensure energy security in the region, especially with renewable energy sources.
Disaster Risk Reduction and Environmental Cooperation
- BIMSTEC Centre for Weather and Climate:
- This initiative is aimed at improving regional disaster preparedness, especially in the face of cyclones and floods that frequently impact the region.
- Sustainable Development Initiatives:
- Focus on climate resilience, conservation of natural resources, and collaborative management of environmental challenges.
BIMSTEC Technology Cooperation
- Innovation Centres:
- These centers promote collaborative research in areas like agriculture, healthcare, and information technology. Countries work together on technology transfer, joint ventures, and sharing expertise.
- ICT Cooperation:
- An emphasis on developing a digital economy through shared technology initiatives and enhancing connectivity via digital platforms.
Tourism Cooperation
- Joint Tourism Promotion:
- The region has worked to market BIMSTEC as a common tourism destination, fostering collaborations to boost visitor numbers and promote cultural exchanges.
- Visa Facilitation:
- Member countries have been working on visa facilitation measures to increase tourism, including policies for easy visa access for tourists traveling within the region.
BIMSTEC Framework
The organization operates through a series of sectoral working groups focused on the following areas:
- Trade and Investment
- Promoting trade and investment within the region, with an emphasis on reducing trade barriers.
- Technology and Innovation
- Fostering collaboration in tech research and development, and technology transfer between countries.
- Energy
- Encouraging sustainable energy initiatives, particularly renewable energy sources.
- Environment
- Enhancing cooperation in addressing environmental challenges and disaster risk management.
- Transport and Connectivity
- Strengthening regional connectivity, including through improvements in transportation infrastructure and regional agreements on trade and connectivity.
- Agriculture
- Promoting agricultural research and food security.
- Tourism
- Enhancing tourism between member nations and promoting the region as a unified travel destination.
Challenges and Opportunities
While BIMSTEC has had successes in fostering economic and political cooperation, it also faces several challenges, including:
- Diverse Political Systems and Economies:
- The countries in BIMSTEC have varying political systems and economic stages of development, which can sometimes make it difficult to find common ground for certain projects.
- Geopolitical Tensions:
- The region’s geopolitical complexities, especially with the involvement of countries like China and the broader Indo-Pacific context, can sometimes strain the effectiveness of BIMSTEC.
- Infrastructural Gaps:
- Despite progress, many BIMSTEC members still face infrastructural challenges that can hinder regional integration and growth.
- Economic Disparities:
- There is significant variation in the economic development levels of member countries, which can create difficulties in achieving uniform development goals and trade agreements.
- Security Issues:
- Some member states face internal security issues, such as terrorism or ethnic conflicts, that can affect cooperation on regional security.
Substantial Opportunities within BIMSTEC’s Framework
- Leveraging Regional Connectivity:
- The strategic location of the Bay of Bengal itself provides opportunities for fostering maritime trade, energy transportation, and regional logistics.
- Sustainability Initiatives:
- Given the shared environmental vulnerabilities, BIMSTEC has a unique opportunity to work together on regional climate change adaptation and sustainable development projects.
- Increasing Intra-regional Trade:
- BIMSTEC countries can work together to boost trade among themselves, moving away from external dependency and creating stronger economic ties.
Opportunities for BIMSTEC
Despite these challenges, BIMSTEC has immense potential to play a significant role in regional development:
- Strategic Location:
- The Bay of Bengal region is a key maritime area for trade, and BIMSTEC countries can leverage this position to enhance trade routes and logistics.
- Shared Environmental Concerns:
- Climate change and environmental degradation are common concerns for BIMSTEC members, offering an opportunity to collaborate on regional initiatives for sustainability and disaster management.
- Increased Economic Integration:
- Boosting trade between member countries and focusing on regional markets can help reduce dependency on non-member states, creating a more resilient and self-sufficient economy.
- Digital Transformation:
- By focusing on ICT and technological innovation, BIMSTEC can lead in creating a connected, tech-driven regional economy.
- Tourism and Cultural Diplomacy:
- Enhanced tourism and people-to-people exchanges can promote regional solidarity and help overcome geopolitical differences.
Recent Developments
In recent years, BIMSTEC has gained renewed attention, particularly with the global emphasis on the Indo-Pacific region. Some key developments include:
- Increased focus on regional security cooperation, especially addressing maritime security and combating terrorism.
- Strengthened partnerships with other regional organizations like ASEAN, as both groups share common goals for regional stability and prosperity.
- Enhanced focus on renewable energy and the implementation of sustainable practices across member states.
Conclusion
- In recent years, BIMSTEC has gained increased attention due to the need for regional integration in South Asia and Southeast Asia, and its role in promoting cooperation in the broader Indo-Pacific region. Through more strategic partnerships and shared goals, BIMSTEC could be a key player in regional geopolitics and economic growth.
















