Introduction
India-Russia relations stand as one of the most resilient and multi-dimensional bilateral partnerships in global diplomacy. Transcending traditional alliances, the bond between New Delhi and Moscow has evolved into a “Special and Privileged Strategic Partnership”, deeply rooted in history, defense cooperation, energy security, geopolitical synergy, and technological collaboration.
In a world undergoing multipolar shifts and strategic contestations, this enduring relationship reflects India’s pursuit of strategic autonomy while navigating complex equations with both Western powers and Eastern allies.
Evolution of India-Russia Relations
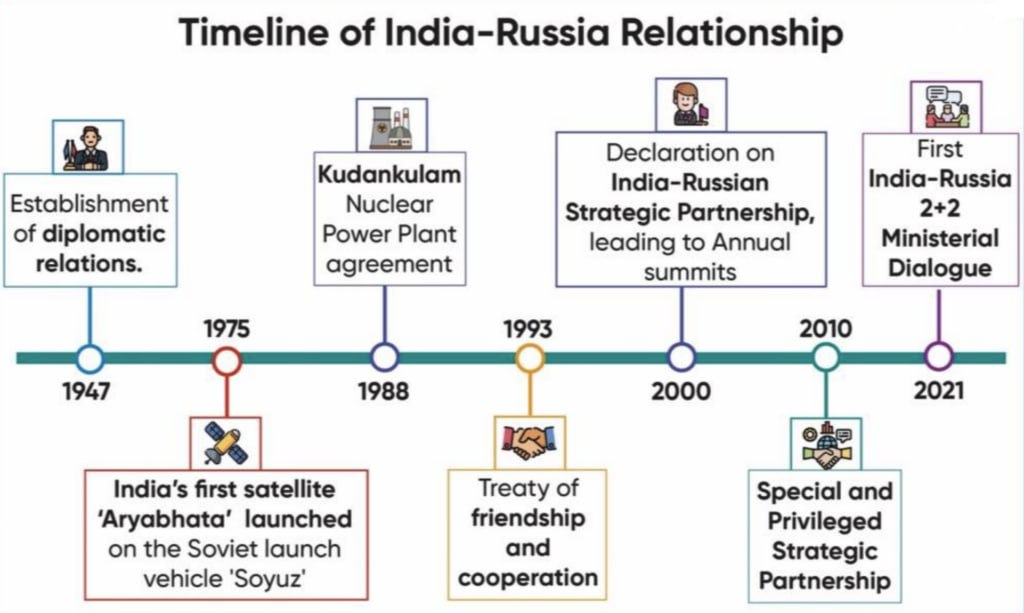
1. Cold War Solidarity (1950–1991)
- India’s ties with the Soviet Union were pivotal during the formative decades of the Cold War.
- Strategic Support:
- The USSR backed India on core issues like:
- Kashmir in international forums,
- Goa’s liberation from Portuguese rule,
- Opposition to Western-led military alliances like SEATO and CENTO.
- The USSR backed India on core issues like:
- 1971 Treaty of Peace, Friendship, and Cooperation:
- Signed ahead of the Bangladesh Liberation War, it ensured Soviet support and deterred U.S.-China military pressure on India.
- USSR played a vital role in India’s industrialization, especially in:
- Steel plants (Bhilai),
- Power plants,
- Space research (early support to ISRO),
- Technical education (IITs).
2. Post-Soviet Adjustment (1991–2000)
- The disintegration of the Soviet Union led to an initial cooling of relations.
- Economic hardship in Russia and India’s liberalization policy shifted focus to the West.
- However, defense and strategic ties remained robust, with Russia supplying military hardware and spare parts to India’s Soviet-origin arsenal.
- India adopted a multi-vector foreign policy, yet retained Moscow as a key partner.
3. Strategic Partnerships and Deepening Engagement (2000–Present)
- 2000:
- Declaration of India-Russia Strategic Partnership during President Vladimir Putin’s visit.
- 2010:
- Upgraded to a “Special and Privileged Strategic Partnership”, reflecting the depth and diversity of cooperation.
- 2024:
- Both nations reaffirmed this during the Indian Prime Minister’s visit to Moscow, committing to boost bilateral trade to $100 billion by 2030.
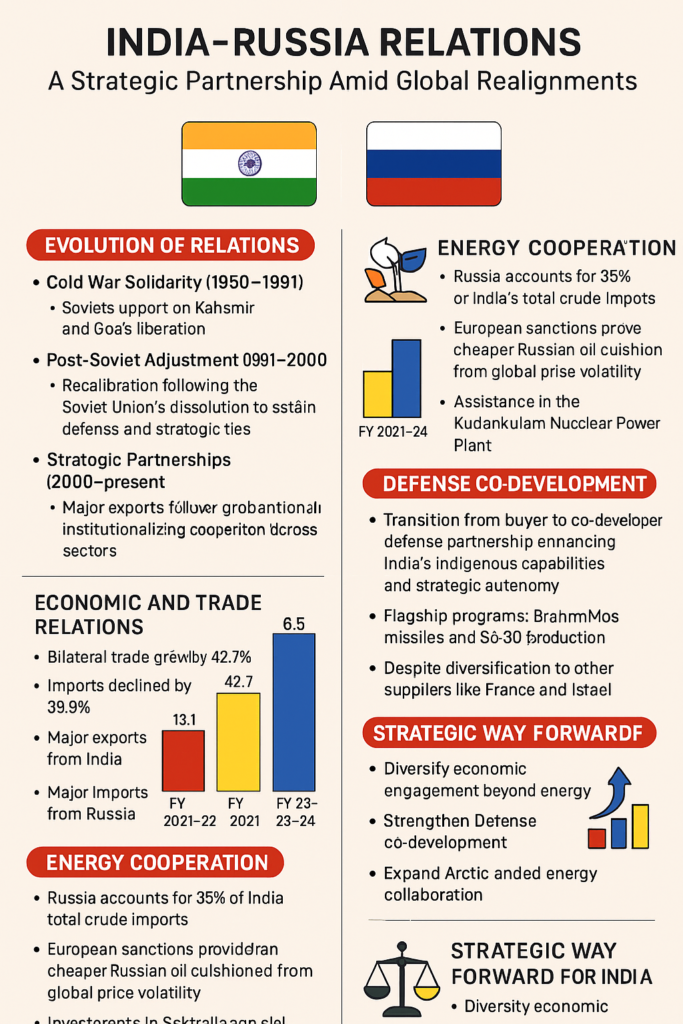
India-Russia Economic and Trade Relations: A Closer Look
Bilateral Trade Milestones:
| Fiscal Year | Bilateral Trade ($ Billion) | Growth Highlights |
|---|---|---|
| 2021-22 | 13.1 | Oil trade begins to surge |
| 2022-23 | 45.4 | Trade quadruples amid Western sanctions |
| 2023-24 | 65.7 | Record high; Exports ↑ 42.7%, Imports ↓ 39.9% |
Major Trade Components:
- India’s Exports to Russia:
- Pharmaceuticals
- Organic chemicals
- Machinery and mechanical appliances
- Tea and coffee
- Russia’s Exports to India:
- Crude oil (35% of India’s imports by 2024)
- Fertilizers
- Mineral fuels
- Defense hardware

Energy as a Cornerstone of Strategic Engagement
- In the face of Western sanctions, India has emerged as a top buyer of Russian crude oil, benefitting from discounted rates.
- Russian oil now constitutes 35% of India’s total oil imports.
- India also invests in Russian energy assets:
- Sakhalin-I and II oil fields
- Vankor and Tomsk projects
- Russian support continues in the Kudankulam Nuclear Power Plant, one of India’s major civilian nuclear energy initiatives.
- Northern Sea Route (NSR) discussions in October 2024 opened new avenues for Arctic energy cooperation.
Defense Cooperation: From Buyer to Co-Developer
India remains one of Russia’s largest defense customers, though the relationship is evolving toward joint production and technology transfer:
| Domain | Collaboration Examples |
|---|---|
| Missile systems | BrahMos Supersonic Cruise Missiles |
| Fighter jets | Su-30MKI Co-production in India |
| Submarines | INS Chakra (leased nuclear sub), Kilo-class |
| Air Defense | S-400 Triumf air defense system |
- 2024: Russia joined India’s “Make in India” initiative for joint production of high-speed electric trains, marking a shift beyond defense.
Multilateral Collaboration: Building a Multipolar World
India and Russia align on creating a multipolar global order and regularly collaborate at:
- BRICS (Pushing for de-dollarization and alternative payment systems),
- SCO (Regional security and anti-terror cooperation),
- G20 (Climate finance, digital economy).
At the 2024 BRICS Summit, India and Russia:
- Advocated for local currency trade,
- Called for reform of international financial institutions,
- Supported expansion of BRICS with more Global South voices.
Technology, Space & Cyber Collaboration
The India-Russia relationship is expanding into high-tech cooperation:
- Space:
- Joint lunar and human spaceflight missions, using Russian modules and Indian launch systems.
- GLONASS:
- Integration of Russian satellite navigation systems in Indian platforms.
- AI & Cybersecurity:
- Frameworks in progress for collaboration in cybersecurity, data protection, and digital infrastructure.
Connectivity Projects: Reshaping Trade Routes
India and Russia are investing in alternative trade corridors that bypass traditional chokepoints:
| Corridor | Key Benefits |
|---|---|
| International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC) | Cuts cargo time by 40%, boosts Central Asian trade |
| Chennai–Vladivostok Maritime Corridor | Reduces shipping days from 40 to 24 |
| Northern Sea Route (NSR) | Arctic shipping with Russian collaboration |
These initiatives will:
- Reduce dependence on Suez or Malacca routes,
- Boost India’s role in Eurasian logistics.
Key Challenges in India-Russia Relations
1. Balancing the West and Russia
- Western allies urge India to reduce ties with Russia over Ukraine.
- India has maintained neutrality, abstaining from UN votes but defending its strategic interests.
- The U.S. has warned of “consequences” but stopped short of imposing red lines.
2. Trade Imbalance
- FY 2023-24:
- Imports from Russia: $61.44 billion
- Exports to Russia: $4.26 billion
- Deficit: $57.18 billion
- The imbalance is driven by crude oil and fertilizer imports.
- Sectors like IT, textiles, and processed foods remain underutilized.
3. Financial Sanctions and Banking Issues
- Rupee-Ruble trade faces bottlenecks due to:
- Fear of secondary sanctions by private banks,
- Logistical disruptions in Vostro account adoption.
4. Russia-China Proximity
- Russia-China trade hit $200 billion in 2023, affecting India’s leverage.
- China’s investments in Arctic and Russian Far East regions may restrict India’s strategic access.
5. Unstable Central Asian Corridors
- INSTC runs through Iran and Kazakhstan, both facing:
- Sanctions and
- Internal unrest, threatening India’s trade ambitions.

Strategic Way Forward for India
1. Diversify Economic Engagement
- Accelerate FTA with Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU).
- Promote Indian sectors like:
- Pharmaceuticals
- IT & software
- Agricultural technology
- Establish SEZs in Russia for Indian exporters.
2. Strengthen Defense Co-Development
- Encourage joint R&D under Make in India.
- Shift focus from imports to licensed production of next-gen systems like drones, EW, and space-based weapons.
3. Expand Arctic and Energy Cooperation
- Invest in Arctic LNG, NSR logistics, and shipping infrastructure.
- Enhance polar research collaboration.
4. Boost Cultural & Educational Exchanges
- Open Indian Cultural Centers in Russian cities.
- Scholarships and student exchange programs.
- Promote regional tourism: e.g., Kazan and Ekaterinburg Consulates in 2024.
5. Green Energy and Rare Earths Collaboration
- Explore solar, wind, and hydrogen energy projects.
- Russia can invest in India’s $250B renewable push.
- Joint ventures in rare earth processing to reduce China dependency.
6. Joint Ventures in Fertilizers
- Localize fertilizer production in India using Russian raw materials.
- Reduce import bills and support Indian agriculture.
| Priority Area | Measures for Strengthening Relations |
|---|---|
| Economic Diversification | Fast-track EAEU-India FTA; boost non-oil sectors like IT, food processing |
| Defense Co-Development | Enhance joint manufacturing under Make in India |
| Energy & Arctic Collaboration | Invest in NSR logistics, LNG terminals, and Arctic exploration |
| Cultural Ties | Open Indian cultural centers; expand student exchange programs |
| Green Energy | Collaborate on solar, wind, hydrogen under India’s $250B green transition |
| Trade Deficit Reduction | Establish SEZs in Russia; incentivize exports in textiles, IT |
| Strategic Diplomacy | Offer Russia strategic alternatives to balance China’s influence |
| Fertilizer Production | Invite Russian investments in local fertilizer plants |
| Digital Economy | Build joint ventures in cybersecurity, AI, and data protection |
| Tourism Cooperation | Launch visa facilitation, joint cultural festivals, curated tourism packages |
Conclusion
India-Russia relations are more than a historical legacy—they represent a pragmatic and strategic engagement in an evolving multipolar world. As global power centers shift and alliances realign, India must skillfully balance its old friendship with Moscow and its growing ties with the West.
By proactively addressing trade deficits, navigating geopolitical fault lines, and investing in forward-looking sectors like space, green energy, and digital security, India can sustain and elevate its partnership with Russia—ensuring its own strategic autonomy and global relevance in the 21st century.

















