
Why in News ?
The 6th BIMSTEC Summit was in the news for adopting the BIMSTEC Charter, which gave the group a formal legal identity for the first time. It streamlined its focus from 14 to 7 key sectors and signed important agreements on legal cooperation, technology, and training. India played a key role by contributing $1 million to the Secretariat and leading the security pillar. The summit also emphasized connectivity and regional recovery post-COVID, making BIMSTEC a rising alternative to SAARC.
Introduction
The 6th BIMSTEC Summit marked a significant milestone in strengthening cooperation among the countries in the Bay of Bengal region. Held under the theme “Towards a Resilient Region, Prosperous Economies, Healthy Peoples”, the summit showcased a shared commitment to regional integration, economic growth, and security.
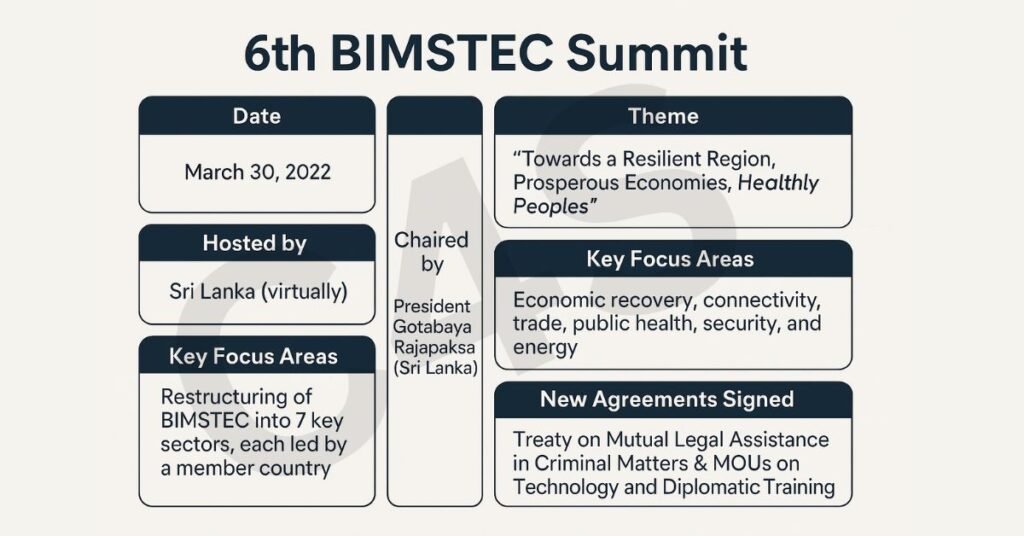
In an era where the world is increasingly leaning on regional cooperation to address global challenges, the 6th BIMSTEC Summit, held on 30 March 2022, marked a historic shift. Hosted virtually by Sri Lanka, this summit wasn’t just another diplomatic formality—it laid the foundation for a stronger, institutionalized, and forward-looking BIMSTEC.
Whether it’s improving regional trade, enhancing security collaboration, boosting connectivity, or building resilience against climate and health crises, this summit covered it all.
What is BIMSTEC?
BIMSTEC, short for Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation, is a regional organization formed in 1997. It connects countries from South Asia and Southeast Asia, aiming to enhance collaboration across various sectors including trade, security, connectivity, and climate resilience.
Members of BIMSTEC:
- Bangladesh
- Bhutan
- India
- Myanmar
- Nepal
- Sri Lanka
- Thailand
Together, these countries represent over 1.7 billion people—nearly 22% of the global population—and a rapidly growing economic region.
6th BIMSTEC Summit
| Aspect | 📖 Details |
|---|---|
| Date | March 30, 2022 |
| Hosted by | Sri Lanka (virtually due to COVID-19) |
| Theme | “Towards a Resilient Region, Prosperous Economies, Healthy Peoples” |
| Chaired by | President Gotabaya Rajapaksa (Sri Lanka) |
| Key Focus Areas | Economic recovery, connectivity, trade, public health, security, and energy |
| Outcome Document | Adoption of the BIMSTEC Charter |
| Major Announcement | Restructuring of BIMSTEC into 7 key sectors (each led by a member country) |
| New Agreements Signed | Treaty on Mutual Legal Assistance in Criminal Matters & MOUs on Technology and Diplomatic Training |
Key Highlights of the 6th BIMSTEC Summit
1. Adoption of the BIMSTEC Charter
For the first time in over 25 years, BIMSTEC adopted a formal Charter, giving the grouping a structured legal and institutional framework—something it was lacking before. This charter lays out:
- Objectives and principles
- Organizational structure
- Rules for membership, decision-making, and functioning
This marked a shift from informal cooperation to a rules-based institutional body.
2. Reorganization into 7 Core Sectors
BIMSTEC streamlined its earlier 14-priority sector model into 7 sectors, each country leading one:
| Sector | Led by |
|---|---|
| Trade, Investment & Development | Bangladesh |
| Environment & Climate Change | Bhutan |
| Security (Counter-terrorism & Transnational Crime) | India |
| Agriculture & Food Security | Myanmar |
| People-to-People Contact | Nepal |
| Science, Technology & Innovation | Sri Lanka |
| Connectivity | Thailand |
This restructuring aimed to avoid duplication of efforts and promote efficient project implementation.
3. Boosting Connectivity and Trade
- BIMSTEC leaders stressed the importance of completing the BIMSTEC Master Plan for Transport Connectivity, covering roads, railways, ports, and air links.
- They also reaffirmed commitment to BIMSTEC Free Trade Area (FTA) negotiations to boost intra-regional trade.
4. Legal and Security Cooperation
- The Treaty on Mutual Legal Assistance in Criminal Matters was signed by all members except Nepal and Thailand (expected to sign later).
- This treaty promotes better cooperation on cross-border crimes like terrorism, drug trafficking, and human trafficking.
5. Technology and Capacity Building
Two major Memorandums of Understanding (MoUs) were signed:
- On Cooperation in Technology Transfer
- On Mutual Cooperation between Diplomatic Training Academies
These will help in sharing knowledge, training officials, and enhancing technological partnerships.
India’s Role at the Summit
India, being a founding member, played a proactive role. Prime Minister Narendra Modi emphasized:
- The importance of regional cooperation post-COVID-19
- Strengthening economic integration via trade and digital platforms
- India also committed US$ 1 million to the BIMSTEC Secretariat to improve its functioning
India’s Role:
- Lead country for the Security pillar
- Announced $1 million contribution to the BIMSTEC Secretariat
- Advocated for:
- Enhanced maritime security
- Disaster management systems
- Better digital and financial inclusion
Why it matters: India sees BIMSTEC as a bridge between South and Southeast Asia and a counterbalance to China’s growing influence in the Indian Ocean.
Why the 6th BIMSTEC Summit Matters
| Reason | Importance |
|---|---|
| Adoption of BIMSTEC Charter | Institutionalized the group with legal backing |
| Legal and security cooperation | Helps tackle cross-border crime and terrorism |
| Boost to regional connectivity | Master Plan aims to improve trade routes and economic ties |
| Sectoral restructuring | Improves efficiency and accountability across core areas |
| Strengthening people-to-people engagement | More cultural and academic exchanges expected |
| Focus on economic recovery post-pandemic | Joint efforts for inclusive and sustainable regional growth |
What Lies Ahead?
- Early ratification of the BIMSTEC Charter by all members
- Timely implementation of the Master Plan for Connectivity
- Greater synergy in disaster response and public health initiatives
- Enhanced coordination on cybersecurity, digital finance, and AI
- BIMSTEC FTA:
- Work on trade liberalization to be expedited
Future Roadmap
- Implementation of Master Plan for Transport Connectivity
- Early finalization of BIMSTEC Free Trade Agreement
- Establishment of BIMSTEC Development Fund
- Enhancing collaboration on disaster management, healthcare, and digital economy
- Greater youth engagement and civil society participation
Conclusion
The 6th BIMSTEC Summit wasn’t just another diplomatic meeting—it was a bold step towards a more structured, active, and integrated regional bloc. By institutionalizing its structure, focusing on critical sectors, and signing key treaties, BIMSTEC has positioned itself to play a vital role in shaping the future of the Bay of Bengal region.
As the world leans more towards regional alliances for resilience, BIMSTEC’s vision of connectivity, prosperity, and mutual support is more relevant than ever.

















