
Introduction
In today’s digital-first world, businesses and individuals rely on cloud-based solutions for efficiency, scalability, and cost savings. One of the most transformative innovations in cloud computing is Software-as-a-Service (SaaS). Unlike traditional software that requires installation on individual devices, SaaS applications are hosted on the cloud and can be accessed from anywhere via the internet.
SaaS has revolutionized industries, allowing businesses to reduce IT costs, streamline operations, and improve collaboration. This blog provides a comprehensive guide to SaaS, covering its working mechanism, benefits, challenges, real-world applications, and future trends.
What is Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)?
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) is a cloud-based software delivery model where applications are hosted by a service provider and made available to users via a web browser. Unlike traditional on-premises software, SaaS does not require installation, maintenance, or hardware infrastructure, as everything is managed by the vendor.
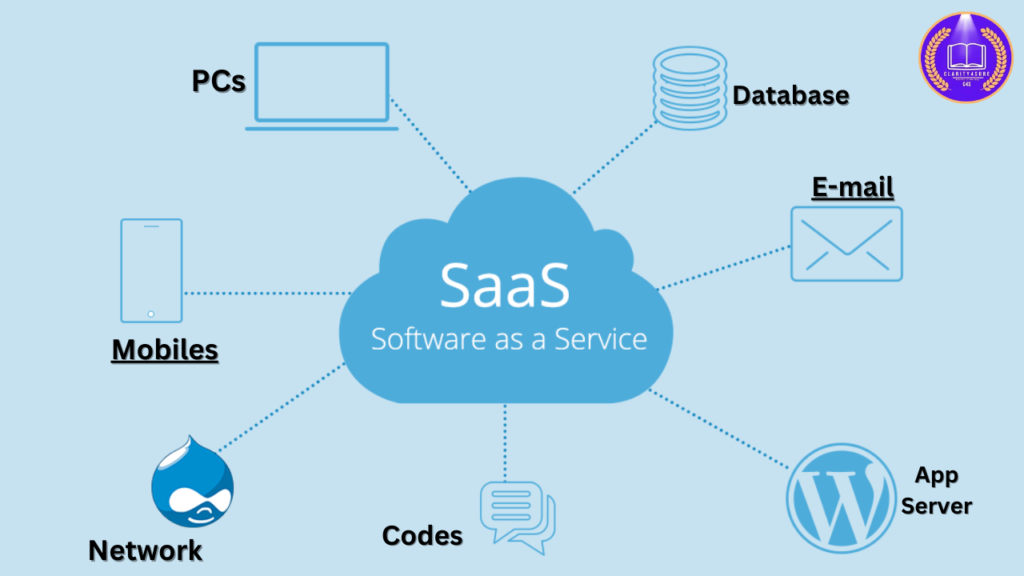
How SaaS Works ?
- Application Hosting –
- SaaS providers host applications on remote cloud servers.
- Internet Access –
- Users access the application via a web browser or dedicated app.
- Subscription Model –
- SaaS software is typically offered on a subscription basis (monthly/annually).
- Automatic Updates –
- The provider manages software updates, security patches, and maintenance.
- Scalability –
- Users can scale services up or down based on their business needs.
Benefits of SaaS
1. Cost Efficiency
- No need for expensive hardware or software licenses.
- Subscription-based pricing allows businesses to pay for what they use.
- Reduced IT maintenance costs, as providers handle updates and support.
2. Accessibility & Remote Work
- SaaS applications can be accessed from any device with an internet connection.
- Ideal for remote teams and businesses with multiple locations.
3. Automatic Updates & Maintenance
- Service providers manage all software updates and security patches.
- No need for manual installation or system downtime for upgrades.
4. Scalability & Flexibility
- Businesses can easily upgrade/downgrade their SaaS plans as per demand.
- Supports business growth without additional infrastructure costs.
5. Security & Compliance
- Leading SaaS providers implement high-end encryption, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and compliance certifications (GDPR, HIPAA, SOC 2, etc.) to ensure data security.
- Regular data backups prevent loss of critical information.
6. Seamless Integration
- SaaS applications often support API integrations with other software (e.g., CRM, ERP, accounting tools).
- Businesses can connect SaaS solutions with their existing workflows.
Challenges of SaaS
1. Dependence on Internet Connectivity
- SaaS applications require a stable internet connection for optimal performance.
- Downtime due to internet failures can disrupt operations.
2. Limited Customization
- While SaaS solutions offer some level of customization, they may not be as flexible as on-premises software.
- Businesses with specific requirements might need custom-built solutions.
3. Data Security & Privacy Concerns
- Since SaaS applications store data on third-party cloud servers, businesses must ensure strong security measures are in place.
- Compliance with data protection regulations (GDPR, CCPA, etc.) is crucial.
4. Vendor Lock-in Risks
- Migrating from one SaaS provider to another can be complex and costly.
- Businesses must carefully evaluate contract terms, exit strategies, and data ownership policies before committing to a SaaS provider.
Popular SaaS Applications & Use Cases
1. Business Productivity & Collaboration
- Google Workspace –
- Cloud-based office tools (Docs, Sheets, Gmail, Drive).
- Microsoft 365 –
- Word, Excel, Teams, and Outlook for businesses.
- Slack, Zoom, Asana –
- Team communication and project management.
2. Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
- Salesforce –
- Leading CRM software for sales and customer engagement.
- HubSpot –
- CRM and marketing automation for businesses.
3. E-Commerce & Retail
- Shopify, BigCommerce –
- SaaS platforms for online store management.
- WooCommerce –
- E-commerce solution for WordPress users.
4. Accounting & Finance
- QuickBooks Online, Xero –
- Cloud-based accounting and bookkeeping.
- Stripe, PayPal, Square –
- Online payment processing and invoicing.
5. Healthcare & Telemedicine
- Teladoc Health –
- Telehealth and virtual consultations.
- Epic Systems –
- Cloud-based Electronic Health Records (EHR).
Types of SaaS Applications
1. Horizontal SaaS
- Generic solutions used across industries.
- Examples: Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, Slack, Dropbox.
2. Vertical SaaS
- Industry-specific solutions tailored for healthcare, finance, manufacturing, etc.
- Examples: Epic (healthcare), Veeva (pharmaceuticals), Procore (construction).
How SaaS is Transforming Industries
1. Small & Medium Businesses (SMBs)
- Affordable and scalable solutions for startups and SMBs.
- Automates operations, accounting, and customer management.
2. Enterprise & Corporate Sector
- Large-scale cloud applications for workflow automation.
- Advanced analytics, AI-driven insights, and automation tools.
3. Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals
- SaaS-based EHR systems, telemedicine platforms, and AI-powered diagnostics.
- Enhances patient management and compliance with healthcare regulations.
4. Education & E-Learning
- Online learning management systems (LMS) such as Moodle, Blackboard.
- SaaS-based virtual classrooms and training platforms like Udemy, Coursera.
Future Trends in SaaS
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) & Machine Learning (ML)
- AI-driven SaaS will provide personalized recommendations, predictive analytics, and automation.
2. Edge Computing & Hybrid Cloud
- Edge computing will reduce latency and improve performance for SaaS applications.
3. Vertical SaaS Growth
- More industry-specific SaaS solutions (e.g., FinTech SaaS, MedTech SaaS).
4. Blockchain & Cybersecurity in SaaS
- Increased focus on data protection, secure transactions, and privacy using blockchain.
5. No-Code & Low-Code Platforms
- More businesses will build custom SaaS applications without coding expertise.
How to Choose the Right SaaS Solution for Your Business
- Assess Business Needs –
- Identify pain points and goals before choosing a SaaS solution.
- Check Security & Compliance –
- Ensure the SaaS provider follows GDPR, HIPAA, SOC 2 security standards.
- Consider Scalability & Pricing –
- Choose a SaaS model that grows with your business.
- Look for Integration Capabilities –
- Ensure seamless integration with existing tools & workflows.
- Evaluate Customer Support & SLA –
- Reliable customer support is essential for troubleshooting.
Conclusion
SaaS is transforming the way businesses operate, providing cost-effective, scalable, and flexible solutions for various industries. From startups to large enterprises, SaaS helps organizations improve productivity, streamline operations, and stay ahead of the competition.
As AI, blockchain, and edge computing continue to evolve, the SaaS market will expand further, offering more advanced, secure, and customizable solutions.

















