
Introduction
A Forward Rate Agreement (FRA) is a financial derivative contract between two parties to exchange interest rate payments based on a specified notional principal amount for a predetermined future period. It is primarily used to hedge against interest rate fluctuations or to speculate on future rate movements.
FRAs are over-the-counter (OTC) contracts that allow market participants to lock in an interest rate for a future period, thus mitigating the risk of adverse rate movements. These agreements are typically used by banks, corporations, and financial institutions involved in interest rate-sensitive transactions.
How a Forward Rate Agreement Works ?
Key Components of an FRA
- Notional Principal Amount:
- The hypothetical amount on which interest payments are calculated (no actual exchange of principal).
- Contract Period:
- The time between the agreement date and the settlement date.
- Settlement Date:
- The date when the contract is settled, and the difference in interest rates is exchanged.
- Reference Interest Rate:
- Typically based on LIBOR, EURIBOR, or other benchmark rates.
- Agreed Interest Rate (FRA Rate):
- The fixed rate agreed upon in the contract.
- Floating Rate:
- The actual market interest rate on the settlement date.
FRA Calculation Formula
The cash settlement amount exchanged between the two parties is calculated as:

where:
- Notional Principal:
- The assumed principal amount.
- FRA Rate:
- The agreed fixed interest rate.
- Floating Rate:
- The reference rate at the time of settlement.
- Days in Contract Period:
- The number of days in the interest period (e.g., 30, 60, 90 days).
- 360:
- The standard day count convention for interest rate calculations.
Example of a Forward Rate Agreement
Let’s assume a company enters into a 3×6 FRA (a contract starting in 3 months and ending in 6 months) to hedge against an expected rise in interest rates.
FRA Details
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Notional Principal | $1,000,000 |
| FRA Rate (Fixed Rate) | 5% per annum |
| Floating Rate at Settlement | 6% per annum |
| Contract Period | 90 days |
| Settlement Date | In 3 months |
Step 1: Compute the Difference in Interest Rates
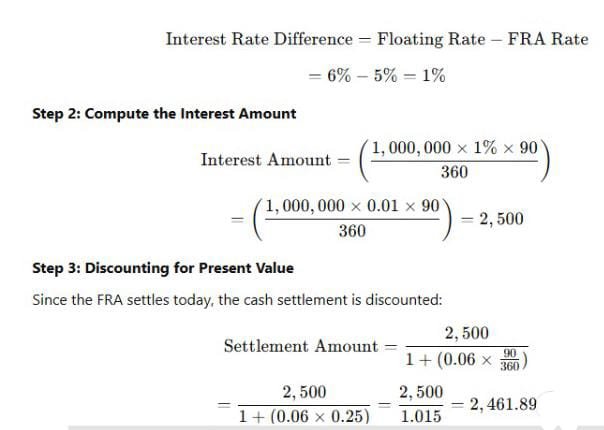
Thus, the party receiving the floating rate will receive $2,461.89 as settlement
Types of FRAs
Forward Rate Agreements (FRAs) come in different forms based on contract duration, reference rates, and the parties’ positions. Below are the primary types of FRAs:
1. Based on Interest Rate Direction
| Type | Description | Who Benefits? |
|---|---|---|
| Buy FRA (Long FRA) | The buyer locks in a fixed interest rate. If floating rates increase, the buyer gains. If floating rates decrease, the buyer pays the difference. | Borrowers who want to hedge against rising interest rates. |
| Sell FRA (Short FRA) | The seller pays a fixed rate and receives a floating rate. If floating rates decrease, the seller benefits. If rates increase, the seller pays the difference. | Investors or lenders looking to hedge against falling interest rates. |
2. Based on Contract Duration (Tenor)
| FRA Type | Interpretation | Example |
|---|---|---|
| 1×4 FRA | A contract starting in 1 month and settling in 4 months (3-month interest period). | If a company expects to take a loan in 1 month, it can lock in the rate now. |
| 3×6 FRA | A contract starting in 3 months and settling in 6 months (3-month interest period). | Used by banks to hedge interest rate fluctuations for future borrowings. |
| 6×12 FRA | A contract starting in 6 months and settling in 12 months (6-month interest period). | Suitable for companies planning long-term debt financing. |
The first number represents the contract start in months, and the second number represents the settlement period.
3. Based on Reference Interest Rates
| FRA Type | Reference Rate | Used In |
|---|---|---|
| LIBOR-based FRA | Linked to LIBOR (London Interbank Offered Rate) | Historically used in global finance (phased out after 2021). |
| EURIBOR-based FRA | Based on EURIBOR (Euro Interbank Offered Rate) | European financial markets. |
| SOFR-based FRA | Uses SOFR (Secured Overnight Financing Rate) | U.S. markets (LIBOR alternative). |
| TONA-based FRA | Uses TONA (Tokyo Overnight Average Rate) | Japan’s financial system. |
4. Based on Settlement Type
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Cash-Settled FRA | The difference between the FRA rate and floating rate is settled in cash (most common). |
| Physically-Settled FRA | Instead of cash settlement, the parties actually exchange interest payments (rarely used). |
5. Based on Market Participants
| FRA Type | Participants |
|---|---|
| Interbank FRA | Contracts between banks to manage interest rate risks. |
| Corporate FRA | Used by companies to hedge interest rate exposure on future borrowings. |
| Speculative FRA | Used by traders who bet on future interest rate movements. |
Uses of Forward Rate Agreements
- Hedging Interest Rate Risk
- Companies with floating-rate debt can use FRAs to lock in rates and manage exposure.
- Banks use FRAs to hedge their loan portfolios against rate fluctuations.
- Speculation on Interest Rate Movements
- Traders can enter into FRAs based on their forecast of interest rate trends.
- Liquidity and Risk Management
- Corporations use FRAs to maintain stable borrowing costs.
- Investors reduce uncertainty related to future interest rates.
Advantages of Forward Rate Agreements
- Customization –
- FRAs are OTC contracts tailored to specific needs.
- No Initial Cash Flow –
- No upfront payments are required.
- Hedging Tool –
- Effectively manages interest rate risks.
- Efficient Risk Transfer –
- Shifts exposure between market participants.
Limitations of Forward Rate Agreements
- OTC Risk –
- Counterparty default risk exists.
- No Liquidity –
- Unlike exchange-traded futures, FRAs are illiquid.
- Requires Accurate Forecasting –
- Poor rate predictions can lead to losses.
- Discounting Effects –
- Settlement amounts must be present-value adjusted.
Comparison: FRA vs Interest Rate Swap vs Futures
| Feature | Forward Rate Agreement (FRA) | Interest Rate Swap | Interest Rate Futures |
|---|---|---|---|
| Market Type | OTC | OTC | Exchange-Traded |
| Customization | High | High | Standardized |
| Liquidity | Low | Moderate | High |
| Settlement | Cash settlement | Periodic payments | Mark-to-market daily |
| Counterparty Risk | Yes | Yes | No (cleared via exchange) |
Conclusion
Forward Rate Agreements (FRAs) are essential financial instruments for managing interest rate risks. They are particularly useful for financial institutions, corporations, and traders who need to hedge against interest rate volatility or speculate on future rate movements. While they offer advantages such as customization and cost-effectiveness, they also come with risks such as counterparty default and liquidity issues.
Understanding how FRAs work, their pricing mechanisms, and their role in risk management is crucial for anyone involved in interest rate-sensitive financial transactions.


















