
Introduction to Virtual Digital Assets (VDA)
In recent years, the rise of digital technology has transformed how we perceive and exchange value. Virtual Digital Assets (VDAs) have emerged as a significant part of this revolution, driven by blockchain technology, decentralization, and cryptographic security. These assets include cryptocurrencies, NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens), stablecoins, and tokenized digital assets.
Governments and regulatory bodies worldwide are working towards defining, regulating, and taxing VDAs to ensure their secure and responsible use in financial markets.
Definition of Virtual Digital Assets (VDA)
According to the Finance Act 2022 (India), a Virtual Digital Asset (VDA) is defined as:
- Any form of digital representation of value that is generated using cryptographic methods.
- A store of value or a unit of exchange, transferred electronically.
- Includes cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and stablecoins.
- Includes NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens), which represent ownership of unique digital or physical assets.
- Excludes digital representations of traditional currencies regulated by governments (like CBDCs – Central Bank Digital Currencies).
Types of Virtual Digital Assets (VDA)
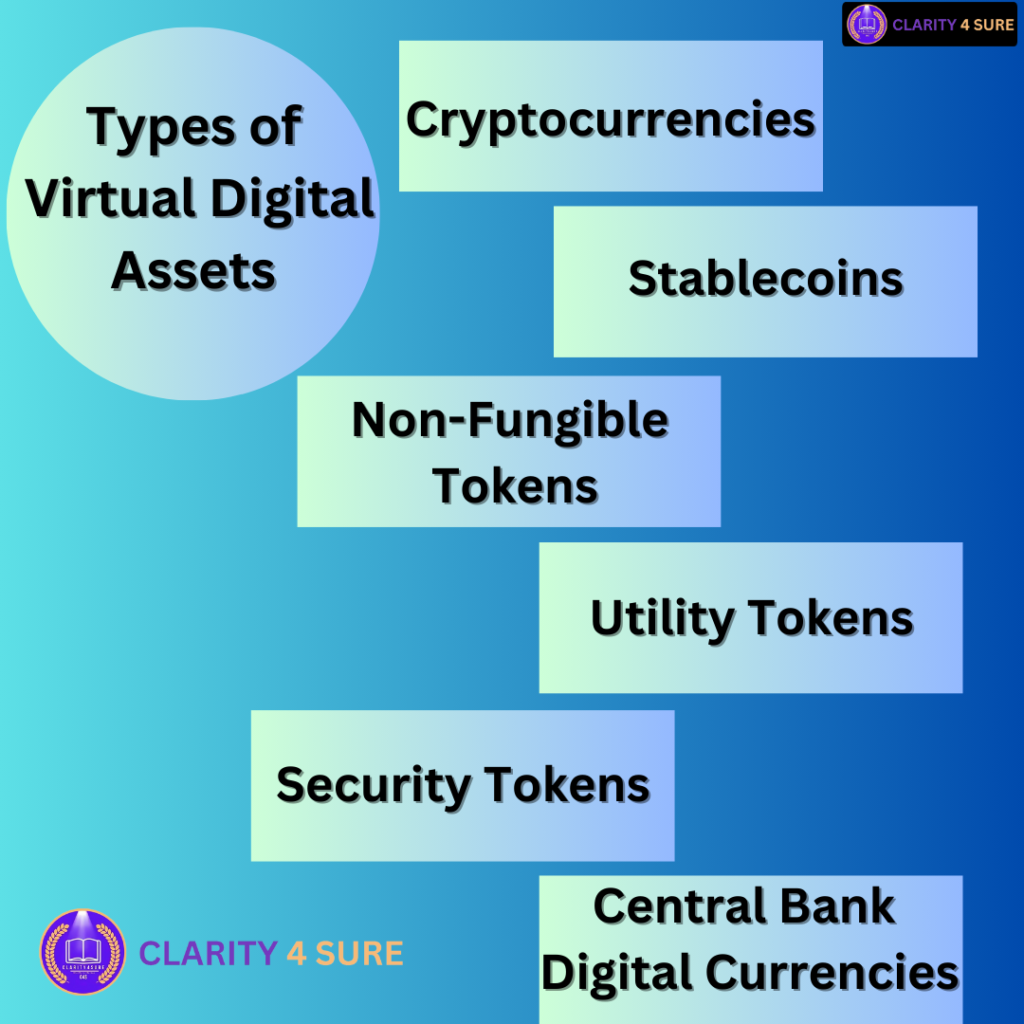
| Type | Definition | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Cryptocurrencies | Digital or virtual currencies secured by cryptography and decentralized networks. | Bitcoin, Ethereum, Ripple, Litecoin |
| Stablecoins | Cryptocurrencies backed by a stable asset like fiat currency (USD, INR) or commodities (gold). | USDT (Tether), USDC, DAI |
| Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) | Unique digital assets that represent ownership of artwork, music, videos, or in-game items. | Bored Ape Yacht Club, CryptoPunks, NBA Top Shot |
| Utility Tokens | Digital assets that provide access to products or services within a blockchain network. | Binance Coin (BNB), Chainlink (LINK) |
| Security Tokens | Tokenized financial assets representing shares, real estate, or investment contracts. | Securitize, tZERO |
| Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) | Digital currencies issued and backed by central banks. | Digital Yuan (China), e-Rupee (India) |
Key Features of Virtual Digital Assets
- Decentralization:
- Most VDAs operate on blockchain technology, eliminating intermediaries like banks and financial institutions.
- Borderless Transactions:
- Digital assets can be transferred globally without traditional banking constraints.
- Security & Transparency:
- Transactions are recorded on an immutable blockchain ledger, reducing fraud risks.
- Programmability:
- Smart contracts enable automated transactions and agreements without manual intervention.
- Scarcity & Value Storage:
- Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin have limited supply, increasing their value over time.
- Interoperability:
- VDAs can be used across multiple blockchain networks and financial ecosystems.
Legal & Regulatory Framework for VDAs
The regulation of Virtual Digital Assets varies across countries. Governments are implementing laws to ensure investor protection, prevent financial crimes, and enable taxation.
India’s VDA Regulations
In India, the Finance Act 2022 introduced taxation and reporting requirements for VDAs:
- Taxation on Crypto Transactions: 30% tax on income from cryptocurrency transactions.
- TDS (Tax Deducted at Source): 1% TDS on cryptocurrency transfers above ₹50,000 per year.
- No Set-off of Losses: Losses from VDA transactions cannot be offset against other income.
- GST on Crypto Services: Exchange platforms and services may be subject to GST (Goods & Services Tax).
Global Regulatory Approaches
| Country | Regulatory Status | Key Highlights |
|---|---|---|
| United States | Partially regulated | SEC regulates security tokens, IRS taxes cryptocurrencies as property. |
| European Union | MiCA (Markets in Crypto-Assets) framework | Implements licensing for crypto service providers and investor protection rules. |
| China | Banned | Cryptocurrency trading and mining are banned, but CBDC (Digital Yuan) is actively promoted. |
| Japan | Regulated | Crypto exchanges must register with the FSA (Financial Services Agency). |
| United Kingdom | Regulated | FCA oversees crypto firms, ensuring compliance with anti-money laundering laws. |
Opportunities & Benefits of VDAs
- Financial Inclusion:
- Enables global access to financial services without the need for traditional banks.
- Borderless Payments:
- Allows instant, low-cost international transactions.
- Investment Opportunities:
- Provides new ways to store and grow wealth through staking, DeFi (Decentralized Finance), and tokenized assets.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi):
- Eliminates intermediaries in lending, borrowing, and trading.
- Ownership & Digital Identity:
- NFTs provide verifiable ownership of digital assets.
- Smart Contracts & Automation:
- Automates financial agreements without legal intermediaries.
Risks & Challenges of VDAs
- Price Volatility:
- Cryptocurrencies are highly volatile, leading to financial risk.
- Regulatory Uncertainty:
- Changing government policies may impact VDA adoption.
- Security Concerns:
- Hacks, scams, and exchange failures pose risks to users.
- Illicit Use Cases:
- Crypto assets may be misused for money laundering and illegal activities.
- Energy Consumption:
- Proof-of-work (PoW) blockchains like Bitcoin consume high amounts of energy.
Future of Virtual Digital Assets
The VDA ecosystem is evolving with advancements in blockchain scalability, central bank digital currencies (CBDCs), tokenization of real-world assets, and Web3 applications. Governments are likely to implement balanced regulations to promote innovation while preventing risks.
Key Trends to Watch:
- CBDC Development –
- Countries are exploring digital national currencies for financial stability.
- Tokenization of Real Assets –
- Real estate, stocks, and commodities may be tokenized on blockchains.
- Metaverse & Gaming NFTs –
- Digital assets will play a crucial role in virtual worlds and gaming economies.
- Interoperability Solutions –
- Cross-chain technologies will improve asset transfers between blockchains.
- Institutional Adoption –
- Large financial firms are increasingly investing in crypto infrastructure.
Conclusion
Virtual Digital Assets (VDAs) represent the future of digital finance, offering a decentralized, secure, and transparent way to exchange and store value. Despite challenges like regulatory uncertainty and price volatility, global adoption is increasing, with governments, institutions, and individuals recognizing their potential.
As blockchain technology continues to evolve, VDAs will become a crucial component of the global financial system. Whether as an investment tool, payment solution, or decentralized application, VDAs are shaping the digital economy of the future.
FAQs About Virtual Digital Assets (VDA)
1. What are Virtual Digital Assets (VDA)?
VDAs include cryptocurrencies, NFTs, stablecoins, and tokenized digital assets that are exchanged electronically.
2. Are cryptocurrencies legal in India?
Cryptocurrencies are not illegal but are taxed under Indian law. India does not recognize them as legal tender.
3. How are VDAs taxed in India?
Profits from VDAs are taxed at 30% with 1% TDS on transactions above ₹50,000 per year.
4. What is the difference between cryptocurrency and CBDC?
Cryptocurrency is decentralized, while CBDC (Central Bank Digital Currency) is issued and controlled by the government.
5. What is the future of VDAs?
The future includes CBDCs, real-world asset tokenization, Web3 adoption, and institutional investments.

















