Context:
India Assembles Human Genomes for Disease and Drug Therapy: India released a year’s compilation of 10,000 human genomes of 83 population groups, roughly 2% of the country’s 4,600 population groups.
Key Highlights:
- Genome India database was hosted at Indian Biological Data Centre, Faridabad, Haryana.
- Significance
- It will help the researchers to understand diseases so that there will be targeted clinical interventions and precision medicine.
Genome
A genome is the complete set of DNA, or genetic material, in an organism. It contains all the information an organism needs to develop and function.
- How is a genome organized?
- A genome is made up of DNA, which is a set of instructions organized into genes and chromosomes.
- Genes are segments of DNA that carry instructions for making proteins.
- Chromosomes are protein structures that carry genetic information from one cell to the next.
- What is a genome?
- The information that an organism needs to develop and function is found in the genome.
- Genes in the genome guide the production of proteins that build and repair tissues and organs.
- What is genomics?
- The study of genomes identifies how genes are expressed and interact with the environment.
- What is the human genome?
- The human genome consists of around 3 billion DNA base pairs, 23 pairs of chromosomes, and 20,000 to 25,000 genes.
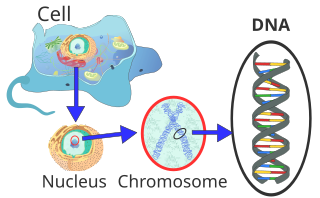
DNA, RNA, and Chromosomes are all parts of the genetic code that store and transmit hereditary information.
DNA
- Structure:
- DNA is a double-stranded helix made of long chains of chemical bases
- Function:
- DNA contains the instructions for making and maintaining living things
- Stability:
- DNA is a relatively stable molecule
RNA
- Structure:
- RNA is a single-stranded molecule made of long chains of chemical bases connected by a sugar backbone
- Function:
- RNA contains instructions for the function of a cell
- Reactivity:
- RNA is more reactive than DNA
Chromosomes
- Structure:
- Chromosomes consist of DNA in the form of coiled bundles
- Function:
- Chromosomes are the reservoir and means of hereditary information
- Components:
- Chromosomes consist of genes, which refer to a DNA segment coding for proteins or RNA molecules
DNA and RNA in chromosomes
- DNA provides the blueprint that RNA translates to proteins
- Chromosomes consist of DNA and genes refer to DNA segments aligned on chromosomes.
















