Daily Current Affairs Quiz
29 January, 2025
International Affairs
1. DeepSeek AI
Context:
A Chinese-made artificial intelligence (AI) model called DeepSeek has shot to the top of Apple Store’s downloads, stunning investors and sinking some tech stocks.
Company Background
- Established
- 2023, in Hangzhou Zhejiang
- Founder
- Liang Wenfeng
What is AI?
- Definition
- AI is a set of technologies that enable computers to perform tasks typically requiring human intelligence. These tasks include learning from data, making decisions and improving performance over time.
How AI Works?
- Mathematics and Logic
- AI uses mathematical algorithms and logic to simulate human reasoning processes.
- Data Analysis
- AI systems analyze large datasets to identify patterns and make predictions.
- Learning from Mistakes
- AI systems can learn and improve by making mistakes in the past which will enhance their accuracy over time.
Capabilities of AI
- Data Analysis
- AI can process vast amounts of data to extract valuable insights and provide recommendations.
- Language Understanding
- AI can understand both spoken and written language enabling tasks like translation and interpretation.
- Decision Making
- By recognizing patterns in data AI can make informed decisions.
- Learning from Experience
- AI continuously learns from datasets, improving its performance as it encounters new information.
Applications of AI
- Healthcare
- AI improves the accuracy of diagnosis, personalizes treatment, patient outcomes, and accelerates research. India’s ICMR also came up with ethical guidelines for AI in healthcare.
- Business
- AI optimizes operations, improves customer service, detects fraud, analyses big data and enhances innovation.
- Education
- AI supports customized learning. Examples include the IIT Kharagpur and Amazon Web Services collaboration to create AI-based teaching tools.
- Judiciary
- AI assists in legal research, case management, and offers virtual legal aid, such as SUVAS and SUPACE.
- Cybersecurity
- AI assists in the detection of cyber threats, analyzing data for vulnerabilities, and automated responses to threats.
IndiaAI Mission
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. With the present state of development, Artificial Intelligence can effectively do which of the following? (2020)
- Bring down electricity consumption in industrial units
- Create meaningful short stories and songs
- Disease diagnosis
- Text-to-Speech Conversion
- Wireless transmission of electrical energy
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (b)
2. BIMSTEC

Origin
The Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC) was established in 1997. The organization was created to promote economic and social development among its member countries.
About
- Headquarter:
- Dhaka, Bangladesh
- Ministry:
- Ministry of External Affairs
- BIMSTEC, which stands for the Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation, is a regional organization comprising seven countries:
- Bangladesh
- India
- Myanmar
- Sri Lanka
- Thailand
- Nepal
- Bhutan
- It was established in 1997 with the aim of fostering cooperation among these countries in various sectors such as trade, technology, energy, environment, and tourism, while promoting regional integration and development.
What is BIMSTEC?
BIMSTEC was established in 1997 and consists of seven member states that are located around the Bay of Bengal. These countries are:
- India
- Bangladesh
- Myanmar
- Sri Lanka
- Thailand
- Nepal
- Bhutan
- The primary objective of BIMSTEC is to foster cooperation across multiple sectors, focusing on economic and technical development, trade, connectivity, and regional security.
- The organization aims to enhance regional integration among its member countries, which are geographically significant and have cultural, historical, and economic ties.
Key Objectives of BIMSTEC
- Economic Cooperation:
- Enhancing economic connectivity and trade relations between member countries through reduction of trade barriers, tariffs, and improving infrastructure.
- Regional Security:
- Promoting peace and security in the region through collaboration in combating terrorism, transnational crime, and addressing maritime security concerns.
- Cultural and People-to-People Connectivity:
- Encouraging cultural exchanges, tourism, and collaboration in education to foster closer ties among the people of member nations.
- Technology and Knowledge Sharing:
- Strengthening collaboration in sectors like information technology, agriculture, energy, and education through sharing of technical expertise and resources.
- Environmental Cooperation:
- Working together on climate change, natural resource management, and disaster response in the region, which is highly prone to natural disasters like cyclones and floods.
National Affairs
1. Annual Status of Education Report (ASER), 2024
Context:
After a prolonged decline due to learning losses during the COVID-19 pandemic, there has now been a modest recovery in foundational literacy and numeracy (FLN) among school students, according to the Annual Status of Education Report (ASER) 2024, released. The survey of almost 6.5 lakh children in 605 villages across the country tested them in basic reading and arithmetic skills and found a slight improvement in comparison to pre-COVID 2018 levels.
Key Highlights:
- Recovery in Foundational Literacy
- Learning loss recovery since COVID. Now showing better scores in early grade reading and numeracy but major gaps persist.
- Reading Skills
- Class 3 Improved significantly but fourths still cannot read properly.
- Class 5 to 8: No change with half of the students in Class 5 unable to read a Class 2 text.
- Arithmetic Skills
- Early grade numeracy still poor with two thirds of Class 3 students failing basic subtraction.
- Class 5 Slight improvement in division skills but still a majority struggle with basic operations.
State Level Inequalities
- Top gaining states
- Gujarat, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Tamil Nadu, Sikkim and Mizoram topped with a gain of 10 percentage points in reading skills.
- Moderate gainers
- Odisha, Haryana, West Bengal and Jharkhand gained between 699 percentage points.
- Slow gainers
- Himachal Pradesh and Bihar registered only 459 percentage points which signifies the uneven distribution of education recovery in regions.
Access to Technology and Digital Divide
- Mobile phone penetration
- 89 of teens 14 to 16 years own a smartphone but only 57 use it for education.
- Gaps in awareness of digital safety
- Boys are more aware of the online safety features than girls.
- It means there is a need for specific digital literacy programs for girls.
- Social media vs learning
- High engagement in social media 76 but relatively lower use for education 57.
Key Takeaways and Recommendations
- Need for stronger early grade interventions to bridge foundational learning gaps.
- States with successful models should be studied and best practices replicated in lagging regions.
- Leverage technology for learning, ensuring better integration of digital tools in education.
- Promote safer online experiences for girls by bridging the gender gap in digital literacy.
Right to Education
Right to education is the right of every child to receive a quality education, regardless of background and circumstances. It is a fundamental human right, enshrined in international legal instruments and the Universal Declaration of Human Rights.
The right to education in India is guaranteed by Article 21A of the Constitution of India. This article was added by the 86th Amendment Act of 2002.
What does Article 21A say?
- It guarantees free and compulsory education for children between the ages of 6 and 14
- It prohibits discrimination in education
- It ensures equal opportunities for education
- It removes financial barriers to education
- It provides adequate infrastructure, facilities, and qualified teachers
Right to Education Act (RTE) of 2009
The Right to Education Act (RTE) of 2009 guarantees free and compulsory education for children between the ages of 6 and 14.
- The RTE Act was effective from April 1, 2010.
- The RTE Act prohibits denial of admission to any child, irrespective of the time of year.
- The RTE Act also prohibits holding back or expulsion of any child until he completes elementary education.
- Globally
- The Abidjan Principles on the Right to Education were adopted in 2019 by a committee of international human rights law experts.
- The UN‘s Human Rights Council has passed a decision to establish a working group to consider the possibility of including early childhood care and education explicitly within the right to education.
2. ISRO’s 100th Launch Milestone
Context:
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) oversee the historic 100th launch from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC) in Sriharikota with the GSLV-F15 mission.
GSLV-F15 Mission
- Date
- The launch date has been set on 29th of January at Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh.
- Vehicle
- It will utilize a GSLV F15 and is well provided with an indigeneous cryogenic stage for the same mission.
- Objective
- To place the NVS02 satellite into a Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO).
Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO)
A GTO is an elliptical orbit through which the satellite passes from geosynchronous transfer orbit into the geosynchronous orbit.
- How it Works?
- Satellites are placed in GTO for intermediary purposes towards the GSO. The GTO orbit has both apogee, which is a point distant from Earth and a perigee as the nearest to Earth.
- At apogee, the satellite will rotate parallel to Earth’s equator and will fire its rocket engine to reach a circular orbit.
- Why it is Used?
- The manufacturers of launch vehicles tend to boast of how much payload they can put into a GTO.
- Satellites in geosynchronous orbits are helpful in communications as they can cover large portions of Earth.
- Related Missions
- GTOSat: A mission that investigates acceleration and loss mechanisms of relativistic electrons in the Earth’s outer radiation belts.
About the NVS02 Satellite
- Purpose
- NVS02 is part of the Navigation with Indian Constellation (NavIC) system.
- Series
- This satellite is the second in the NVS series designed to enhance India;s regional navigation capabilities.
- Improve Features
- It is one of the five follow on second generation NavIC satellites NVS01 to NVS05 dedicated toward improving and ensuring continuity of navigation services
NavIC Indias Regional Navigation Satellite System
- Service
- Provides accurate Position Velocity and Timing (PVT) services.
- Covers
- India and an area of about 1500 km beyond the Indian landmass.
- Services
- Standard Positioning Service (SPS)
- Provides position accuracy better than 20 meters and timing accuracy better than 40 nanoseconds.
- Restricted Service (RS)
- More security and encryption is provided along with the navigation service to the authorized users.
- Standard Positioning Service (SPS)
Importance of the Mission
- Milestone
- It marks ISROs 100th launch from the Sriharikota spaceport that reflects decades of achievements in space travel.
- Strategic Advantage
- The NavIC system will further the self reliance of India in navigation technology not relying on other foreign systems such as GPS.
- Continuity of Service
- It enhances the NavIC constellation to provide uninterrupted navigation services to users in India and the neighboring regions.
3. WHO Recommends Lower Sodium Salt
Context:
The World Health Organization (WHO) has issued new guidelines recommending the replacement of regular table salt with lower sodium salt substitutes to reduce sodium intake and improve cardiovascular health.
Key Recommendations:
- Salt Reduction
- Target Adults should consume less than 2 grams of sodium per day.
- Substitutions
- Use normal sodium chloride (NaCl), while replacing household portions partly with potassium chloride (KCl).
- Exclusions
- Avoid application for pregnant ladies, children and individuals who suffer kidney failures or illnesses causing abnormal loss of potassium.
- Processed Food Applications
- Not an application to manufactured food, not applicable in food packets and food that is consumed from hotels or restaurants.
Health Effectiveness of Reducing Sodium
- Overconsumption
- Overconsumption of sodium results in hypertension, thereby increasing the chances of getting heart diseases, strokes and kidney disease. 19 million deaths per year are due to high sodium consumption.
- Lowering sodium intake can help avert noncommunicable diseases (NCDs) including cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) and gastric cancer.
- Oversalt Food in India
- People in India oversalt their food. There should be for making low sodium salt available and affordable to the masses, so that at the population level there will be a change of behavior.
Normal Sodium Chloride (NaCl) vs Potassium Chloride (KCl)
Sodium chloride and potassium chloride are salts, differing in usage as well as the characteristics of them.
- Properties Structure
- Sodium chloride is a crystal, while potassium chloride is an ionic solid.
- Electronegativity
- Potassium chloride has a higher electronegativity than sodium chloride. Cost: Sodium chloride is generally cheaper than potassium chloride.
Uses
- Water softening
- Both salts are used in water softeners to replace hard water minerals.
- Electrolyte replenisher
- Both salts are used to replenish electrolytes. Food processing: Potassium chloride is used as a substitute for sodium chloride in salted meat products.
- Healthcare
- Potassium chloride is used to treat hypokalemia.
- Fire extinguisher
- Potassium chloride was once used as a fire extinguishing agent. Optical crystal: Potassium chloride is used as an optical crystal.
- Optical crystal
- Potassium chloride is used as an optical crystal.
Health
- Sodium: Consuming too much sodium can increase blood pressure.
- Potassium: Increasing potassium intake can help decrease blood pressure.
4. The Nicobarese
Context:
A new genetic study published in the European Journal of Human Genetics has found that the Nicobarese people of the Indian Ocean have ancestral ties to the Htin Mal community of the Laos, Thailand region, challenging previous migration timelines.
Key Findings:
- Researchers analyzed genetic data from 1559 individuals across South and Southeast Asia.
- The Nicobarese migrated to the Nicobar Islands about 5000 years ago instead of the previously estimated 11000 years ago. Their lineage of genetics was tied to that of Southeast Asian populations hence supportive of Indian Ocean crossings.
- While the Onge and Great Andamanese have ancient genetic lineages M31, M32 that date back 50000 to 70000 years the connections for the Nicobarese are more recent and with Austroasiatic speaking groups.
The Nicobarese
The Nicobarese are an aboriginal group of people living in the Nicobar Islands that form part of India’s union territory of Andaman and Nicobar Islands. They speak Austroasiatic languages.
- Characteristics
- The Nicobarese are of Mongloid stock.
- They are mainly horticulturists and pig-herders.
- They live in large, permanent villages, mostly near the coast.
- They are not divided into tribes, but there are territorial distinctions.
- The Nicobarese are ethnically linked to the Austroasiatic peoples of South and Southeast Asia.
- History
- The Nicobarese colonized the archipelago of Nicobar early in the Holocene.
- The Nicobar Islands were once a major trading post for travelers heading eastward to the Far East.
- The traders would exchange goods such as silk handkerchiefs, coats, and hats for coconuts with the Nicobarese.
- The Nicobar Islands became a part of India in 1956.
- Culture
- The Nicobarese language is tonal and polysyllabic. The grammatical structure is not Chinese.
- Many words in Nicobarese language are borrowed from Chinese.
- The preserved Nicobarese language exists in isolation, largely among mountain and jungle-dwelling groups.
5. Godavari-Banakacherla Project
Context:
Telangana government protested the project claiming Andhra Pradesh didn’t inform the Godavari and Krishna River Management Boards as required by the Andhra Pradesh Reorganisation Act 2014.
Water Sharing Dispute
- Since 2014 bifurcation
- Telangana and Andhra Pradesh which is the upstream and downstream have disagreed over the allocations. Telangana projects like Palamuru Rangareddy. Lift Irrigation Scheme could affect downstream projects such as Banakacherla.
Inter-State Water Disputes
6. Freedom of Speech
Context:
Pakistan’s upper house of parliament passed a controversial Bill that critics argue is designed to suppress freedom of speech.
Article 19 of the Indian Constitution Right to Freedom
Article 19 of the Constitution of India provides fundamental freedoms to citizens mainly on freedom of speech and expression and also provides for reasonable restrictions that the state can impose.
Important Provisions under Article 19
All citizens shall have the right to:
- Freedom of Speech and Expression 19(1)(a)
- The right to speak freely with words, writing or any form of gesture This right comprises press freedom right to information and internet freedom.
- Right to Assemble Peaceably and Without Arms 19(1)(b)
- This is the right of citizens to assemble peacefully without carrying arms and for example protest hold meetings or demonstrations.
- Right to Form Associations or Unions 19(1)(c)
- Citizens have the right to form associations, societies, political parties, trade unions and other organizations.
- Right to Move Freely Throughout the Territory of India 19(1)(d)
- Individuals have the right to travel or move about freely within the country without unnecessary restrictions.
- Right to Reside and Settle in Any Part of India 19(1)(e)
- Freedom to reside and settle in any part of India.
- Note Clause f Right to property
- It was deleted by the 44th Amendment Act 1978 and is now a legal right under Article 300A.
- Right to carry on any occupation trade or business 19(1)(g)
- Freedom to practice any profession or trade or business.
Restrictions by Reasonable Means Under Article 19(2)
While Article 19(1) provides fundamental rights, Article 19(2) provides the state the right to put reasonable restrictions for the following purposes.
- Sovereignty and Integrity of India
- Security of the State
- Friendly Relations with Foreign States
- Public Order
- Decency or Morality
- Contempt of Court
- Defamation
- Incitement to an Offence
These limitations provide with the cause that freedom of speech and other rights cannot be hurt for national interest or in the publics favor or even individual rights.
Importance of Article 19
Ensures democratic rights and freedom of expression It guards civil liberties sanctioning the freedom to express dissent or peaceful protests. Balances individual rights with the national interest with practical limitations Therefore its a cornerstone of a free and open society in India.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. What do you understand by the concept of “freedom of speech and expression”? Does it cover hate speech also? Why do the films in India stand on a slightly different plane from other forms of expression? Discuss. (2014)
7. The Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes (Prevention of Atrocities) Act, 1989 (POA Act)
Context:
One of the cofounders of information technology (IT) services major Infosys, Kris Gopalakrishnan, and a former director of the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) Bengaluru, Padmanabhan Balaram, have been named besides 16 others in a complaint filed under the Prevention of SC/ST Atrocities Act, according to a report The case was filed at Bengaluru’s Sadashiva Nagar Police Station following directives from the 71st City Civil and Sessions Court (CCH).
About the SC/ST Prevention of Atrocities Act, 1989
The Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes (Prevention of Atrocities) Act, 1989, is a law in India that prevents crimes against members of the Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes. It also provides for special courts to try these crimes and rehabilitation and relief for victims.
Objective and Background
- It was enacted with a view to preventing atrocities on SCs and STs with the aim to end caste atrocities and violence.
- Based on Articles 15 and 17 of the Indian Constitution with the objective of providing protection to these vulnerable groups.
- It is an extension of the Untouchability Offences Act, 1955 and the Protection of Civil Rights Act 1955.
Key Provisions
- It specifically defines offenses against SC/ST members such as violence harassment and social discrimination.
- The punishment for the offenders is severe which is usually more severe than that under the Indian Penal Code.
- Section 18 bars anticipatory bail but allows courts to consider bail based on preliminary inquiry.
- Mandates special courts for speedy trials and SCS/T Protection Cells led by senior police officers.
Recent Amendments
- 2015 Amendment
- Strengthened the protection for SC/STs adding new offenses like garlanding with footwear, manual scavenging and imposing social ostracism.
- 2018 Amendment
- Abolished the need for Senior Superintendent of Police approval to make arrests hence the arrest can be made directly in atrocity cases.
Weaknesses of SC/ST Act, 1989
- Lack of Infrastructure
- Special Courts usually lack infrastructure resulting in a huge pendency and delay in justice.
- Poor Rehabilitation
- Very little rehabilitation is provided for the victims the Act merely provides for very vague social and economic rehabilitation.
- Lack of Awareness
- Often the recipients and the law enforcing agencies remain ignorant about the provisions hence the law is either misused or not used fully.
- Scope of Covered Crimes
- Blackmailing with resultant atrocities on SC/STs is also not covered in the Act.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Mains
Q. What are the two major legal initiatives by the State since Independence addressing discrimination against Scheduled Tribes (STs)? (2017)
Banking/Finance
1. IND-US Currency Swap
Context:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI)‘s announcement of a USD- INR buysell swap auction worth 5 billion for a six month tenor has significantly impacted both the foreign exchange (FX) and bond markets Heres a breakdown of the major movements and market reactions
Impact on Forward Premiums
- Decline in Forward Premiums
- The forward premia saw one month USD-INR premia falling by a sharp 35 bps.
- One year premia declined by a smaller 10 bps bringing them down to 219.
- The fall in premia highlights adjustments from the trading position to the prospect of liquidity effects created by the policy moves so a shift in the expectations of markets could be expected to occur after an auction of swap.
- Market adjustment
- The anticipated liquidity injection was responded to by market participants through a readjustment in forward contract positions indicating anticipation of liquidity easing in the system.
Spot Market Activity
- Rupee Depreciation
- The Indian rupee depreciated by 0.2 weakened to 86.53 against the US dollar.
- This decline was due to a general global risk off sentiment with the resurfacing of concerns on trade tariffs during the tenure of US President Donald Trump
- The rupee as with most Asian currencies felt the brunt of this sentiment which also heavily impacted emerging market assets.
- Global Sentiment
- The overall risk off sentiment due to trade related jitters, complemented by other geopolitical factors contributed to the weakening rupee. This made the investors cautious and thereby preferred safer assets and step away from other riskier currencies of emerging economies like the Indian rupee.
- Spot Market Closing
- The rupee had settled at 86.34 per dollar and its subsequent weakening was in line with the broader global economic uncertainty.
Bond Market Reaction
- Bond Yield Softening
- The 10year benchmark bond yield softened by 6 bps early in the day initially reflecting positive market sentiment due to the RBIs liquidity support.
- However, the yield ultimately ended 1 basis point bps higher closing at 689. This was largely due to profit taking by state owned banks that sold bonds at a profi.t
- Liquidity Infusion Impact
- The RBIs liquidity infusion measures which were aimed at easing tight liquidity conditions in the market initially helped soften bond yields.
- Profit Taking by Traders
- Traders and banks began selling bonds as prices had moved up to levels of 662 to 665 in bond yields, where many had priced in expectations of a 50basis point rate cut.
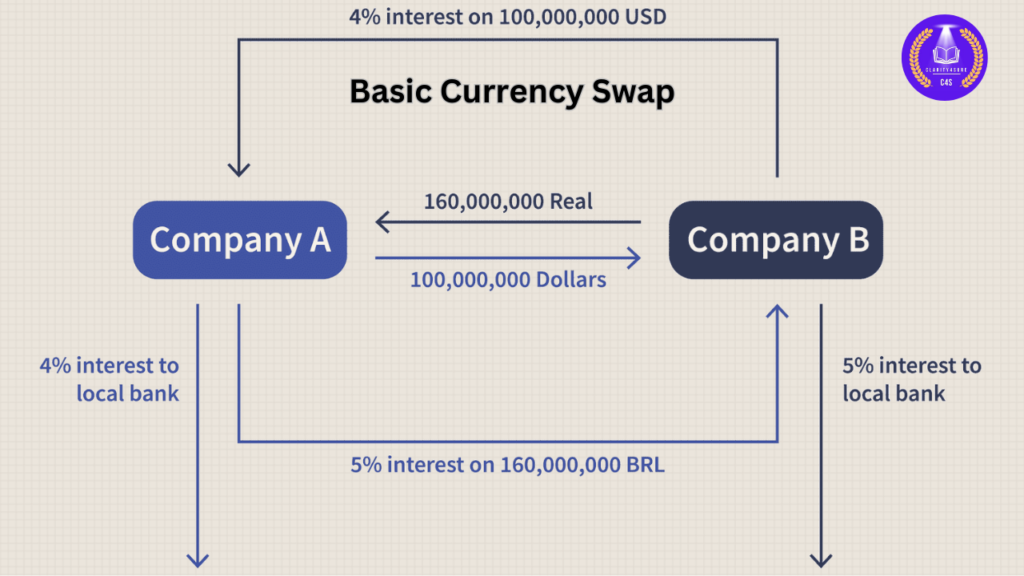
2. USD/INR Currency Swap
Origin
- Currency swaps were originally conceived in the 1970s to circumvent foreign exchange controls in the United Kingdom. At that time, UK companies had to pay a premium to borrow in US Dollars. To avoid this, UK companies set up back-to-back loan agreements with US companies wishing to borrow Sterling.
About
- In today’s interconnected global financial markets, currency swaps have become an essential tool for managing currency risks and accessing foreign currency liquidity.
- Among these, the USD/INR currency swap is one of the most widely utilized, particularly for Indian entities seeking to hedge currency exposure or raise foreign currency capital.
What is a USD/INR Currency Swap?
- A currency swap is a financial contract in which two parties agree to exchange principal and interest payments in different currencies for a specified period. Specifically, a USD/INR currency swap involves the exchange of U.S. Dollars (USD) and Indian Rupees (INR).
Here’s a simplified explanation of how it works:
- Principal Exchange:
- The two parties (usually corporations or financial institutions) agree to exchange USD for INR at a predetermined exchange rate. This initial exchange of principal is done at the start of the swap.
- Interest Payments:
- Periodically, the parties will make interest payments in the two currencies. One party may pay a fixed interest rate in INR, while the other may pay a floating rate in USD (or vice versa). The payments depend on the terms agreed upon in the contract.
- Final Exchange of Principal:
- At the end of the swap’s term, the principal amounts are exchanged back. The INR holder gives back USD, and the USD holder returns INR. This exchange may be at the same initial rate or at a rate based on market conditions at that time.
RBI’s Role in Currency Swaps
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) plays a significant role in managing the exchange rate stability of the Indian Rupee (INR) through various mechanisms, including currency swaps.
- The RBI uses currency swaps to control the value of the INR and to manage its foreign exchange reserves.
Here are the key reasons why the RBI might use currency swaps:
- Liquidity Management:
- Currency swaps help the RBI manage liquidity in the domestic market, particularly in terms of foreign exchange reserves and market interventions.
- Stabilizing Exchange Rates:
- By engaging in currency swaps, the RBI can smooth out large fluctuations in the exchange rate of INR against the USD, maintaining a more stable market.
- Increasing Foreign Exchange Reserves:
- By swapping INR for USD or vice versa, the RBI can increase its foreign exchange reserves, ensuring that it has sufficient reserves to meet India’s import requirements, external debt obligations, and to maintain investor confidence.
- Hedging Against External Shocks:
- A currency swap can help hedge against sudden shocks in the foreign exchange market, such as external geopolitical or economic crises that may cause significant depreciation of the INR.
3. RBI Guidelines on Penal Charges
Context:
The Ministry of Finance notified that penal charges imposed by banks and non-banking financial companies (NBFCs) for noncompliance with loan terms will not attract an 18 per cent goods and services tax (GST).
Key Highlights:
- Penal Charges
- Not Taxable under GST Banks and NBFCs are exempted from charging 18% GST on penal charges imposed as a result of loan term noncompliance.
- RBI Circular dated August 18, 2023
- The RBI has issued an August 18 ,2023 circular that has commanded banks and NBFCs to change penal interest to penal charges when a borrower fails to comply with loan terms.
- Objective
- The changes effective from January 1 2024, aim to promote credit discipline among borrowers.
- Exclusions
- The RBIs guidelines exclude certain financial products like credit cards, external commercial borrowings, trade credits and structured obligations which are governed by separate rules.
- Clarification on Penal Charges
- The Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs clarified that penal charges are not payments for tolerating an act but are penalties for breaching loan agreements ensuring the focus remains on loan performance not breaches.
Penal Charges
Penal charges are fees charged by lenders on the defaulting borrower for failure to pay loans or breach of the loan agreement. It is a measure to deter defaulting borrowers and ensure financial discipline.
How are penal charges calculated?
- Penal charges are charged by the lender on the defaulted amount
- Penal charges are charged on a pro rata basis on the default period
- Penal charges are not included in the rate of interest
What are penal charges?
- Over drafting a bank account, Late payment of interest, and Late payment of installment.
What are the RBI’s directives on penal charges?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has guidelines that prohibit banks and finance companies from charging penal interest on loan defaults. Instead, they must charge penal charges, which are fixed fees.
- Penal charges cannot be added to the loan amount
- Penal charges cannot be capitalized, meaning no further interest can be computed on them
- Penal charges must be reasonable and levied in a non-discriminatory manner
Who suffers from penal charges?
- The same penal charges apply to the same loan product for retail and corporate borrowers.
4. RBI Regulations and Criteria for NBFCs to Become Banks
Procedure of NBFC to become a Bank
- Application
- The NBFC files an application with the RBI Regional Office.
- Review
- The RBI reviews the promoters senior management and CIBIL record of the NBFC.
- License After due scrutiny the RBI issues the NBFC license
- Reporting
- Submits financial and prudential reports on a regular basis to the RBI.
Role of RBI in NBFC Regulation
- Registers and grants licenses to NBFCs.
- Sets policies and issues directions to NBFCs.
- Inspects and supervises NBFCs.
- Ensures compliance and exercises surveillance over the activities of NBFCs.
- It has the powers to penalize NBFCs in case of breach of the RBI Act.
Conversion Criteria of NBFC into Banks
- Financial Activity
- Over 50% of total assets must be financial in nature.
- Income from Financial Assets
- More than 50% of gross income must come from financial assets.
- Reserve Fund
- NBFCs should add at least 20% of the net profit every year to the reserve fund.
- Regulatory Compliance
- Includes membership with Credit Information Companies (CICs) registration with FIU-IND and CKYC CERSAI.
- Antimoney Laundering (AML) and Counter Financing of Terrorism (CFT)
- The NBFC should receive training in the AML/CFT protocols.
- Risk Management
- There must be a board approved risk management policy in place.
- The RBI assumes a vital role in the administration and regulation of NBFCs.
It ensures that the NBFCs satisfy different criteria and policies. To be a bank an NBFC must comply with stringent norms relating to financial activity source of income regulatory compliance and risk management.
Other Requirements
- The NBFC must have a minimum capital adequacy ratio of 10%.
- The NBFC must have net NPAs of no more than 5%.
- The NBFC must have a lock-in period of at least five years.
- The NBFC must not default on public deposits.
- The NBFC must open 25% of its branches in rural and semi-urban areas.
- The NBFC must meet a priority sector lending target of 40% of net bank credit.
5. Foreign Bank Account
Context:
Rams Problem Ram an NRI in the US was having a tough time when his parents in India tried to remit 10 lakh to his US bank account after selling a property. The transfer from India to a foreign account was a hassle especially with the TCS requirement for amounts over 7 lakh.
Solution: NRO Account
- NRO Account
- Rams banker friend who is an Overseas Citizen of India advised him to send the amount to an NRO (Non Resident Ordinary account) in India rather than to his US account.
What is an NRO Account?
- An NRO account is used by NRIs, OCIs and PIOs to deposit income gifts or capital gains earned in India.
- This means there will be no requirement to submit forms or deal with TCS making it easier for Rams parents.
Advantages of an NRO Account
- Funds in an NRO account can easily be used for transactions conducted within India or invested into financial instruments such as stocks bonds and mutual funds.
- The money first needs to be transferred to an NRE Non Resident External account in order to be repatriated taxfree for international transfers.
Foreign Currency Non Resident FCNR
- FCNR Accounts
- The NRIs and OCIs can open Foreign Currency NonResident (FCNR) accounts for locking up funds in foreign currency denominated fixed deposits. This helps to get back the amount in their home country and avoids forex risks.
Types of foreign bank accounts in India
- Foreign currency account: A current, savings, or term deposit account held in a foreign currency.
- Non-Resident Ordinary (NRO) account: A bank account in Indian rupees for non-resident Indians (NRIs) to manage income earned in India.
- Non-Resident External (NRE) account: A bank account for NRIs to conduct banking transactions in India.
- Resident Foreign Currency (RFC) account: A savings account for NRIs who have returned to India and hold funds in foreign currency.
- EEFC account: An account for making money in foreign currency through exports or other international activities.
Documents required to open a foreign bank account
- Proof of identity, such as a passport, driving license, or national ID
- Proof of address, such as a bank statement or utility bill
- Employment, income, and tax details
- Additional documents, depending on qualification status, local laws, and regulations
Foreign Bank Accounts Benefits Tax Implications and Eligibility
What is a Foreign Bank Account?
A foreign bank account also known as an offshore bank account is an account held in a country other than the account holders country of residence or citizenship.
Why Open a Foreign Bank Account?
- Investment
- Opportunities provision for various financial instruments along with investment, avenues available within the overseas country.
- Economic Shocks Protection
- Protects assets from economic shocks in ones home country.
- Higher Interest Rates
- Certain overseas banks provide savings interest rates that are higher than those offered at home.
Agriculture
1. Agritech: Transformation of Indian Agriculture
Context:
Indian agriculture is the source of employment for over 158 million people and contributes. The sector is undergoing a technological revolution. The population is projected to touch 15 billion by 2030 and hence innovations in agritech are the need of the hour to ensure food security and meet the challenges in the sector.
Key Developments
- Agritech Ecosystem Growth
- From less than 50 in 2013 to more than 3000 today the Indian agritech sector has seen a lot of growth in the number of startups.
- Over 1300 startups are applying AI/ML and IoT to innovative solutions for farming. Growing awareness among farmers and rural, internet penetration and government support fuel these numbers.
Governments Digital Agriculture Mission
- Digital Agriculture Mission
- The allocation for this mission is 2817 crore This involves the setting up of AgriStack as a farmer centric Digital Public Infrastructure.
- AgriStack will be giving digital identities to 11 crore farmers and has received support from 19 states in the form of MoUs signed with the Ministry of Agriculture.
Emerging Technologies in Farming
- Drone Technology
- Drones are transforming agriculture by permitting aerial planting crop monitoring and nutrient application which helps increase productivity through precision and in time e.g. Namo Drone Didi Scheme.
- Smart Farming Equipment
- Automated tractors are equipped with GPS ensuring minimum fuel usage while reducing the tiredness of operators due to operational efficiency.
- IoT Sensors
- With sensors constantly monitoring soil moisture, nutrient levels and crop health in realtime data is translated into actionable insights for farmers with the use of AI algorithms
- Automated Irrigation
- With the help of both weather data and readings of soil moisture accurate watering to conserve resources is given by automated systems.
- Mobile Based Applications
- Mobile apps are democratizing access to agricultural knowledge providing features such as crop disease identification weather updates and market price information in local languages enabling farmers to make informed decisions
- Financial Inclusion in Agriculture
- Platforms like SBIs YONO Krishi and emerging agrifintech solutions are helping overcome the challenge of limited access to financial services for rural farmers.
- Climate Resilience and Sustainability
- As weather patterns are affected smart farming technologies promise increased efficiency in the use of resources and no more waste. For instance the Saagu Baagu pilot in Telangana utilizes, AIbased advisories to help 7000 chilli farmers optimize their production.
- Using solar panels on farmland or agrivoltaics leads to increased crop yields and electricity to solve both energy and agriculture needs.
Challenges
- Digital Literacy and Data Access
- The digital divide in the rural sector has become very big. Most of the farmers have not acquired data processing tools skills nor access to the right software while using the technologies.
- Data Privacy and Implementation
- Data privacy is of prime importance and the Digital Personal Data Protection Act 2023 is supposed to take up this issue appropriately. The government is struggling to update the land records and authenticate the data of farmers for AgriStack and only 43 million farmers data have been authenticated.
- Resource Accessibility
- The software tools and the expertise in data processing are not available in sufficient numbers and thus the agritech applications cannot be achieved in full.
- The Road Ahead
- Economic Potential: The agritech sector would boost farmer incomes by 2535, thus adding another 95 billion to the economy of India. However only 15 of its market potential of 24 billion has been tapped so far leaving wide scope for further growth.
- Role of FPOs
- Farmer Producer Organisations (FPOs) will play a crucial role in facilitating technology adoption linking farmers with technology and with buyers and transforming the way farming communities interact with innovations.
- Affordability and Local Context
- The keys to successful adoption of agritech solutions will lie in making available affordable and localized innovations tailored to the needs of small and marginal farmers so that it hits grass roots.
- Public and Private Collaboration
- This includes the integration of government support private sector innovation and community led adoption as a model for more resilient efficient and sustainable agricultural practices.
Facts To Remember
1. SU-57, F-35 fighter jets to join Aero India event next month
Fifth generation fighter jets of Russia and the U.S. are set to enthral the crowds at the Yelahanka Air Force station, Bengaluru, during Aero India next month. Their combined presence in Indian air space comes amid a deep crisis in the Indian Air Force with major delays in fighter inductions and the induction of the under development indigenous fifth generation fighter atleast a decade away.
2. Domestic market in positive territory for second consecutive session
Benchmark domestic equity indices today extended gains for the second consecutive session. The 30-share index at the Bombay Stock Exchange, Sensex, surged 631 points, or 0.83 percent, to close at 76,533.
3. Centre approves National Critical Mineral Mission essential for promoting green technologies
The government has approved the National Critical Mineral Mission with an outlay of more than 34 thousand crore rupees.
4. JPC on Waqf (Amendment) Bill, 2024 adopts its draft report with amendment on 14 clauses related to Bill
The Joint Committee of Parliament on the Waqf (Amendment) Bill, 2024 today adopted its draft report. Talking to media in New Delhi, the Chairman of the 31-member panel, Jagdambika Pal, said the Committee has adopted amendments to 14 clauses related to the Bill.
5. Sri Lanka’s Central Bank predicts negative inflation in near term, targets 5% by mid-2025 amid economic recovery
Sri Lanka’s Central Bank expects headline inflation to remain negative in the near term in the crisis-stricken island. In its latest policy review, the Central Bank has said that inflation is expected to gradually rise to the target of 5 per cent by mid-2025.
6. Jasprit Bumrah wins Sir Garfield Sobers Trophy as ICC men’s cricketer of the year 2024
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) successfully launched its new generation satellite NVS-02 from Sriharikota in Andhra Pradesh today.
7. PM Modi inaugurates 38th National Games in Dehradun
Prime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurated the 38th National Games in Dehradun, the capital of Uttarakhand, yesterday evening.
















