
Origin
The first Primary Agricultural Credit Society (PACS) was established in 1904, following the enactment of the Cooperative Credit Societies Act. As of December 2022, there were 1.02 lakh PACS in India. However, only 47,297 of them made a profit by the end of March 2021.
What is a Primary Agricultural Credit Society (PACS)?
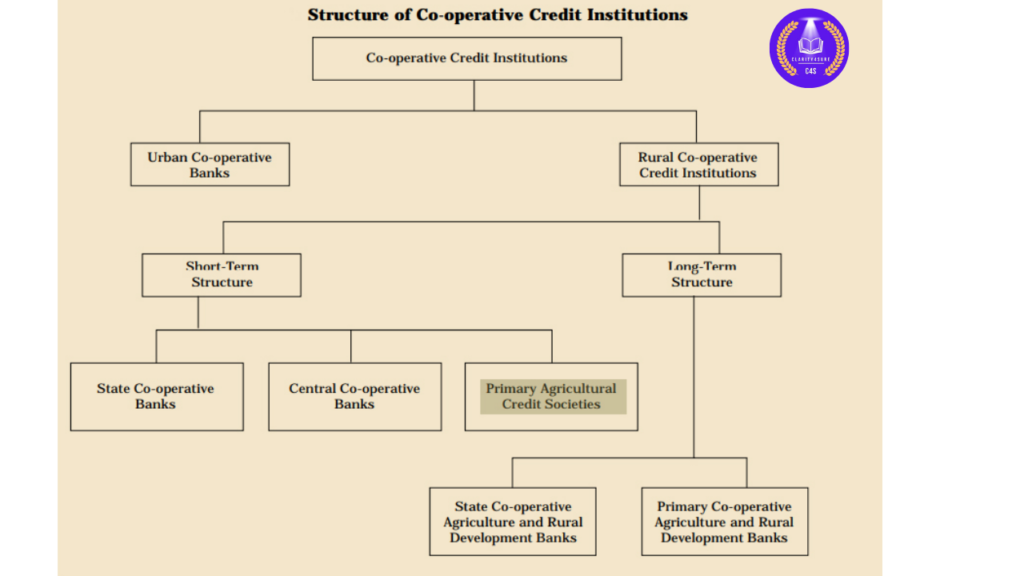
- PACS are village level cooperative credit societies that serve as the last link in a three-tier cooperative credit structure headed by the State Cooperative Banks (SCB) at the state level.
- Credit from the SCBs is transferred to the District Central Cooperative Banks (DCCBs), that operate at the district level.
- The DCCBs work with PACS, which deal directly with farmers.
- Since these are cooperative bodies, individual farmers are members of the PACS, and office-bearers are elected from within them. A village can have multiple PACS.
- PACSs provide short-term, and medium-term agricultural loans to the farmers for the various agricultural and farming activities.
- Regulation:
- PACS are registered under Cooperative Societies Act and are administered by concerned State Registrar of Cooperative Societies (RCS).
- SCBs/DCCBs are also registered under provisions of State Cooperative Societies Act of State concerned and are regulated by RBI. However, PACS are outside purview of Banking Regulation Act, 1949 and are not regulated by RBI.
- PACS are registered under Cooperative Societies Act and are administered by concerned State Registrar of Cooperative Societies (RCS).
- Refinancing:
- They are refinanced by NABARD through DCCBs and SCBs.
- Functions:
- Gives short-term credit loans and collects repayment from rural borrowers.
- They can also provide other input services, like seed, fertilizer, and pesticide distribution to member farmers.
- Significance:
- PACS play a key role in financial inclusion.
- PACS account for 41 % of the KCC loans given by all entities in the Country and 95 % of these KCC loans through PACS are to the Small and Marginal farmers (2022).
- Current Status:
- There are more than 65000 functional PACS across country.
Number of PACS in India
- The first PACS was formed in 1904.
- Currently, there are more than 1,00,000 PACS in the country with a huge member base of more than 13 crore farmers.
- However, only 63,000 of them are functional.
Aim of Digitizing PACS
- It aims at bringing greater transparency and accountability in their operations and enabling them to diversify their business and undertake more activities.
- It aims to help PACS become a nodal centre for providing various services such as Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT), Interest Subvention Scheme (ISS), Crop Insurance Scheme (PMFBY), and inputs like fertilizers and seeds.
Significance of PACS
- Access to Credit:
- PACS provide small farmers with access to credit, which they can use to purchase seeds, fertilizers, and other inputs for their farms. This helps them to improve their production and increase their income.
- Financial Inclusion:
- PACS help to increase financial inclusion in rural areas, where access to formal financial services is limited. They provide basic banking services, such as savings and loan accounts, to farmers who may not have access to formal banking services.
- Convenient Services:
- PACS are often located in rural areas, which makes it convenient for farmers to access their services. This is important because many farmers are unable to travel to banks in urban areas to access financial services.
- PACS have the capacity to extend credit with minimal paperwork within a short time.
- Promoting Savings Culture:
- PACS encourage farmers to save money, which can be used to improve their livelihoods and invest in their farms.
- Enhancing Credit Discipline:
- PACS promote credit discipline among farmers by requiring them to repay their loans on time. This helps to reduce the risk of default, which can be a major challenge in the rural financial sector.
Issues with PACS
- Inadequate Coverage:
- Though geographically active PACS cover about 90% of 5.8 villages, there are parts of the country, especially in the north-east, where this coverage is very low.
- Further, the rural population covered as members is only 50% of all the rural households.
- Inadequate Resources:
- The resources of the PACS are much too inadequate in relation to the short-and medium-term credit needs of the rural economy.
- The bulk of even these inadequate funds come from higher financing agencies and not through owned funds of societies or deposit mobilization by them.
- Overdues and NPAs:
- Large over-dues have become a big problem for the PACS.
- As per the RBI report, PACS had reported lending worth Rs 1,43,044 crore and NPAs of Rs 72,550 crore. Maharashtra has 20,897 PACS of which 11,326 are in losses
- They curb the circulation of loanable funds, reduce the borrowing as well as lending power of societies, and give them the bad image of the societies of defaulting debtors are willful.
- Large over-dues have become a big problem for the PACS.
Initiatives to strengthen PACS
- Formation of new Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs) by PACS:
- 1,100 additional FPOs to be formed by PACS with support of National Cooperative Development Corporation (NCDC).
- National Cooperative Development Corporation (NCDC):
- Established in 1963, NCDC provides loans and grants to State Governments for financing primary and secondary level cooperative societies.
- Diversifying business portfolio
- Model Byelaws to make PACS multipurpose:
- Enable PACS to diversify their business by undertaking more than 25 business activities. E.g. dairy, fishery, floriculture, setting up godowns etc.
- PACS to function as Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samriddhi Kendras:
- To provide fertilizers, pesticides and various other agri inputs to farmers at a single shop.
- PACS to operate as Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Jan Aushadhi Kendras:
- To ensure availability of generic medicines to rural citizens.
- PACS to operate as Common Service Centers (CSCs)
- Model Byelaws to make PACS multipurpose:
Way Forward
- These more than a century-old institutions deserve another policy push and can occupy a prominent space in the vision of Atmanirbhar Bharat as well as Vocal for Local of the Government of India, as they have the potential to be the building blocks of an Atmanirbhar village economy.
- PACS have played a crucial role in the rural financial sector and have the potential to play an even greater role in the future.
- To achieve this, PACS must be made more efficient, financially sustainable, and accessible to farmers.
- At the same time, the regulatory framework must be strengthened to ensure that PACS are effectively governed and able to serve the needs of farmers.


















