
Introduction
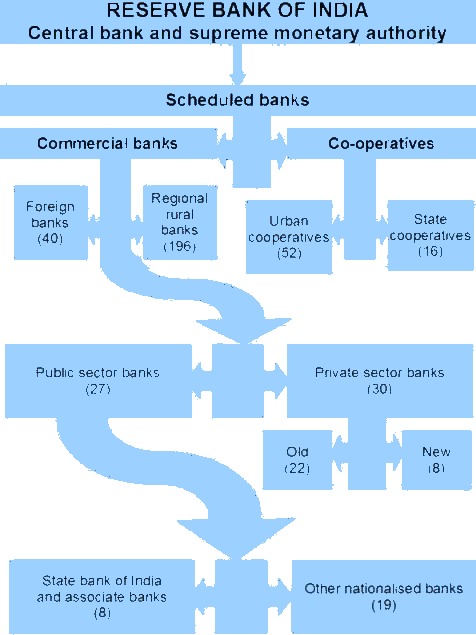
The Indian banking system plays a pivotal role in economic development and financial inclusion. Among its core components are the Scheduled Commercial Banks (SCBs), which form the backbone of formal credit delivery in the country. These banks operate under the regulatory framework of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and are listed in the Second Schedule of the RBI Act, 1934.
What are Scheduled Commercial Banks?
Definition:
Scheduled Commercial Banks (SCBs) are banks that are:
- Included in the Second Schedule of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934, and
- Fulfill the criteria laid down by the RBI, such as having a paid-up capital and reserves of at least ₹5 lakh and conducting business in the interests of depositors.
These banks can avail of facilities like refinance from the RBI, and are subject to CRR (Cash Reserve Ratio) and SLR (Statutory Liquidity Ratio) requirements.

Classification of Scheduled Commercial Banks
Scheduled Commercial Banks are broadly classified into the following:
| Type of SCB | Description |
|---|---|
| Public Sector Banks (PSBs) | Majority owned by the Government of India |
| Private Sector Banks | Majority ownership lies with private entities or individuals |
| Foreign Banks | Incorporated outside India but operating through branches in India |
| Regional Rural Banks (RRBs) | Joint venture of Central Govt., State Govt., and Sponsor Banks for rural development |
| Small Finance Banks (SFBs) | Cater to underserved sections including small business units, micro & small industries |
| Payments Banks | Provide banking services such as deposits and remittances with certain restrictions |
Key Features of Scheduled Commercial Banks
- Inclusion in RBI’s Second Schedule
- Eligible for borrowing from the RBI
- Subject to CRR, SLR, and other RBI regulations
- Can open branches across India and abroad
- Must maintain capital adequacy norms (Basel norms)
- Offer a wide range of banking services to individuals, businesses, and the government
Public Sector Banks (PSBs)
These are banks where the majority (≥51%) stake is held by the Government of India.
Examples:
- State Bank of India (SBI)
- Punjab National Bank (PNB)
- Bank of Baroda (BoB)
Features:
- Large network of branches in rural and urban areas
- Focus on government schemes and financial inclusion
- Backed by sovereign guarantee
Private Sector Banks
These are banks where the majority stake is held by private entities.
Types:
- Old Private Sector Banks: e.g., Karur Vysya Bank, South Indian Bank
- New Private Sector Banks: e.g., HDFC Bank, ICICI Bank, Axis Bank
Characteristics:
- Technology-driven services
- Competitive interest rates
- Efficient customer service
Foreign Banks
These banks are headquartered outside India but operate branches or subsidiaries within India.
Examples:
- Citibank
- HSBC
- Standard Chartered
Features:
- High-end financial services
- Cater to multinational corporations and HNIs
- Limited physical presence
Regional Rural Banks (RRBs)
RRBs are created to serve rural and semi-urban areas, with emphasis on agriculture and allied sectors.
Key Points:
- Sponsored by a Public Sector Bank
- Joint ownership: GoI (50%) + State Govt (15%) + Sponsor Bank (35%)
- Offer priority sector lending
Small Finance Banks (SFBs)
These are niche banks designed to provide financial services to underserved and unbanked populations.
Functions:
- Accept deposits
- Provide loans to micro industries, small businesses, and the unorganized sector
Examples:
- Ujjivan Small Finance Bank
- AU Small Finance Bank
- Equitas Small Finance Bank
Payments Banks
These banks operate with certain restrictions but aim to enhance financial inclusion.
Limitations:
- Cannot issue credit cards
- Cannot lend money
- Can accept deposits up to ₹2 lakh (as of latest RBI update)
Examples:
- India Post Payments Bank
- Paytm Payments Bank
- Airtel Payments Bank
Role and Importance of Scheduled Commercial Banks
Economic Development
- Mobilize savings and allocate credit efficiently
- Enable industrial and agricultural financing
Employment Generation
- Provide jobs directly in the banking sector
- Indirectly promote entrepreneurship through credit
Financial Inclusion
- Implementation of government schemes like PMJDY, MUDRA
- Bring banking to the unbanked
Monetary Policy Transmission
- Act as intermediaries for RBI’s monetary policy instruments
Role in the Indian Economy
| Area | Contribution |
|---|---|
| Financial Inclusion | Expanding banking access in rural and remote areas |
| Credit Distribution | Loans to agriculture, MSMEs, housing, and infrastructure |
| Economic Growth | Facilitating capital formation and entrepreneurship |
| Government Schemes | Implementation of PMJDY, MUDRA, KCC, etc. |
| Monetary Policy | Instruments of RBI monetary policy transmission |
Challenges Faced by Scheduled Commercial Banks
- Rising NPAs (Non-Performing Assets)
- Cybersecurity threats
- Increasing competition from NBFCs and FinTechs
- Operational inefficiencies in PSBs
- Customer service issues in remote areas
Scheduled vs Non-Scheduled Banks
| Feature | Scheduled Banks | Non-Scheduled Banks |
|---|---|---|
| Listed in RBI Schedule | Yes | No |
| Borrowing from RBI | Eligible | Not eligible |
| CRR/SLR Compliance | Mandatory | Not required |
| Scope | National/International | Mostly local |
| Stability | Higher due to regulations | Comparatively less |
Regulatory Framework
- Reserve Bank of India (RBI): Primary regulator
- Banking Regulation Act, 1949
- RBI Act, 1934
- Basel Norms for capital adequacy
- Financial Stability and Development Council (FSDC) for coordination
Conclusion
Scheduled Commercial Banks are the pillars of India’s financial system, facilitating credit flow, financial inclusion, and economic stability. With continuous reforms, digitization, and regulatory oversight, they are poised to play a greater role in India’s transformation into a $5 trillion economy. However, maintaining asset quality, improving governance, and ensuring customer satisfaction remain key priorities.
FAQs on Scheduled Commercial Banks
Q1. What is the difference between Scheduled and Non-Scheduled Banks?
A: Scheduled banks are listed under the Second Schedule of the RBI Act, 1934 and are regulated by the RBI. Non-scheduled banks are not listed and do not have access to RBI refinancing.
Q2. How many SCBs are there in India?
A: As of 2025, there are 12 Public Sector Banks, 21 Private Sector Banks, 43 Foreign Banks, 43 Regional Rural Banks, 11 Small Finance Banks, and 6 Payments Banks.
Q3. Can Scheduled Banks issue credit cards?
A: All SCBs except Payments Banks can issue credit cards, subject to RBI guidelines.















