Context
Data from the Controller General of Accounts show severe underutilization of funds under the Prime Minister’s Internship Scheme (PMIS), pointing to weaknesses in the scheme’s design, demand, and implementation barely a year after its launch.
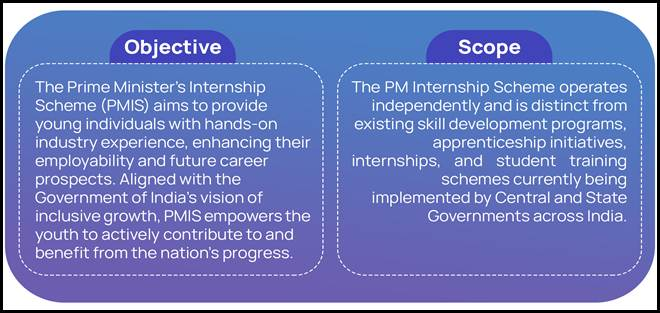
What is the Prime Minister’s Internship Scheme (PMIS)?
- About: The PMIS, under the Ministry of Corporate Affairs, announced in the Union Budget 2024–25, aims to provide one crore internship opportunities over five years in top 500 companies to enhance the employability of youth aged 21–24 years.
- Benefits: The scheme offers a Minimum Stipend of Rs 5,000 per month, a One-Time Grant of Rs 6,000, and Insurance Coverage under PM Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana and PM Suraksha Bima Yojana, along with exposure to diverse sectors and leading companies.
- Internship Duration: The internship lasts 12 months, with at least half of the period spent in real workplace or job-based experience, not classroom training.
- Eligibility: Candidates must be 21–24 years old, possess Minimum Class 10 Qualification or above (ITI, Polytechnic, Graduation etc.), and should not be engaged in Full-Time Employment or Regular Education (distance or online education allowed).
- Ineligible Candidates: Graduates from IITs, IIMs, NLUs, IISERs, holders of professional or postgraduate degrees (CA, CMA, CS, MBA, MBBS, etc.), candidates trained under National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (NAPS)/ National Apprenticeship Training Scheme (NATS).
- Income of any family member exceeds Rs 8 lakh for FY 2023-24 , families with regular government employees, and applicants already in any government skill, apprenticeship, or internship programme are ineligible.
- Significance: PMIS aims to enhance employability by providing structured, real-world industry exposure to youth.
- Bridge the education–industry gap through hands-on training in top companies.
- Expand access to internships beyond elite institutions and urban centres.
- Support youth from low-income households with financial assistance during internships.
- Build a skilled workforce aligned with industry needs and national economic growth.

Key Concerns Regarding the Prime Minister’s Internship Scheme (PMIS)
- Very little money has actually been used:
- By November 2025, the Ministry of Corporate Affairs had spent only about 4% of its FY26 budget, even though more than ₹11,500 crore was allocated, most of it for PMIS. This shows that while big plans were announced, the system is not able to implement them properly.
- Many people apply, but few accept internships:
- Even though there are lots of applications, fewer than one-third of the offered internships are accepted. This suggests the scheme is not matching what candidates want — whether in terms of location, type of work, or opportunities.
- Very few interns finish the programme:
- Only a small number of participants have completed their internships. This raises doubts about how well the programme supports interns and keeps them engaged.
- Stipend is too low:
- The monthly payment of ₹5,000 is not enough to cover basic living expenses, especially in cities. Because of this, many people are not interested in joining or continuing.
- Trust and credibility issues:
- The government’s goal of providing one crore internships sounds very ambitious, but the weak performance in the pilot phase makes people question whether the scheme can actually achieve it.
India’s Major Skill Development Initiatives
- Skill India Mission: A flagship initiative to skill, reskill, and upskill youth through industry-relevant training. It focuses on employability, entrepreneurship, and future-ready skills, with over 6 crore individuals trained, including in AI, robotics, green energy, and Industry 4.0.
- Restructured Skill India Mission (2022–26), merges Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana 4.0 (PMKVY 4.0), the Pradhan Mantri National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (PM-NAPS), and the Jan Shikshan Sansthan (JSS) Scheme into a single Central Sector Scheme.
- All courses under the Skill India Program are aligned with the National Skills Qualifications Framework (NSQF) and integrated with DigiLocker and the National Credit Framework.
- Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY): Launched in 2015, PMKVY provides free, short-term skill training to enhance employability.
- Across four phases, it has trained over 1.63 crore candidates (as of July 2025), with a focus on reskilling, upskilling, and recognition of prior learning.
- Jan Shikshan Sansthan (JSS): A community-based vocational programme for non-literates, neo-literates, and school dropouts, offering flexible and low-cost training.
- Over 26 lakh beneficiaries were trained between FY 2018–19 and 2023–24.
- Pradhan Mantri National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (PM-NAPS): Aims to expand apprenticeships by providing 25% stipend support through DBT to youth aged 14–35.
- As of May 2025, 43.47 lakh apprentices have been engaged across States and UTs.
- Rural Self Employment and Training Institutes (RSETIs): Bank-led residential training centres focused on entrepreneurship and self-employment for rural youth.
- RSETIs trained over 5.67 million candidates as of June 2025.
- Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Grameen Kaushalya Yojana (DDU-GKY): A demand-driven, placement-linked skilling scheme under NRLM targeting rural youth unemployment.
- It promotes wage employment and inclusive rural development.
- PM Vishwakarma Yojana: Launched in 2023 to support traditional artisans and craftspeople in 18 trades.
- PM Vishwakarma Yojana provides skill training, toolkits, collateral-free credit, digital incentives, and market linkages.
- Skill India Digital Hub (SIDH): A technology-enabled platform using Aadhaar-based verification for skilling delivery.
- SIDH supports real-time monitoring and integrates skilling with education and entrepreneurship systems.
- Centres of Excellence at NSTIs: Established in 2025 at Hyderabad and Chennai to strengthen advanced skilling. They focus on instructor training and emerging areas such as AI, robotics, and green technologies.
Measures to Strengthen the Prime Minister’s Internship Scheme (PMIS)
- Fix the stipend based on cost of living:
- The monthly payment should be different for different regions, depending on how expensive it is to live there. Other countries like Germany and Indian schemes like NAPS already follow similar ideas. A realistic stipend will encourage more people to accept and complete internships.
- Make learning goals clear and give proper certificates:
- Every internship should have clear skills that the intern is expected to learn. At the end, they should receive a nationally recognised certificate linked to the NSQF, so the internship actually helps them get jobs later.
- Make companies more responsible:
- Since companies are chosen based on their CSR spending, they should also report results — like how many interns completed the programme, what skills they gained, and how many got jobs. This should be part of their CSR reporting, similar to social audits in government welfare schemes.
- Match candidates and companies better:
- Many interns drop out because they are not matched properly with roles. The scheme should check a person’s skills, location preference, and suitable industry before assigning internships — similar to how Skill India digital platforms try to match people with the right opportunities.
- Reward companies for good outcomes:
- Like in NATS and other global youth employment programmes, companies should get incentives if more interns complete their training or are hired after the internship.
- Spread awareness through local institutions:
- Instead of focusing mainly on cities or top colleges, the scheme should also use ITIs, polytechnics, and district employment offices to reach more young people, just like PMKVY does.
















