Context:
With tensions escalating between Israel and Iran, India is closely monitoring the potential impact on its strategic infrastructure investments — particularly the Chabahar Port and the International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC).
International North–South Transport Corridor (INSTC)
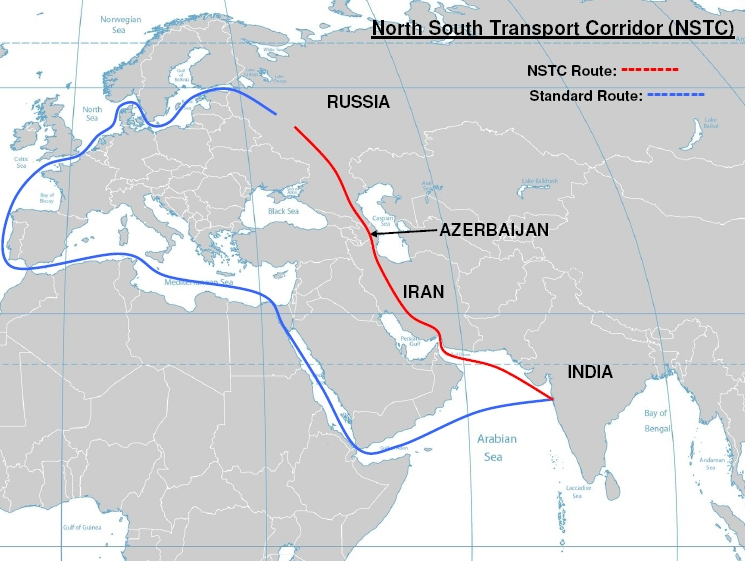
The International North–South Transport Corridor (INSTC) is a 7,200-kilometre multi-modal trade corridor that connects India with Iran, Central Asia, Russia, and Europe through an integrated network of ship, rail, and road routes. It aims to reduce the time and cost of cargo movement between major trade hubs such as Mumbai, Moscow, Tehran, Baku, Bandar Abbas, and Astrakhan.
Originally signed on 16 May 2002 by India, Iran, and Russia, the project has since expanded to include several Eurasian economies.
Key Objectives
- Trade Efficiency: Reduce transportation costs and time compared to traditional sea routes via the Suez Canal.
- Strategic Connectivity: Strengthen trade links between India, Central Asia, the Caucasus, Russia, and European markets.
- Cost & Time Savings: FFFAI estimates the route is 30% cheaper and 40% shorter than existing traditional options.
Synchronisation with Ashgabat Agreement
INSTC aligns with the Ashgabat Agreement, a multilateral pact aimed at facilitating goods transit between Central Asia and the Persian Gulf.
Members (Year of Joining):
- Oman (2011), Iran (2011), Turkmenistan (2011), Uzbekistan (2011), Kazakhstan (2015), India (2018)
INSTC Member Countries
Full Members:
- India
- Iran
- Russia
- Azerbaijan
- Armenia
- Kazakhstan
- Belarus
- Turkey
- Tajikistan
- Kyrgyzstan
- Oman
- Ukraine
- Syria
Observers:
- Bulgaria
Note: Turkmenistan is not a formal member but has been invited to join by India.
Geostrategic and Economic Significance
- Enables India’s outreach to Central Asia and Russia without relying on traditional sea routes via Suez.
- Provides a strategic alternative to China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
- Facilitates regional integration by building physical and institutional connectivity infrastructure.
- Enhances India’s Act East and Connect Central Asia policies.















