Daily Current Affairs Quiz
22 November, 2025
National Affairs
1. Centre Notifies Four New Labour Codes
Source: PIB
Context:
The Central Government has officially notified all four Labour Codes, replacing 29 old labour laws (some from the 1930s–1950s). These Codes are being projected as a big step toward modernising India’s labour market.
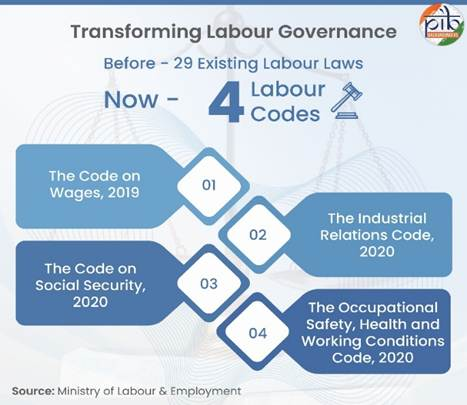
The Four Labour Codes
- Code on Wages (2019)
- Industrial Relations Code (2020)
- Code on Social Security (2020)
- Occupational Safety, Health and Working Conditions (OSHWC) Code (2020)
Key Objectives of the Labour Codes
- Simplification & Streamlining: Rationalises 29 labour laws into four comprehensive Codes.
- Enhanced Worker Protection: Covers wages, safety, social security, and welfare.
- Future-Ready Workforce: Supports flexible, formal employment with social protection.
- Inclusive Growth: Promotes gender equality, youth participation, and gig/migrant worker coverage.
- Ease of Compliance for Employers: Single registration, single license, single return.
Labour Codes and Key Features (India, 2025)
Code on Wages, 2019
- Universal Minimum Wage: Ensures minimum wage for all workers across organized & unorganized sectors.
- National Floor Wage: Central minimum benchmark; states cannot fix wages below this level.
- Gender-Neutral Pay: Prohibits wage discrimination across genders, including transgender workers.
- Overtime at 2× Rate: Mandatory for work beyond standard hours.
- Inspector-cum-Facilitator: Shifts focus from penal action to compliance guidance.
- Decriminalized Offences: Minor violations replaced by monetary penalties for compliance-friendly governance.
Industrial Relations Code, 2020
- Fixed-Term Employment (FTE): Time-bound contracts with full benefits, gratuity eligibility after 1 year.
- Re-skilling Fund: 15 days’ wages for retrenched employees for training & employability.
- Trade Union Recognition: Union with ≥51% membership recognized; otherwise, negotiating council formed.
- Higher Layoff Threshold: Approval for layoffs/closures raised from 100 → 300 workers.
- Strike Notice Rule: 14-day notice required to minimize disruption and promote negotiations.
- Expanded Definitions: Includes journalists, sales staff, supervisory employees earning ≤₹18,000.
Code on Social Security, 2020
- Universal Social Security: Life, health, maternity, old-age benefits extended to unorganized, gig, and platform workers.
- ESIC & EPF Expansion: Pan-India coverage; EPF inquiries time-bound & transparent.
- Social Security Fund: Dedicated fund for unorganized/gig workers, financed via aggregator contributions and penalties.
- Self-Assessed Cess: Builders can self-assess construction cess digitally.
- Gratuity for FTEs: Eligible after 1 year, improving project-based worker protections.
- Uniform Wage Definition: Standardizes wage components for correct EPF/ESIC/gratuity calculation.
Occupational Safety, Health & Working Conditions (OSHWC) Code, 2020
- Single Registration/Return: One unified system replaces multiple registrations.
- Migrant Worker Benefits: Includes self-migrated workers; annual travel allowance & portability of entitlements.
- Women’s Night Work: Allowed with consent & safety provisions; promotes equality & inclusion.
- National Worker Database: Digital database for unorganized/migrant workers; enables benefits & skill mapping.
- Working Hours Limit: 8 hours/day, 48 hours/week.
- Safety Committees: Required in establishments with ≥500 workers; joint employer–employee governance.
- Decriminalized Penalties: Minor offences converted into fines/compounding for compliance-oriented approach.
Significance
- Social Security Expansion: Workforce coverage increased from 19% (2015) → 64% (2025); Labour Codes further widen net.
- Pro-Worker & Pro-Employment: Protects informal, gig, migrant, and youth workers while enabling modern, flexible work arrangements.
- Boosts Industrial Growth & Employment: Simplified compliance and flexible frameworks enhance productivity.
- Inclusive & Gender-Sensitive: Equal pay, safety standards, and workforce participation encouraged.
2. Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS)
Source: TH
Context:
India’s ICDS marks 50 years since its 1975 launch, continuing as a key programme for child nutrition, early learning, and maternal health.
About ICDS
- Type: India’s largest early childhood care and nutrition programme.
- Coverage: Children aged 0–6 years, pregnant women, and lactating mothers.
- Delivery Mechanism: Anganwadi Centres (AWCs) staffed by Anganwadi Workers (AWWs) and Helpers.
History
- Launch Date: 2 October 1975.
- Pilot Blocks: Dharani (Amravati) & Dharavi (Mumbai).
- Expansion: Over five decades, ICDS has grown to nearly 14 lakh Anganwadi Centres nationwide, becoming one of the world’s largest community-based child development initiatives.
Aims
- Improve nutritional and health status of children (0–6 years).
- Lay foundations for psychological, physical, and social development.
- Reduce child mortality, morbidity, malnutrition, and school dropouts.
- Ensure inter-departmental coordination for holistic child development.
- Empower mothers through nutrition and health education.
Key Features
- Six Core Services:
- Supplementary nutrition
- Pre-school education
- Health check-ups
- Immunisation
- Referral services
- Nutrition-health education
- Collaboration: Services converge with NRHM for immunisation, ANCs, and health referrals.
- Target Group: Children below 6 years, pregnant women, lactating mothers, and women aged 15–45.
- Scale Example: Maharashtra runs over 10 lakh Anganwadi and mini-Anganwadi centres.
Banking/Finance
1. India’s UPI to be Interlinked with Eurosystem’s TIPS for Cross-Border Payments
Source: BS
Context:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI), NPCI International Payments Ltd. (NIPL), and the European Central Bank (ECB) have agreed to begin the realisation phase of linking India’s Unified Payments Interface (UPI) with the TARGET Instant Payment Settlement (TIPS) system of the Eurozone.
Key Highlights:
- RBI & NIPL Engagement: The RBI, along with NPCI International Payments Ltd (NIPL), has been collaborating with the European Central Bank (ECB) to operationalise the UPI–TIPS link.
- Implementation: The next phase involves technical integration, risk management, and settlement arrangements for seamless cross-border payments.
- NIPL Role: NIPL, a wholly-owned subsidiary of NPCI, promotes India’s home-grown payment systems, such as UPI and RuPay, overseas.
- Current UPI International Reach:
- UPI acceptance enabled in Singapore, Bhutan, Nepal, Sri Lanka, UAE, Mauritius, Qatar, France.
- 2 million+ international merchants onboarded for UPI acceptance.
- India supports countries like Namibia, Trinidad and Tobago, Peru to develop UPI-like systems.
- Talks underway with 7–8 more countries to expand UPI’s global reach.
About TARGET Instant Payment Settlement (TIPS)
- TIPS is a real-time payment system operated by the Eurosystem, which is the central banking system of the Euro Area.
- It allows instant settlement of payments in euros, 24/7, across participating banks in Europe.
Key Features:
- Instant Payments: Transfers between banks happen in seconds, any time of the day or week.
- Final and Irrevocable Settlement: Payments processed through TIPS are final, reducing settlement risk.
- Cross-Border Capability: TIPS supports payments across Euro Area countries, enabling seamless pan-European transfers.
- Central Bank Operated: Managed by Eurosystem (ECB and national central banks), ensuring safety and trust.
- Integration with Other Systems: Can be linked with other payment systems (like India’s UPI) to enable cross-border instant transfers.
2. SEBI Board to Review Mutual Fund & Stock Broker Regulations
Source: TH
Context:
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) will review its mutual fund (MF) and stock broker regulations at its upcoming board meeting on December 17, 2025.
Key Focus Areas:
- Mutual Funds:
- Review of MF product offerings, transparency norms, and risk disclosure requirements.
- Possible discussion on amendments to SEBI MF Regulations to improve investor safety and reduce operational risks.
- Strengthening governance frameworks within asset management companies (AMCs).
- Stock Brokers:
- Assessment of broker compliance, client fund protection, and adherence to capital adequacy norms.
- Review of trading and settlement mechanisms to improve efficiency and reduce market risks.
- Potential updates to regulations on margin requirements, risk management, and dispute resolution.
Purpose:
- Enhance investor confidence in capital markets.
- Align regulations with international best practices.
- Streamline compliance framework for market intermediaries, fostering growth in equities and mutual fund participation.
3. Credit-Deposit (CD) Ratio
Source: BS
Context:
India’s commercial banks’ credit-deposit (CD) ratio has crossed 80%, a level often viewed as the upper bound of the Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) comfort zone. CD ratio indicates the proportion of loans extended by banks relative to their deposits. Current CD ratio (fortnight ended October 31, 2025): 80.21%. Historically, 75–80% is considered a comfortable range.
About Credit-Deposit (CD) Ratio
- The Credit-Deposit (CD) ratio is the proportion of a bank’s total loans (credit) to its total deposits.
- Formula:
- CD Ratio (%)=(Total Advances (Loans)/Total Deposits)×100
Purpose/Significance:
- Banking Efficiency: Measures how efficiently banks are using deposits to lend.
- Liquidity Indicator:
- Low CD Ratio (<50–60%) → Bank is lending less; excess deposits may remain idle.
- High CD Ratio (>75–80%) → Bank is lending more; risk of liquidity crunch if deposit growth lags.
- Economic Insight: High CD ratios reflect strong credit demand; low ratios may indicate weak lending or excess liquidity.
- Regulatory Benchmark: RBI generally views 60–75% as a healthy CD ratio range, balancing liquidity and credit growth.
This ratio helps assess banking sector health and the availability of credit to the economy.
Reasons for Rise in CD Ratio
- Credit growth outpacing deposit growth:
- Year-on-year credit growth (October 2025): 11.3%
- Year-on-year deposit growth (October 2025): 9.7%
- Factors boosting credit demand:
- Lower interest rates after 100 bps repo rate cut
- GST rate rationalisation
- Income tax incentives
- Improving consumption and corporate investment demand
- Large corporate borrowings and slow deposit mobilisation (partly due to funds flowing into mutual funds) also contribute.
Impact of Monetary Policy
- Weighted average lending rates on fresh and outstanding loans have declined by 58 bps and 55 bps, respectively.
- Weighted average term deposit rates on fresh and outstanding deposits fell by 106 bps and 22 bps, respectively.
- Small savings rates remain higher than formula-based rates, attracting some retail funds.
- Anticipated further repo rate cut (expected 3–5 December) could exacerbate deposit mobilisation challenges.
4. Insurance Reforms Set to Boost Sector Growth
Source: BL
Context:
The Government has listed the Insurance Laws (Amendment) Bill, 2025 for the Winter Session of Parliament. The bill aims to accelerate growth, deepen insurance penetration, improve ease of doing business, and fulfill the FY26 Budget announcement of raising FDI limit in insurance from 74% to 100%.
Key Provisions of the Bill
- FDI Enhancement
- FDI limit increased to 100% for companies investing the entire premium in India.
- Conditionalities and guardrails for foreign investment will be reviewed and simplified.
- Expected to attract stable foreign investment, enhance competition, facilitate technology transfer, and improve insurance penetration.
- Composite Licensing
- Insurers can obtain a single licence to operate in multiple segments: life, health, and general insurance.
- Promotes operational flexibility, innovation, and regulatory simplification.
- Capital & Regulatory Adjustments
- Lower entry capital allowed for under-served segments (not less than ₹50 crore).
- Net Owned Funds for foreign reinsurers reduced from ₹5,000 crore to ₹1,000 crore.
- Conditions on Key Management Persons, Board composition, and dividend repatriation to be reviewed to facilitate foreign participation.
- Insurance Penetration & Development Goals
- Supports the government’s “Insurance for All by 2047” vision.
- Enhances accessibility, affordability, and availability of insurance products nationwide.
- Anticipated to improve insurance density, reduce protection gaps, and enhance service quality.
Rationale
- Indian insurance sector projected to grow 7.1% annually over next 5 years, outpacing global growth.
- Aligns India with global practices: countries like Canada, Brazil, Australia, and China permit 100% FDI in insurance.
- Greater foreign participation expected to:
- Increase competition
- Improve product offerings
- Boost technology adoption and knowledge transfer
- Strengthen the overall financial sector ecosystem
Agriculture
1. e‑NAM Expansion: Digital Empowerment of Indian Farmers
Source: BL
Context:
The Government of India continues to strengthen e‑NAM (National Agriculture Market), a digital platform connecting APMC mandis nationwide. The expansion aims to provide better price discovery, transparency, and market access to farmers while integrating modern digital agri-services.
Key Highlights:
- Commodity Expansion:
- 9 new commodities added, including Green Tea, Mustard Oil, Lavender Oil, Mentha Oil, and Broken Rice.
- Total tradable commodities now stand at 247, with standardized quality parameters for fair pricing.
- Integration with Private Services:
- e‑NAM now links with private agri-service providers offering warehousing, assaying, logistics, fintech, and quality checks under the Platform of Platforms model.
- Digital Payments & Efficiency:
- Payments processed via UPI, RTGS, NEFT, ensuring timely and secure settlement for farmers.
- Mobile app features provide gate entry, MIS dashboards, and farmer database integration for transparency.
- Market Reach & Volume:
- Expansion enables inter-mandi and inter-state trade, increasing farmer access to larger markets.
- Trade turnover projected to cross ₹80,000 crore in FY24.
- Quality-Based Bidding:
- Assaying and defined tradable parameters promote better pricing for higher-quality produce, incentivizing farmers to improve output standards.
e‑NAM (National Agriculture Market)
What it is:
- e‑NAM is a digital trading platform launched by the Government of India on 14 April 2016.
- It integrates APMC (Agricultural Produce Market Committee) mandis across India to create a unified national market for agricultural commodities.
- Farmers can sell their produce online to buyers across the country, ensuring better price discovery, transparency, and reduced intermediation.
Key Features:
- Market Integration: Connects multiple mandis to facilitate inter-mandi and inter-state trade.
- Digital Payments: Ensures secure and timely payment through digital methods like UPI, RTGS, and NEFT.
- Standardized Quality: Commodities are assayed and graded to ensure fair pricing for quality produce.
- Inclusivity: Helps small and marginal farmers access larger markets beyond their local mandis.
- Technology-Driven: Features like mobile apps, dashboards, and MIS improve transparency and efficiency.
Facts To Remember
1. IAF’s Tejas crashes at Dubai Air Show; pilot dead
An Indian Air Force (IAF) Tejas fighter jet crashed during the Dubai Air Show on Friday , claiming the life of the pilot, Wing Commander Namansh Syal.
2. Govt to Launch First Retail Investment in National Highways via InvIT
The Union Government will issue national highway (NH) units for retail investors under its first public Infrastructure Investment Trust (InvIT) in February 2026.
3. National One Health Mission Assembly 2025 Concludes in New Delhi
The two-day National One Health Mission Assembly 2025 concluded today in New Delhi.
4. India Sees 21% Drop in TB Cases, 25% Fall in Mortality
India has achieved a significant decline in both TB incidence and mortality, driven by strengthened surveillance, early detection and expanded treatment coverage.
5. World Television Day Highlights Role of Television in India
Today is World Television Day. The Day recognises television as a vital medium in informing, educating, and influencing public opinion, and in fostering communication and global understanding. The day is observed globally on November 21
6. First India-born cheetah gives birth to five cubs at Kuno National Park in Madhya Pradesh
First India-born cheetah gives birth to five cubs at Kuno National Park in Madhya Pradesh.
















