
Introduction
The United States Agency for International Development (USAID) is a U.S. government agency responsible for providing foreign aid, humanitarian assistance, and economic development worldwide. Established in 1961, USAID plays a crucial role in disaster relief, health programs, economic development, and democracy promotion.
USAID’s activities are often compared with other regional organizations like BIMSTEC (Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation), which focuses on economic and technical collaboration among South and Southeast Asian countries.
USAID: History and Evolution
USAID was created by President John F. Kennedy on November 3, 1961, through the Foreign Assistance Act of 1961. It consolidated multiple aid programs under one organization to enhance the effectiveness of U.S. foreign aid.
Key Historical Milestones
- 1961 –
- USAID is established to coordinate U.S. international development efforts.
- 1970s –
- Focus expands to humanitarian aid, food security, and disaster relief.
- 1980s –
- Involvement in democratic governance and free-market reforms.
- 1990s –
- Efforts to support former Soviet states in transitioning to democracy.
- 2000s –
- Major contributions to global health programs, including HIV/AIDS and malaria.
- 2010s –
- Disaster relief efforts in Haiti, Syria, and Africa; increased focus on climate change.
- 2020s –
- Support for Ukraine, COVID-19 response, and economic recovery programs.
| Year | Key Development |
|---|---|
| 1961 | USAID established under the Foreign Assistance Act by President John F. Kennedy. |
| 1970s | Focus on food security, education, and disaster relief. |
| 1980s | Expands into democracy promotion and free-market reforms. |
| 1990s | Assistance to former Soviet states for democratic transition. |
| 2000s | Global health programs (HIV/AIDS, malaria), counterterrorism aid. |
| 2010s | Disaster relief in Haiti, Syria, and African nations; focus on climate change. |
| 2020s | COVID-19 response, support for Ukraine, renewable energy projects. |
USAID’s Mission and Objectives
USAID’s primary goal is to reduce global poverty, strengthen democratic governance, and provide humanitarian aid.
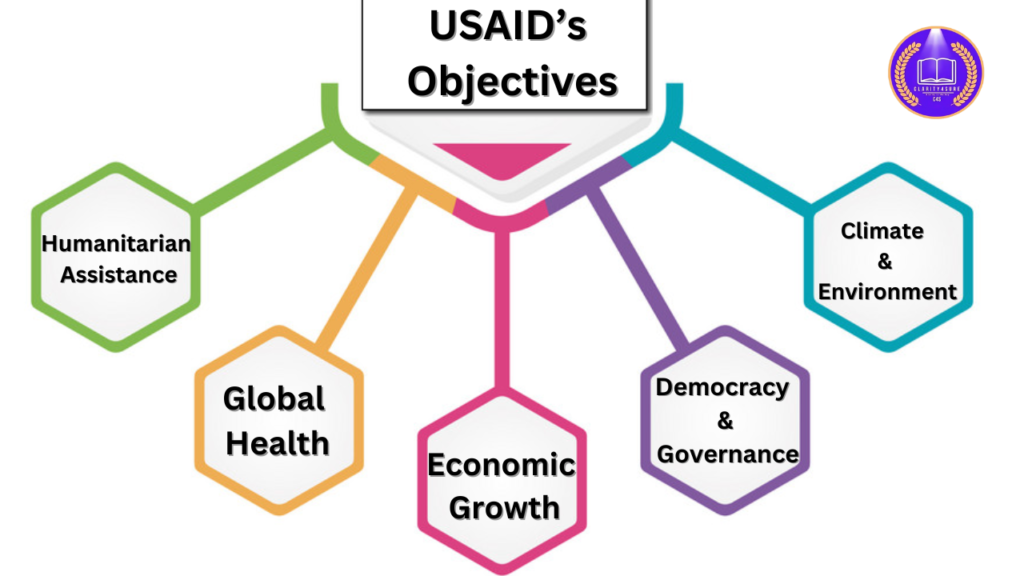
| Objective | Key Focus Areas |
|---|---|
| Humanitarian Assistance | Disaster relief, refugee support, emergency aid. |
| Global Health | HIV/AIDS prevention, maternal health, disease control. |
| Economic Growth | Trade, entrepreneurship, workforce development. |
| Democracy & Governance | Electoral processes, human rights, anti-corruption. |
| Climate & Environment | Renewable energy, climate resilience, conservation. |
| Education | Literacy programs, skill development, digital learning. |
USAID’s Funding and Budget
USAID receives its funding from the U.S. Congress, primarily through the annual foreign aid budget.
| Year | USAID Budget (in Billions) |
|---|---|
| 2019 | $39 billion |
| 2020 | $41 billion |
| 2021 | $43 billion |
| 2022 | $45 billion |
| 2023 | $47 billion |
- Largest Funding Recipients (2023):
- Ukraine –
- Humanitarian and military aid.
- Afghanistan –
- Economic recovery and crisis response.
- Ethiopia & Sudan –
- Conflict response and food security.
- Haiti –
- Disaster relief and health programs.
USAID’s Global Impact: Key Programs & Initiatives
USAID operates in over 100 countries, implementing targeted programs in various sectors:
Global Health Initiatives
- PEPFAR (President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief) –
- Focuses on HIV/AIDS treatment and prevention.
- Global Health Security Agenda –
- Strengthens countries’ healthcare systems to prevent pandemics.
- COVID-19 Response –
- Supplied vaccines, medical kits, and economic relief worldwide.
Economic Growth and Trade
- Feed the Future –
- Reduces hunger and supports agriculture in developing nations.
- Power Africa –
- Expands electricity access across African nations.
- Prosper Africa –
- Promotes trade and investment between the U.S. and Africa.
Democracy and Governance
- Election Monitoring & Voter Education –
- Supports free and fair elections.
- Anti-Corruption Efforts –
- Strengthens legal frameworks and judicial independence.
Humanitarian Assistance
- Crisis Response in Syria, Ukraine, and Afghanistan –
- Provides emergency aid and reconstruction support.
- Food Assistance Programs –
- Addresses food shortages in conflict zones and disaster-hit areas.
USAID’s Impact on Different Regions
| Region | Key Focus Areas |
|---|---|
| Africa | Agriculture, Energy, Democracy, Health (HIV/AIDS, Malaria) |
| Asia | Trade, Infrastructure, Climate Change, Human Rights |
| Latin America | Anti-corruption, Migration, Economic Growth |
| Middle East | Post-conflict reconstruction, Humanitarian aid |
| Europe & Eurasia | Democracy, Economic Stability, Ukraine Assistance |
USAID’s Budget and Funding
USAID’s funding comes from the U.S. Congress, mainly through the annual Foreign Assistance Budget.
| Year | Total USAID Budget (in billions) |
|---|---|
| 2019 | $39 billion |
| 2020 | $41 billion |
| 2021 | $43 billion |
| 2022 | $45 billion |
| 2023 | $47 billion |
- Largest Recipients of USAID Funds (2023):
- Ukraine –
- Humanitarian and military support.
- Afghanistan –
- Post-war economic recovery.
- Ethiopia & Sudan –
- Conflict response and food security.
- Haiti –
- Earthquake relief and development.
USAID vs. BIMSTEC: A Comparative Analysis
Since USAID is a global aid agency, while BIMSTEC is a regional cooperation organization, their roles differ significantly. However, both aim to promote economic growth, development, and stability.
| Feature | USAID | BIMSTEC |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Government agency (U.S.) | Regional organization |
| Year Established | 1961 | 1997 |
| Headquarters | Washington, D.C., USA | Dhaka, Bangladesh |
| Main Focus | Foreign aid, humanitarian assistance, global development | Economic and technical cooperation among South & Southeast Asian countries |
| Funding Source | U.S. Congress | Member states’ contributions |
| Member Countries | Operates in 100+ countries | 7 (Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Myanmar, Nepal, Sri Lanka, Thailand) |
| Key Areas of Work | Health, democracy, economic growth, disaster relief | Trade, infrastructure, connectivity, security |
| Budget | $47 billion (2023) | Smaller compared to USAID, primarily project-based funding |
| Decision-Making | U.S. government-driven | Consensus-based among members |
Why BIMSTEC is Important for South Asia?
- Enhances trade connectivity in the Bay of Bengal region.
- Stronger economic integration among South and Southeast Asian nations.
- Avoids Indo-Pakistan conflicts, unlike SAARC.
Challenges and Criticism of USAID
| Challenges | Details |
|---|---|
| Political Influence | Aid often aligns with U.S. foreign policy interests. |
| Bureaucracy | Slow fund allocation and project execution. |
| Corruption Risks | Some funds are misused by corrupt local governments. |
| Aid Dependency | Some nations rely too much on foreign aid rather than developing self-sufficiency. |
| Operational Risks | Aid workers face security threats in conflict zones. |
Recent Controversies:
- Afghanistan (2021):
- Billions spent on rebuilding efforts, yet governance remains unstable.
- Haiti (2010 Earthquake):
- Delays in aid distribution led to criticism.
- Palestinian Aid Cuts & Reinstatements:
- Aid policies change with U.S. administrations.
Future of USAID: Trends and Priorities
As global challenges evolve, USAID is shifting focus towards climate resilience, digital inclusion, and pandemic preparedness.
Key Future Priorities:
- Climate Change Mitigation –
- Increased investment in renewable energy.
- Technology & Digital Innovation –
- Expanding digital access in developing nations.
- Health Security –
- Strengthening systems to prevent future pandemics.
- Stronger Local Partnerships –
- More collaboration with NGOs and private sectors.
Conclusion
USAID has been a cornerstone of U.S. foreign assistance, shaping global economic development, humanitarian relief, and democratic reforms for over 60 years. While BIMSTEC focuses on regional cooperation, USAID operates on a global scale, influencing economic policies and humanitarian responses worldwide.
















