Daily Current Affairs Quiz
22 & 23 June, 2025
International Affairs
1. U.S. Launches Strikes on Iran’s Nuclear Sites
Context:
In a dramatic escalation of the Israel-Iran conflict, the United States launched direct strikes on Iran’s nuclear facilities, dropping 30,000-pound bombs on key uranium enrichment sites. The unprecedented attack marks a significant shift in U.S. engagement, prompting fears of a full-blown regional war. This Mission was named as “Operation Midnight Hammer”.
Iran’s Nuclear Facilities Targeted in Airstrikes
The US-Israel joint strike, part of a coordinated military operation, hit three of Iran’s most sensitive nuclear sites:
1. Fordow Fuel Enrichment Plant
- Location: Deeply buried under a mountain near Qom.
- Function: Enriches uranium up to 60% purity.
- Significance: Its depth made it nearly immune to conventional strikes—until the use of MOPs.
2. Natanz Nuclear Facility
- Status: Iran’s largest uranium enrichment complex.
- Assets: Hosts thousands of advanced centrifuges in subterranean halls.
- Strategic Importance: Considered the backbone of Iran’s enrichment program.
3. Isfahan Nuclear Complex
- Capabilities: Includes uranium conversion facilities and nuclear research reactors.
- International Oversight: Monitored by the IAEA, which confirmed enriched uranium production.
Consequences of U.S. Involvement
- Destabilize Middle East: The move could destabilize the broader Middle East, entangle major powers like Russia and China, and undermine ongoing efforts to revive the Iran nuclear deal (JCPOA).
- Geopolitical Fallout: Iran views the U.S. attacks as a crossing of a “red line” and has declared that diplomacy has failed.
- Increased Regional Risk: If Iran retaliates against U.S. forces or bases, the war could spiral into a full-scale regional conflict.
- Global Ramifications: Trust in U.S.-led diplomacy may erode, smaller nations may accelerate nuclear ambitions (e.g., North Korea, possibly Iran).
- West Asia Instability: Israel’s aggressive strategy, now backed by U.S. firepower, has plunged the region into deeper insecurity.
TH
2. Strait of Hormuz
Why in News?
Iran’s parliament, the Majlis, has reportedly approved the closure of the Strait of Hormuz in response to the attacks by the U.S. on Iranian nuclear facilities, the country’s state-owned media PressTV reported.
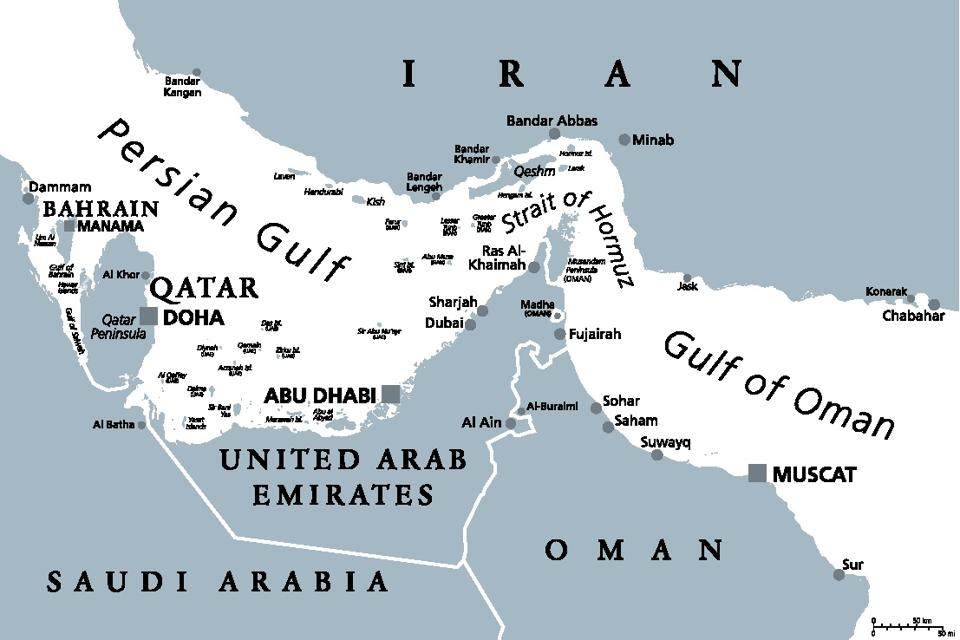
What is the Strait of Hormuz?
The Strait of Hormuz is one of the most strategically important maritime chokepoints in the world. Situated at the mouth of the Persian Gulf, it connects the Persian Gulf to the Gulf of Oman and the Arabian Sea, serving as a vital artery for global energy transport.
Geographical Significance
- Location: Lies between Iran (north) and Oman & the UAE (south).
- Width: Approximately 33 km wide at its narrowest point.
- Shipping Channel: Only 3 km wide in each direction for navigation.
Global Energy Lifeline
- Oil Transport: About 20% of all seaborne crude oil passes through the Strait.
- OPEC Dependence: Major oil exporters like Saudi Arabia, Iran, the UAE, Kuwait, and Iraq rely on this route.
- LNG Transit: Nearly all LNG exports from Qatar—the world’s largest LNG exporter—also pass through the Strait.
Alternate Routes & Strategic Moves
Due to the Strait’s vulnerability to geopolitical tensions:
- Saudi Arabia and the UAE have invested in alternate routes.
- This includes constructing oil pipelines that bypass the Strait of Hormuz, reducing dependency on this chokepoint.
Importance in Global Affairs
Any disruption to navigation in the Strait of Hormuz can:
- Impact global oil prices.
- Trigger military tensions, especially involving Iran and Western powers.
- Affect global energy security, making it a critical focal point in geopolitics.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. Which one of the following straits is nearest to the International Date Line? (2008)
(a) Malacca Strait
(b) Bering Strait
(c) Strait of Florida
(d) Strait of Gibraltar
Ans: (b)
National Affairs
1. e-Raktkosh Portal
Context:
In a major move aimed at saving lives and reducing costs for patients with rare blood groups and genetic blood disorders, the Union Health Ministry is set to integrate the Rare Donor Registry of India (RDRI) with e-Rakt Kosh, the national blood bank management and availability platform.
e-Raktkosh Portal
e-Raktkosh is a comprehensive, centralized IT solution developed to streamline and standardize the functioning of blood banks across India. It supports transparency, traceability, and efficiency in the blood donation life cycle.
- Launched on: 7th April 2016
- By: Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW)
- Objective: To ensure compliance with Drugs & Cosmetics Act and National Blood Policy standards
Key Features of e-Raktkosh
- Centralized Blood Inventory Management System
- Donor Management System (Biometric)
- Blood Grouping and TTI Screening
- Antibody Screening Mechanisms
- Bio-Medical Waste Management for discarded blood
- Ensures availability, accessibility, and safety of blood
Understanding Blood Disorders
What is a Blood Disorder?
A blood disorder is a medical condition that affects the components of blood—red blood cells (RBCs), white blood cells (WBCs), plasma, or platelets—and hinders their normal function.
- Can be common (e.g., anemia) or rare (e.g., thalassemia)
- May impact oxygen transport, immunity, or clotting
2. Delhi’s First Artificial Rain Project to Tackle Pollution
Context:
The Delhi government, in partnership with IIT-Kanpur and the Department of Environment, is launching its first cloud seeding (artificial rain) pilot project to combat severe winter air pollution.
What is Artificial Rain?
- Definition: A weather modification technique to induce rainfall by dispersing chemicals into clouds.
- Chemicals Used: Silver iodide, potassium iodide, dry ice, rock salt.
- Purpose: Enhance condensation in clouds to trigger rainfall and wash out pollutants.
Why Delhi Needs It
- Pollution Spike: Delhi frequently records PM2.5 and PM10 levels in the ‘severe’ category.
- Sources of Pollution:
- Vehicle and industrial emissions
- Construction dust
- Crop stubble burning in neighbouring states
- Unfavourable meteorological conditions
- Health Risk: Hazardous air quality impacts respiratory and cardiovascular health.
Cloud Seeding
What is Cloud Seeding?
Cloud seeding is a scientific technique used to enhance precipitation by artificially dispersing chemical substances—such as silver iodide, potassium iodide, or dry ice—into clouds. These act as condensation or ice nuclei, encouraging the formation of raindrops or snowflakes.
- Purpose: To induce or increase rainfall/snowfall
- Common Chemicals: Silver iodide, potassium iodide, dry ice
- Mechanism: Enhances microphysical processes in clouds by accelerating droplet formation
Applications of Cloud Seeding
- Air Pollution Control: Helps settle airborne pollutants (like PM2.5 and PM10) by promoting rainfall, especially during high AQI periods
- Water Resource Management: Increases water availability in reservoirs, agriculture, and drought-prone areas
- Climate and Environmental Benefits: Contributes to ecosystem health, agricultural productivity, and weather stabilization
- Health Benefits: Improves air quality, reducing respiratory diseases linked to pollution
Types of Cloud Seeding
- Static Cloud Seeding
- Introduces ice-forming nuclei into cold clouds
- Converts supercooled water into ice crystals or snowflakes
- Typically used to induce precipitation in stable cloud systems
- Dynamic Cloud Seeding
- Aims to stimulate vertical air currents
- Enhances cloud growth and precipitation through energy amplification
- More complex and relies on meteorological conditions
- Hygroscopic Cloud Seeding
- Uses fine salt particles (e.g., sodium chloride) to attract moisture
- Increases cloud droplet size, making them heavy enough to fall as rain
- Effective in warm and moist cloud conditions
- Glaciogenic Cloud Seeding
- Induces ice formation in supercooled liquid clouds
- Leads to precipitation as snow or rain
- Commonly used in mountainous regions to increase snowpack, aid in drought relief, and combat pollution
UPSC Prelims PYQ 2025
Q. Artificial way of causing rainfall to reduce air pollution makes use of
(a) silver iodide and potassium iodide
(b) silver nitrate and potassium iodide
(c) silver iodide and potassium nitrate
(d) silver nitrate and potassium chloride
Ans: (a) silver iodide and potassium iodide
Banking/Finance
1. SEBI Initiates Comprehensive Review of Mutual Fund Regulations
Context:
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has launched a comprehensive review of the mutual fund (MF) regulatory framework to make it more investor-centric and industry-friendly, while improving the overall ease of doing business for stakeholders.
Key Objectives of the Review
- Simplification of Existing Rules:
- The current MF regulations are among the lengthiest in India’s securities law framework and require updating to stay relevant in light of:
- Changing investor behaviour
- Technological innovation
- Industry expansion
- The current MF regulations are among the lengthiest in India’s securities law framework and require updating to stay relevant in light of:
- Draft Regulations Underway:
- SEBI has begun the process of preparing draft regulations, which will be released for public feedback and stakeholder consultation before finalisation.
Focus Areas of Reform
- Investor-Centric Approach:
- Enhance investor protection
- Improve transparency and disclosures
- Encourage better advisory services
- Ease of Doing Business:
- Simplify compliance for Asset Management Companies (AMCs)
- Reduce regulatory burden without compromising accountability
- Advisory Functions:
- A separate consultation paper on MF advisory norms is being prepared to address product suitability and quality of advice.
Strategic Significance
- SEBI views mutual funds as a core pillar of inclusive financial growth and a key driver in expanding retail investor participation.
- The reforms aim to build a robust, transparent, and efficient mutual fund ecosystem, aligned with global best practices.
2. SEBI Eases Startup Regulations and Introduces Major Reforms for AIFs, REITs, and PSUs
Context:
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), in its latest board meeting, introduced a comprehensive set of regulatory changes aimed at improving the capital-raising ecosystem for startups, simplifying delisting norms for PSUs, and enhancing operational flexibility for AIFs, REITs, and InvITs. These changes come amid global financial uncertainties and are expected to boost domestic fundraising and investment flows.
Key Reforms for Startups
- ESOP Clarity for Founders: Startups can now issue and allow the exercise of ESOPs to founders/promoters if granted at least one year before the filing of the Draft Red Herring Prospectus (DRHP).
- Dematerialisation Mandate: Senior management must now dematerialise their shareholdings before DRHP filing.
- Lock-in Period Scrapped: One-year lock-in for shares derived from Compulsorily Convertible Securities (CCS) removed, easing participation in Offer for Sale (OFS).
- Reverse Flipping Incentivised: Reforms will support Indian listings of startups initially launched abroad.
- Promoter Contribution Expanded: Shares held by foreign VC funds, AIFs, and public financial institutions can now count toward minimum promoter contribution in IPOs.
Co-Investment Vehicle (CIV) Framework under AIFs
- New CIV Framework: Category I and II AIFs can now form Co-Investment Vehicles (CIVs), simplifying co-investments for AIF investors.
- Streamlined Investment Process: Investors can co-invest in portfolio companies without routing through external PMS structures or breaching restrictions on unlisted companies.
REITs and InvITs Regulation Changes
- Unit Classification: Units held by related parties will no longer be counted as public holding.
- Cash Flow Flexibility: Holding companies can offset negative standalone net distributable cash flows against income from Special Purpose Vehicles (SPVs) before distribution, with disclosures.
- Reduced Minimum Investment: For privately placed InvITs, the minimum allotment size has been reduced from ₹1 crore to ₹25 lakh.
Simplified PSU Delisting Norms
- Eased Exit for Majority-Govt PSUs: New delisting norms apply to PSUs where the government holds at least a 90% stake. Around five listed PSUs could benefit.
BS
3. SEBI Proposes Guardrails for AI and ML in Indian Securities Markets
Context:
In a timely and forward-looking move, the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has released a discussion paper titled “Guidelines for Responsible Usage of AI/ML in the Indian Securities Market.” This consultation initiative aims to regulate the rapid rise of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) applications—particularly algorithmic trading—on Dalal Street.
Why It Matters?
While AI doesn’t introduce fundamentally new risks to markets, it can amplify existing vulnerabilities such as market manipulation, flash crashes, systemic contagion, and biased decision-making. SEBI’s proactive stance is meant to ensure investor protection, financial stability, and ethical use of AI technologies in securities trading.
Key Elements of SEBI’s Proposed Framework
- Model Governance and Testing:
- Mandate for rigorous pre-deployment testing and periodic audits of AI/ML models.
- Explainability and traceability of model decisions to be ensured.
- Bias, Fairness, and Privacy:
- Guidelines on mitigating algorithmic bias, protecting investor data, and ensuring model integrity.
- Disclosure Requirements:
- Entities must disclose the nature of AI/ML systems used, data sources, model purpose, and decision-making logic to SEBI.
- Third-Party and Non-Traditional Players:
- Regulatory purview to expand to cover third-party algo vendors, fintech startups, and non-registered intermediaries using AI for financial services.
- Investor Protection and Oversight:
- Emphasis on human-in-the-loop supervision, especially as markets inch closer to agentic AI—AI systems that can act autonomously in investing.
Implications
- Market participants will need to revisit their AI governance frameworks, particularly around model validation and compliance reporting.
- Startups and fintechs must prepare for regulatory scrutiny if offering AI-based trading or advisory services.
- Investors may benefit from more transparent and explainable AI tools, subject to new disclosures and testing standards.
4. Credit Rating Agencies Seek Government Intervention
Contex:
Credit Rating Agencies (CRAs) in India have approached the Ministries of Finance and Corporate Affairs, seeking immediate regulatory clarity on rating unlisted debt instruments worth over ₹1 lakh crore. These include Pass-Through Certificates (PTCs) and unlisted corporate bonds—a vital part of the country’s wholesale debt ecosystem.
What’s the Issue?
- Regulatory Overlap: SEBI regulates CRAs but only for listed securities.
- Unlisted instruments like PTCs and company fixed deposits fall outside both SEBI’s and RBI’s clear jurisdiction.
- In 2023, SEBI required CRAs to obtain an NOC from RBI for rating unlisted papers.
- While RBI allowed ratings for Certificates of Deposit (CDs), it remains silent on PTCs and unlisted bonds, leaving a regulatory grey zone.
Why This Matters
- Market Size: Unlisted instruments like PTCs help lenders (NBFCs, banks) unlock liquidity from retail loan pools.
- Investor Confidence: Ratings influence pricing, risk evaluation, and compliance standards for institutional investors.
- Capital Requirements: Banks prefer rated instruments due to lower capital provisioning needs.
TET
5. Bank of Maharashtra Partners with SBI Card to Launch Co-Branded Credit Cards
Context:
In a strategic move to strengthen its retail offerings, Bank of Maharashtra (BoM) has announced a co-branding partnership with SBI Card to launch co-branded credit cards aimed at fulfilling the financial and lifestyle needs of its customer base.
Key Highlights of the Partnership
- Tailored Credit Cards: The co-branded cards will feature:
- Reward points on purchases
- Cashback offers on selected transactions
- EMI facilities
- Exclusive merchant discounts across major categories like dining, travel, and e-commerce
- Distribution Channels:
- Available through both digital platforms and branch-based channels
- Seamless and easy onboarding process for eligible customers nationwide
- Collaborative Strengths:
- BoM’s extensive banking network and trusted customer relationships
- SBI Card’s credit card expertise, digital capabilities, and diverse product suite
6. Outward Direct Investment (ODI)
Context:
India is witnessing a significant surge in outward direct investment (ODI) by domestic corporations, raising questions about whether this reflects increasing global competitiveness or underlying concerns about the business environment at home. Indian outward investment has jumped from $4 billion in 2014–15 to $29 billion in 2024–25, a 625% increase over a decade.
What is ODI?
Overseas Direct Investment (ODI) refers to investments made by Indian individuals or companies in businesses, assets, or operations located outside India. These investments typically involve ownership, control, or significant influence in foreign enterprises through subsidiaries, joint ventures, or branches.
Key Features of ODI
- Control & Influence: ODI involves significant control or influence, generally defined as ownership of at least 10% in the foreign entity.
- Purpose:
- Business expansion
- Market diversification
- Access to strategic resources
- Risk distribution across geographies
- Investment Forms:
- Equity participation in foreign companies
- Establishing manufacturing/service units abroad
- Real estate purchases and infrastructure projects
Major Destinations for Indian ODI
- Singapore
- United States
- United Kingdom
- United Arab Emirates (UAE)
- Saudi Arabia
- Oman
- Malaysia
Significance of ODI for India
- Technology & Skill Transfer: Facilitates the inflow of modern practices and R&D back into India.
- Global Market Access: Enables Indian companies to tap into international consumer bases and supply chains.
- Brand Promotion: Enhances the global brand visibility of Indian enterprises.
- Employment Generation: Creates jobs both in the host country and within India through backward linkages.
- Resource Utilisation: Leverages raw materials available in both India and the host country for value addition.
- Boost to Trade: Strengthens foreign trade by building international production and export networks.
- Foreign Exchange Earnings: Generates long-term foreign currency inflows from profits, royalties, and dividends.
TH
7. Digital Payment Intelligence Platform (DPIP)
Context:
In response to the rising tide of digital payment frauds, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has initiated the development of a Digital Payment Intelligence Platform (DPIP) — a cutting-edge Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) aimed at strengthening fraud risk management across India’s financial ecosystem.
Key Objectives of DPIP
- Real-Time Intelligence Sharing: Enable participating banks to share and access real-time data on suspicious digital transactions.
- Centralised Threat Detection: Collect and analyse transaction data across sources to identify patterns, anomalies, and potential fraud.
- Unified Fraud Management: Establish a pan-industry mechanism to prevent cross-platform and cross-institutional fraud attempts.
- Digital Public Infrastructure: Position DPIP as part of India’s evolving DPI framework, much like UPI and Aadhaar.
Why the Urgency? – Rising Digital Payment Frauds
- Surge in Fraud Cases:
- FY25 fraud value surged to ₹36,014 crore, nearly 3x higher than FY24’s ₹12,230 crore.
Expected Benefits of DPIP
- Enhanced Transaction Security: Real-time alerts and monitoring will help identify and prevent fraud at the source.
- Improved Consumer Trust: Secured digital ecosystems will promote greater adoption of digital payments.
- Data-Driven Regulation: The RBI will gain sharper insights for future policy interventions and risk assessment.
- Scalability Across Platforms: The platform can integrate with UPI, RuPay, Internet Banking, and emerging payment modes.
Agriculture
1. India Emerges as World’s Top Rice Producer
Context:
India has overtaken China to become the world’s largest rice producer, with a record output of 149 million tonnes in 2025, and continues to be the top global rice exporter since 2012, accounting for nearly 40% of world trade. This agricultural milestone is a result of coordinated efforts from farmers, scientists, and policymakers.
Key Highlights
- Technological & Policy Support:
- Early adoption of IR8 in 1966 catalyzed the rice revolution.
- India’s extensive rice-breeding programs have developed high-yield, pest-resistant, climate-resilient varieties.
- Minimum Support Price (MSP), input subsidies, and assured procurement incentivized growth.
- India’s Global Standing:
- Leading exporter of rice and second-largest wheat producer.
- Emerged as a key food grain powerhouse despite small landholdings and a large population.
Challenges to Sustainability
- Water Overuse:
- Paddy cultivation uses up to 15,000 litres of water per kg—2.5 times the actual requirement.
- Rice consumes 45–50% of irrigation water, threatening water tables, especially in Punjab and Tamil Nadu.
- Excessive irrigation leads to higher greenhouse gas emissions from paddy fields.
- Sustainable Alternatives:
- Direct Seeding of Rice (DSR) and Alternate Wetting and Drying (AWD) methods can:
- Save 30–60% water.
- Reduce emissions and input usage.
- Maintain crop yield.
- Direct Seeding of Rice (DSR) and Alternate Wetting and Drying (AWD) methods can:
2. Tractor-Operated Plastic Mulch Layer-Cum-Planter
Context:
Union Minister of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare Shri Shivraj Singh Chouhan visited the ICAR-Central Institute of Agricultural Engineering (CIAE) in Bhopal to review its research contributions and push for accelerated development and dissemination of farmer-centric technologies, particularly for small and marginal farmers.
Tractor-Operated Plastic Mulch Layer-Cum-Planter
ICAR-CIAE demonstrated a multi-functional, tractor-operated implement that integrates plastic mulch laying, drip lateral installation, and seed planting in one pass, reducing manual labour and operational cost drastically.
Technical Specifications:
- Mechanism:
- Hydraulic system powers an eccentric slider crank mechanism.
- Vacuum seed metering via aspirator blower connected to tractor PTO.
Benefits:
- Labour savings: 26 man-days/ha (89%)
- Cost savings: ₹6,600/ha (43%)
- Suitable for planting high-value crops like:
- Melon, cucumber, sweet corn, baby corn, green pea, okra, and beans.
Relevance
The Minister’s visit and the technology demonstration align with national goals of:
- Enhancing mechanization in smallholder farming
- Promoting climate-smart and resource-efficient agriculture
- Strengthening food security through technology diffusion
Facts To Remember
1. No 90m this time but Neeraj bests Weber for the title
Olympic medal-winning Neeraj Chopra clinched his first Diamond League title in two years, upstaging German rival Julian Weber without having to hit the 90m mark in a strong field here.
2. Pakistan to Recommend Donald Trump for 2026 Nobel Peace Prize Over India-Pakistan Mediation
The Government of Pakistan announced on Saturday that it will formally recommend former U.S. President Donald Trump for the 2026 Nobel Peace Prize, citing his “decisive diplomatic intervention” during the recent India-Pakistan conflict.
3. INS Tamal to be Commissioned in Russia on July 1: India’s Last Foreign-Built Frigate
The Indian Navy will commission its latest and final foreign-built stealth frigate, INS Tamal, on July 1, 2025, at Kaliningrad, Russia. Built at the Yantar Shipyard, INS Tamal marks the completion of India’s long-standing Krivak-class warship programme with Russia. Future warships will now be built domestically under the “Atmanirbhar Bharat” initiative.
















