
Introduction
The Liquidity Coverage Ratio (LCR) is a crucial financial metric introduced as part of the Basel III regulatory framework to ensure that financial institutions maintain an adequate level of high-quality liquid assets (HQLA) to survive short-term liquidity disruptions. The LCR enhances financial stability by requiring banks to withstand a 30-day liquidity stress scenario without relying on external funding.
What is Liquidity Coverage Ratio (LCR)?
- The Liquidity Coverage Ratio (LCR) is defined as:
- LCR= (High-Quality Liquid Assets (HQLA) / Total Net Cash Outflows) x 100
- The ratio ensures that banks have sufficient HQLA to cover potential cash outflows in a stress scenario over 30 days. The regulatory requirement set by the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS) mandates that banks must maintain an LCR of at least 100%.
LCR Requirements in India
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) mandates that all scheduled commercial banks (SCBs), excluding regional rural banks (RRBs), local area banks (LABs), and payments banks, must maintain a minimum LCR of 100%.
Regulatory Timeline for LCR Implementation in India

The RBI adopted a phased approach to implement LCR for Indian banks:
| Year | LCR Requirement (%) |
|---|---|
| January 1, 2015 | 60% |
| January 1, 2016 | 70% |
| January 1, 2017 | 80% |
| January 1, 2018 | 90% |
| January 1, 2019 | 100% (Fully Implemented) |
Since January 1, 2019, Indian banks must maintain a minimum LCR of 100%, meaning they should hold enough HQLA to cover net cash outflows over a 30-day stress period.
Components of LCR
1. High-Quality Liquid Assets (HQLA)
HQLA consists of assets that can be quickly converted into cash without significant loss of value. These assets are categorized into Level 1 and Level 2 assets:
| Category | Description | Haircut Applied | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Level 1 Assets | Most liquid and safe assets | 0% | Cash, central bank reserves, sovereign bonds |
| Level 2A Assets | Less liquid but still highly reliable | 15% | Government securities, covered bonds |
| Level 2B Assets | Riskier and less liquid assets | 25% – 50% | Corporate bonds, equities |
Banks must hold a significant portion of their HQLA in Level 1 assets to ensure stability during crises.
2. Total Net Cash Outflows
Total net cash outflows are calculated as: Net Cash Outflows=Total Expected Outflows−Total Expected Inflows\text{Net Cash Outflows} = \text{Total Expected Outflows} – \text{Total Expected Inflows}
Where:
- Expected Outflows:
- Bank liabilities such as deposits and borrowings that could be withdrawn within 30 days.
- Expected Inflows:
- Payments received by the bank, including interest income and loan repayments.
The BCBS assigns different run-off rates to liabilities based on their stability. The table below highlights key outflow factors:
| Liability Type | Run-Off Rate | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Retail Deposits (Stable) | 5% | Insured savings deposits |
| Retail Deposits (Less Stable) | 10% | Uninsured savings accounts |
| Wholesale Deposits | 40% – 100% | Corporate deposits, interbank loans |
| Credit and Liquidity Facilities | 10% – 100% | Revolving credit lines |
Banks must assume that a certain percentage of deposits and liabilities will be withdrawn during a stress period.
Calculation of LCR with Example
Let’s assume XYZ Bank has the following balance sheet items:
Step 1: Identify HQLA
| Asset Type | Amount ($ million) | Haircut Applied | Adjusted Value ($ million) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cash & Reserves | 500 | 0% | 500 |
| Government Bonds (Level 1) | 400 | 0% | 400 |
| Corporate Bonds (Level 2B) | 200 | 50% | 100 |
| Total HQLA | 1,000 | – | 1,000 |
Step 2: Calculate Expected Cash Outflows
| Liability Type | Amount ($ million) | Run-Off Rate | Outflow ($ million) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stable Retail Deposits | 1,000 | 5% | 50 |
| Unstable Retail Deposits | 800 | 10% | 80 |
| Wholesale Deposits | 500 | 40% | 200 |
| Revolving Credit Facilities | 300 | 100% | 300 |
| Total Outflows | 2,600 | – | 630 |
Step 3: Calculate Expected Cash Inflows
| Asset Type | Amount ($ million) | Expected Inflow Rate | Inflow ($ million) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Loan Payments Due | 600 | 50% | 300 |
| Interest Income | 200 | 100% | 200 |
| Total Inflows | 800 | – | 500 |
Step 4: Compute Net Cash Outflows
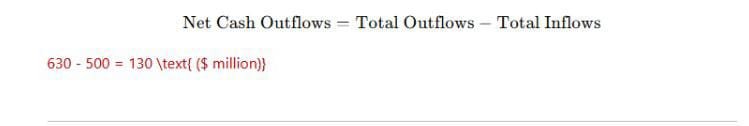
Step 5: Compute LCR

Since the LCR is well above 100%, XYZ Bank is in a strong liquidity position.
Impact of LCR on Indian Banks
1. Strengthening Financial Stability
- The LCR requirement ensures that banks hold sufficient liquid assets, reducing the risk of bank runs and financial crises.
2. Enhanced Deposit Protection
- The framework helps banks manage deposit withdrawals efficiently during a crisis.
3. Impact on Bank Profitability
- Holding large amounts of HQLA (like government securities) reduces bank profitability, as these assets generate lower returns than loans.
4. Encouraging Risk Management
- Indian banks must improve their liquidity risk assessment to optimize cash flows and investment strategies.
Regulatory Requirements and Compliance
Basel III Minimum Requirement
- The Basel III framework requires banks to maintain an LCR of at least 100% at all times.
Regional LCR Guidelines
| Region | Minimum LCR Requirement | Regulatory Authority |
|---|---|---|
| USA | 100% | Federal Reserve (Fed) |
| EU | 100% | European Banking Authority (EBA) |
| UK | 100% | Prudential Regulation Authority (PRA) |
| India | 100% | Reserve Bank of India (RBI) |
Banks that fail to maintain the required LCR may face regulatory penalties, capital restrictions, or mandatory corrective actions.
Importance of LCR in Banking
- Prevents Liquidity Crises –
- Ensures banks can survive short-term cash shortages.
- Boosts Market Confidence –
- A high LCR signals financial stability.
- Reduces Systemic Risk –
- Helps prevent banking system collapses.
- Ensures Regulatory Compliance –
- Banks must meet LCR requirements to avoid penalties.
- Enhances Risk Management –
- Encourages banks to maintain sufficient liquid assets.
Challenges in Maintaining LCR
Despite its benefits, maintaining a high LCR poses challenges:
- Reduced Profitability –
- Holding high levels of liquid assets may lower returns.
- Operational Complexity –
- Banks must monitor daily cash flows and regulatory requirements.
- Market Volatility –
- Market fluctuations may impact asset liquidity.
- Regulatory Variations –
- Different jurisdictions impose varying LCR requirements.
Conclusion
The Liquidity Coverage Ratio (LCR) is a key liquidity risk measure ensuring banks have sufficient high-quality liquid assets (HQLA) to survive a 30-day financial stress period. By maintaining an LCR above 100%, banks can enhance financial stability, reduce risks, and improve investor confidence.
Understanding and managing LCR effectively is crucial for financial institutions aiming to balance liquidity, profitability, and regulatory compliance.















