
Introduction
The Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT) is the apex policy-making body for matters related to direct taxation in India. It functions under the Department of Revenue, Ministry of Finance, and plays a crucial role in framing policies, enforcing tax laws, and ensuring efficient administration of direct taxes such as income tax and corporate tax. As a key pillar of India’s taxation system, the CBDT contributes significantly to resource mobilization for nation-building and economic development.
What is CBDT?
The Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT) is a statutory authority formed under the Central Boards of Revenue Act, 1963.
It provides essential inputs for policy and planning of direct taxes in India and administers the direct tax laws through the Income Tax Department.
- Full Form:
- Central Board of Direct Taxes
- Formation:
- 1944 (as Central Board of Revenue); 1964 (as CBDT after bifurcation)
- Parent Department:
- Department of Revenue, Ministry of Finance
- Governing Act:
- Central Boards of Revenue Act, 1963
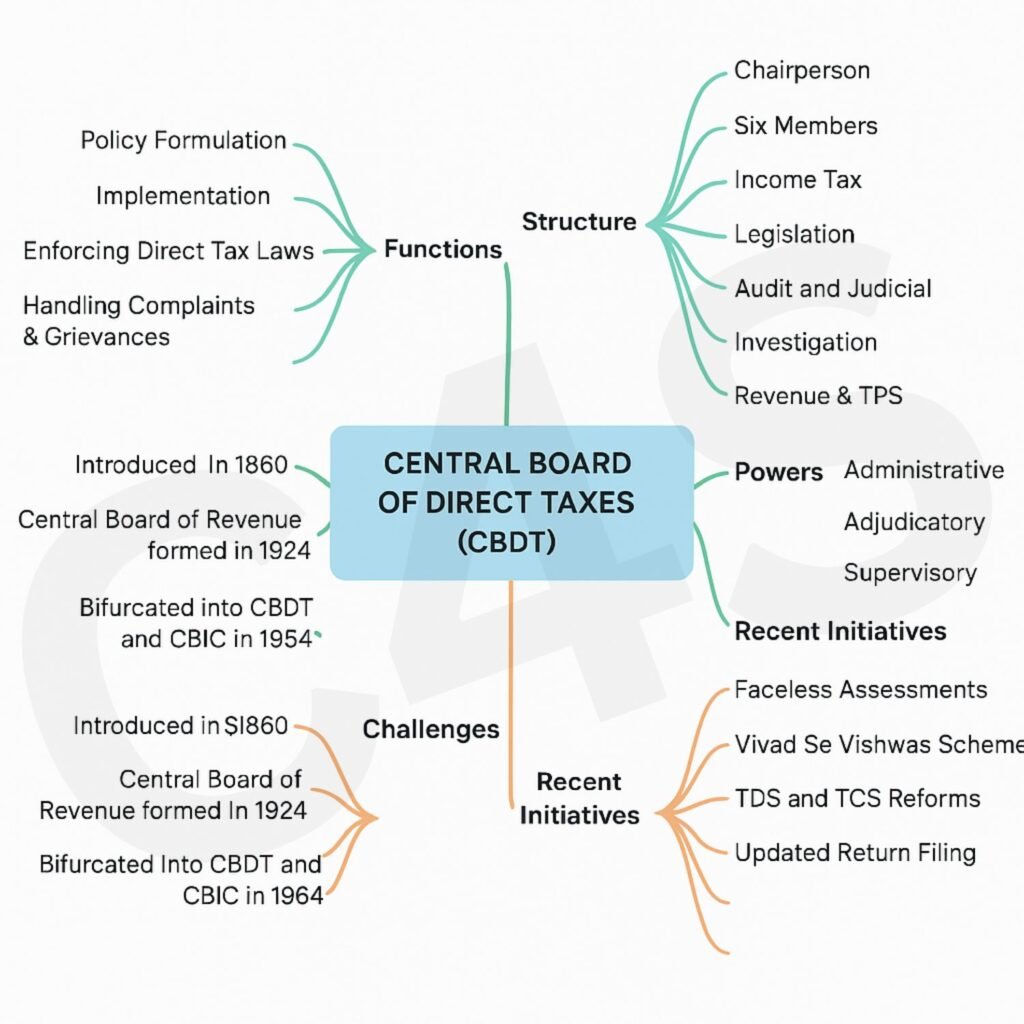
Historical Background
- 1860:
- Introduction of income tax in India by James Wilson (British Finance Member).
- 1924:
- Formation of the Central Board of Revenue for administering both direct and indirect taxes.
- 1964:
- The Central Board of Revenue bifurcated into:
- Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT)
- Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC)
- The Central Board of Revenue bifurcated into:
Thus, CBDT exclusively deals with direct taxes.
Structure of CBDT
The CBDT is composed of a Chairperson and six Members, who are usually officers of the rank of Special Secretary to the Government of India.
| Designation | Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Chairperson | Overall policy-making and administration |
| Member (Income Tax) | Administration of Income Tax Act |
| Member (Legislation) | Drafting laws, rules, notifications |
| Member (Revenue & Tax Payers Services) | Tax collection, grievance redressal |
| Member (Investigation) | Investigations related to tax evasion |
| Member (Audit and Judicial) | Auditing tax matters, judicial representations |
| Member (TPS & Systems) | Technology infrastructure and taxpayer services |
The board operates through several field formations across India like Principal Chief Commissioners, Chief Commissioners, and Commissioners of Income Tax.
Functions of CBDT
The functions of the CBDT are divided into two main categories: Policy Formulation and Implementation.
1. Policy Formulation
- Proposing and drafting tax laws.
- Developing strategies for tax collection.
- Formulating policies for tax administration and tax payer services.
2. Implementation
- Enforcing direct tax laws.
- Supervising the functioning of the Income Tax Department.
- Handling complaints and grievances of taxpayers.
- Managing investigations into tax evasion and black money.
- Administering treaties related to double taxation avoidance (DTAA).
- Advising the government on international tax issues.
Powers of CBDT
The CBDT enjoys several statutory powers under the Income Tax Act, 1961, and other laws:
- Administrative Powers:
- Transfers, postings, promotions, and disciplinary actions against Income Tax Officers.
- Adjudicatory Powers:
- Settling disputes and issuing clarifications.
- Rule-making Powers:
- Issuing rules, circulars, and guidelines.
- Investigation Powers:
- Conducting raids, searches, and seizures under the Income Tax Act.
- Supervisory Powers:
- Monitoring the performance of field offices.
Important Role of CBDT in Indian Taxation System
| Role | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Revenue Mobilization | Ensures tax collection to fund national programs. |
| Policy Advisor | Provides policy inputs to the government. |
| Taxpayer Services | Promotes voluntary compliance through efficient service. |
| International Cooperation | Engages in information exchange with foreign tax authorities. |
| Curbing Black Money | Active role in fighting tax evasion and illegal financial flows. |
Recent Initiatives by CBDT
- Faceless Assessments and Appeals:
- CBDT introduced faceless assessments, reducing physical interface between taxpayers and officers, aiming for transparency and efficiency.
- Vivad Se Vishwas Scheme (2020):
- Resolution scheme to reduce pending income tax litigations.
- TDS and TCS Reforms:
- CBDT has consistently revised rates and compliance norms for Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) and Tax Collected at Source (TCS).
- e-Verification Schemes:
- Launched to encourage digital compliance and reduce harassment.
- Updated Return Filing (Section 139(8A)):
- Facility to file updated returns within two years from the end of the relevant assessment year.
Impact of CBDT’s Reforms on Indian Taxation
The reforms introduced by the CBDT over the past few years have had a transformative impact on India’s tax system:
1. Increased Tax Compliance and Collection Efficiency
- Reforms such as e-filing, TDS/TCS simplifications, and faceless assessments have led to an increase in voluntary tax compliance, as taxpayers find the process more transparent and less burdensome. The efficiency of tax collection has improved due to automation, leading to higher tax revenues for the government.
2. Reduced Litigation and Faster Dispute Resolution
- With the introduction of the Vivad Se Vishwas Scheme, faceless assessments, and faceless appellate tribunals, the volume of tax-related litigation has decreased significantly. Taxpayers now have more efficient and transparent channels to resolve disputes with the tax authorities, leading to faster decision-making and a reduction in the backlog of cases.
3. Enhanced Trust Between Taxpayers and Government
- Initiatives such as the Taxpayers’ Charter and e-verification schemes have increased taxpayer confidence in the tax administration system. The clear-cut expectations outlined in the Taxpayers’ Charter, along with the reduction in physical interface with tax officers, have enhanced trust and compliance.
4. International Cooperation in Taxation
- The Advanced Pricing Agreements (APA) mechanism and other international tax initiatives have helped in reducing cross-border tax disputes, preventing double taxation, and ensuring that international businesses comply with Indian tax regulations. This cooperation has also bolstered India’s reputation in the global financial community.
5. Improved Digital Tax Administration
- CBDT’s push towards digitization, such as e-filing, Centralized Processing Centres (CPC), and faceless systems, has modernized tax administration. These measures have made India’s tax system more efficient, reducing opportunities for corruption and human errors, and offering a more user-friendly experience for taxpayers.
Challenges Faced by CBDT
- Tackling tax evasion and black money generation.
- Enhancing voluntary tax compliance.
- Balancing ease of doing business with strict tax enforcement.
- Managing international taxation complexities like transfer pricing.
- Handling huge litigation volumes pending at various appellate forums.
CBDT vs CBIC
| Parameter | CBDT | CBIC |
|---|---|---|
| Full Form | Central Board of Direct Taxes | Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs |
| Administers | Direct Taxes (e.g., Income Tax, Corporate Tax) | Indirect Taxes (e.g., GST, Customs Duty) |
| Formation Year | 1964 | 1964 |
| Governing Acts | Income Tax Act, Wealth Tax Act (repealed), etc. | GST Act, Customs Act, Central Excise Act |
Importance of CBDT for UPSC and Competitive Exams
- It is part of India’s financial governance structure.
- Related to topics like Taxation Reforms, Transparency and Accountability, and Good Governance.
- Questions related to CBDT frequently appear in exams like UPSC CSE, NABARD Grade A, RBI Grade B, and various state services.
Conclusion
The Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT) stands at the heart of India’s direct taxation system, influencing both policy and practice. It ensures a seamless, taxpayer-friendly, and transparent tax environment in India while contributing significantly to the nation’s fiscal health. As India moves towards digital governance and a more formalized economy, the role of the CBDT becomes even more crucial. For aspirants and professionals alike, understanding the functioning of CBDT is essential for appreciating the complexities of India’s economic and administrative landscape.















