
Introduction
A Follow-on Public Offering (FPO) is a process where a company that has already gone public issues additional shares to investors. It is a crucial mechanism for companies to raise additional capital after an Initial Public Offering (IPO). FPOs serve various purposes, including business expansion, debt reduction, acquisitions, or improving financial liquidity.
This blog provides a detailed overview of Follow-on Public Offerings, covering:
- The different types of FPOs
- The process of issuing an FPO
- The advantages and risks associated with FPOs
- A recent update on FPO trends with tabular data
- A comparison between IPOs and FPOs
Why Do Companies Choose an FPO?
Companies opt for an FPO for several strategic reasons, including:
1. Raising Capital for Expansion
One of the primary reasons for an FPO is to secure funds for business expansion, such as entering new markets, developing new products, or acquiring other companies.
2. Paying Off Debt
Many companies conduct FPOs to reduce their debt burden and improve their financial stability. A company with high debt levels may use an FPO to repay loans and lower interest payments.
3. Improving Liquidity
Issuing more shares in the market can increase trading volume and liquidity, making it easier for investors to buy and sell shares.
4. Strengthening Market Position
An FPO can signal to the market that the company is growing and in need of capital for future investments, which can attract more investors.
5. Providing an Exit for Early Investors
Non-dilutive FPOs allow early investors or company insiders to liquidate their holdings without affecting the company’s financial structure.
Recent Follow-on Public Offerings (FPOs) in 2025
The table below highlights some of the latest FPOs in early 2025, showcasing how companies utilize additional offerings for different financial goals.
| Date | Company | Industry | Amount Raised (in million USD) | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2025-02-20 | Entergy Corporation | Energy | 1,890.2 | Debt repayment and infrastructure investment |
| 2025-02-20 | Trilogy Metals Inc. | Mining | 50.0 | Exploration and development projects |
| 2025-02-20 | InvenTrust Properties Corp. | Real Estate | 250.0 | Property acquisition and expansion |
| 2025-01-15 | Tesla Inc. | Automotive | 5,000.0 | Expansion of EV production capacity |
| 2025-01-10 | Moderna Inc. | Biotechnology | 1,200.0 | R&D and global vaccine distribution |
Types of Follow-on Public Offerings
FPOs are generally classified into two types:
1. Dilutive FPO
In a dilutive FPO, a company issues new shares, increasing the total number of outstanding shares. This process dilutes the ownership percentage of existing shareholders but provides the company with direct capital for growth.
Example:
A company with 10 million shares issues 2 million more through an FPO. As a result, each shareholder’s percentage of ownership is reduced.
2. Non-Dilutive FPO
In a non-dilutive FPO, existing shareholders—such as early investors, venture capitalists, or company executives—sell their shares to the public. In this case, the total number of outstanding shares remains unchanged, and the company itself does not receive any proceeds from the offering.
Example:
If a major investor who owns 2 million shares in a company decides to sell them via an FPO, these shares will be sold to new investors, but the company does not gain any additional capital.
The Follow-on Public Offering (FPO) Process
An FPO involves multiple steps that require careful planning and execution.
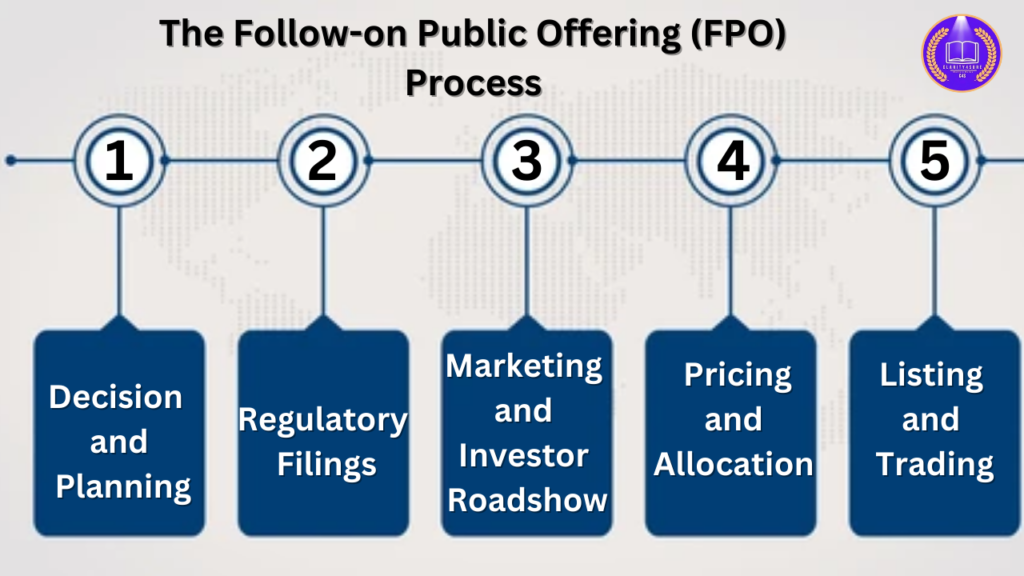
1. Decision and Planning
- The company’s board of directors and executives decide whether an FPO is necessary based on financial needs and market conditions.
- They hire investment banks or underwriters to manage the offering.
2. Regulatory Filings
- The company must file with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) (in the U.S.) or relevant regulatory bodies in other countries.
- Documents like the prospectus and filings on financials, risk factors, and objectives are submitted for approval.
3. Marketing and Investor Roadshow
- The company and underwriters conduct a roadshow to present the offering to institutional and retail investors.
- Investor interest determines the pricing of the shares.
4. Pricing and Allocation
- The FPO price is set based on demand, company valuation, and existing market conditions.
- Institutional investors often get first access, followed by retail investors.
5. Listing and Trading
- Once shares are allocated, they are listed on the stock exchange, and trading begins.
- Stock price fluctuations occur based on investor sentiment and company performance.
Advantages of an FPO
Capital Raising for Business Growth
- Expansion of operations –
- Funds can be used to open new facilities, hire employees, or expand into new markets.
- Investment in research & development (R&D) –
- Supports the development of new products, technologies, or services.
- Acquisitions and mergers –
- Enables companies to acquire competitors or complementary businesses.
Debt Reduction and Financial Stability
- Repayment of loans –
- Reduces interest expenses and financial liabilities.
- Improved credit rating –
- Lower debt levels can improve the company’s creditworthiness.
- Stronger financial position –
- Reduces financial risk and enhances investor confidence.
Increased Stock Liquidity
- Higher trading volume –
- More shares available for trading lead to smoother transactions.
- Better price discovery –
- Market participants can determine fair value more accurately.
- Easier entry and exit for investors –
- Investors can buy or sell shares without impacting stock price significantly.
Lower Cost Compared to an Initial Public Offering (IPO)
- Reduced regulatory burden –
- Less stringent filing and approval processes than an IPO.
- Lower underwriting and legal costs –
- Requires fewer marketing efforts compared to an IPO.
- Utilization of existing investor base –
- Less need for extensive promotions to attract buyers.
Greater Market Visibility and Brand Recognition
- Attracts new investors –
- Media coverage and analyst reports increase awareness.
- Improves company reputation –
- Shows financial strength and long-term vision.
- Encourages long-term investment –
- Enhances credibility with institutional investors.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Capital Raising | Allows the company to raise more funds for growth, acquisitions, or debt reduction. |
| Increased Liquidity | Additional shares increase market liquidity, making it easier for investors to buy/sell shares. |
| Market Credibility | A successful FPO can improve investor confidence and strengthen the company’s market reputation. |
| Lower Cost than IPO | Compared to an IPO, an FPO requires less marketing and regulatory effort, reducing costs. |
Risks of an FPO
Shareholder Dilution
- Reduced ownership percentage –
- Existing shareholders’ ownership stake decreases due to the issuance of new shares.
- Lower earnings per share (EPS) –
- Increased outstanding shares can reduce EPS, impacting stock valuation.
- Potential decline in voting power –
- Shareholders may lose influence over company decisions.
Stock Price Decline
- Market perception of financial weakness –
- Investors may see the FPO as a sign that the company is struggling.
- Supply-demand imbalance –
- More shares in the market can lower stock prices due to increased supply.
- Short-term volatility –
- Stock prices may fluctuate before stabilizing post-FPO.
Negative Investor Sentiment
- Concerns about overvaluation –
- Investors may feel the company is overpricing shares in the FPO.
- Fear of future dilution –
- If the company issues more shares later, it can deter long-term investors.
- Reduced institutional interest –
- Large investors might avoid companies that frequently raise capital through FPOs.
Regulatory and Compliance Risks
- Stringent reporting requirements –
- Companies must disclose financial details, business risks, and fund usage.
- Regulatory approvals and delays –
- Obtaining clearance from market regulators can slow down the fundraising process.
- Legal complexities –
- Potential lawsuits from investors if the FPO is perceived as misleading or poorly executed.
High Costs Associated with the FPO Process
- Marketing and roadshow expenses –
- Costs for attracting institutional and retail investors.
- Underwriting and advisory fees –
- Investment banks and financial advisors charge high fees for managing FPOs.
- Legal and compliance costs –
- Regulatory filings and legal procedures add to expenses.
| Risk Factor | Impact on Company & Investors |
|---|---|
| Dilution of Shares | In a dilutive FPO, existing shareholders’ stake gets reduced, potentially lowering stock value. |
| Market Volatility | If an FPO is not well-received, the company’s stock price can decline. |
| Investor Confidence | If the reason for the FPO is poor financial performance, investors may lose trust. |
| Regulatory Challenges | The FPO process must comply with financial regulations, which can delay execution. |
Comparison: IPO vs. FPO
| Feature | IPO (Initial Public Offering) | FPO (Follow-on Public Offering) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | First time a company issues shares to the public | Additional shares issued by an already public company |
| Purpose | Raise funds for the first time to expand business | Raise additional capital or allow existing shareholders to sell |
| Stockholder Impact | Creates new shareholders | May dilute existing shareholders’ ownership (in dilutive FPOs) |
| Market Perception | Highly anticipated event, creates excitement | Market response depends on company performance |
| Regulatory Complexity | Requires extensive regulatory approval | Less regulatory scrutiny compared to IPOs |
Before investing in an FPO consider
- The company’s financial health
- The purpose of the FPO
- Market conditions and investor demand
Conclusion
A Follow-on Public Offering (FPO) is a strategic tool for companies to raise additional capital after an IPO. While it can help expand operations, reduce debt, and improve liquidity, it also comes with risks like dilution and market volatility.
For investors, analyzing why a company is issuing an FPO is critical. If the offering is meant for growth and expansion, it can be a great investment opportunity. However, if it’s driven by financial struggles, caution is advised.
With several major companies launching FPOs in 2025, the trend of raising additional funds post-IPO is growing, making it essential for investors to stay informed and make educated decisions



















