Daily Current Affairs Quiz
16 January, 2025
International Affairs
1. Israel-Palestine War
Context:
Israel and Hamas agreed to a ceasefire deal to pause the devastating war in the Gaza Strip, raising the possibility of winding down the deadliest and most destructive fighting between the bitter enemies.
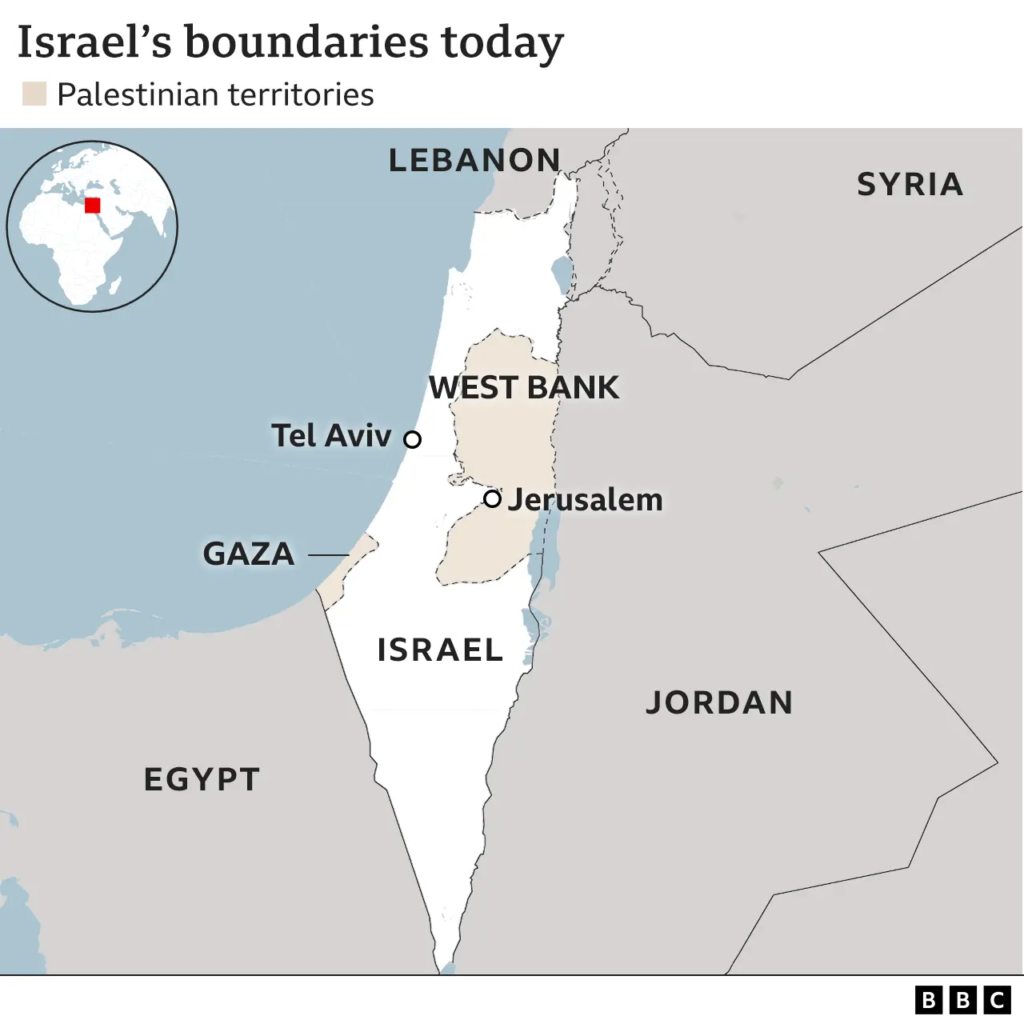
Background
- The conflict, started because of an attack by Hamas, claimed the lives of 1,200 Israelis while the capture of 250 others caused economic havoc on the Israeli side.
Role of Countries in Mediation
- U.S., Egypt, and Qatar facilitated talks between Israel and Hamas.
Course of the War
The Israel-Palestine conflict is a deeply rooted conflict in historical, religious, and political factors. The modern conflict began in the early 20th century, although the region’s significance dates back to ancient times, with Jerusalem being sacred to Jews, Christians, and Muslims.
Historical Context
- Ancient History
- The region of Israel has been long a place of religious significance, especially to Jews, Christians, and Muslims.
- The region’s ancient history deeply relates with the lives of Abraham, King David, and Solomon. Over the years, the region was conquered and ruled by the Romans and later the Byzantines.
- Modern History
- The Zionism movement, initiated in the late 19th century by prominent thinkers such as Theodor Herzl, advocated for a Jewish state in Palestine under Ottoman rule.
- After the defeat of the Ottomans during World War I, Britain was granted the League of Nations mandate over Palestine and, due to the high rates of immigration into the country, tensions between the Arab majority and Jewish population increased.
Declarations
- Balfour Declaration (1917)
- This declaration by Britain supported the establishment of a homeland for Jews in Palestine, scaring the Arabs.
- The United Nations Partition Plan (1947)
- The UN then proposed partition of Palestine into one Jewish and an equal Arab state and accepted by Jews but rejected by Arabs. So, soon violence broke out that eventually led to the declaration of Israeli as an independent country in 1948.
- Arab-Israeli War (1948)
- Following the declaration of Israel’s independence, neighboring Arab states attacked, displacing hundreds of thousands of Palestinians. Palestinians refer to this event as the Nakba, or “catastrophe.”
Ongoing Conflicts

- Wars and Conflicts
- Key issues were: Israeli-Palestinian conflict is a dispute over land—specifically, who has the right to live in the territory between the Jordan River and the Mediterranean Sea, and under what conditions they can do so.
- Israel’s occupation of Palestinian territories in the West Bank and Gaza Strip, and the status of Jerusalem.
- Key issues were: Israeli-Palestinian conflict is a dispute over land—specifically, who has the right to live in the territory between the Jordan River and the Mediterranean Sea, and under what conditions they can do so.
- Hamas
- Hamas is a militant organization that runs the Gaza strip. This organization was formed in 1987 and has been engaged in frequent wars with Israel. Holds beliefs with no compromise on cession of Palestinian territory.
- Israel views it as a terrorist group.
- Jerusalem
- Jerusalem is a very crucial and disputed city in the conflict, which both Israelis and Palestinians claim as their capital. The city contains religious sites sacred to Jews (such as the Western Wall), Muslims (Al-Aqsa Mosque), and Christians (Church of the Holy Sepulchre).
Postwar Gaza: Primary Uncertainties and Challenges
Uncertainty in Return of the Palestinians
- Displaced Palestinians
- Uncertainty about when, and how many, of the displaced Palestinians will return to their homes.
- Demand of Hamas
- Among the top demands of Hamas were the total withdrawal of Israel troops and an end to the war.
- Government
- Uncertainty over who will now govern Gaza after the conflict.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q 1. Which one of the following countries of South-West Asia does not open out to the Mediterranean Sea? (2015)
(a) Syria
(b) Jordan
(c) Lebanon
(d) Israel
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q1. ‘Too little cash, too much politics, leaves UNESCO fighting for life.’ Discuss the statement in the light of US’ withdrawal and its accusation of the cultural body as being ‘anti-Israel bias’. (2019)
Q2 . “India’s relations with Israel have, of late, acquired a depth and diversity, which cannot be rolled back.” Discuss. (2018)
2. US Lifts Restrictions on Indian Nuclear Entities
Context:
The United States Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) had lifted its restrictions on three Indian nuclear entities, which was imposed during the Cold War era: Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC), Indira Gandhi Atomic Research Centre (IGCAR) and Indian Rare Earths (IRE).
- Objective: It is hoped that the removal would be a catalyst in enhancing cooperation among the Indian nuclear institutions and the companies of the U.S., so that civilian nuclear technology can start flowing into the country.
Background and Statements
- Jake Sullivan Speech: US National Security Adviser announced to remove the norms at IIT-Delhi speech that have, since long, held back the country in enforcing the 2008 civil nuclear agreement.
2008 Civil Nuclear Agreement
The US-India 2008 civil nuclear agreement allows India to purchase civilian nuclear power and fuel on the basis of the 123 Agreement. Both India’s Minister of Finance Mr. Pranab Mukherjee and USA’s Secretary Ms. Condoleezza Rice signed the contract on October 10, 2008.
Advantages created by the Contract
- Energy safety
- India gained the opportunity for energy security supply
- Environmental Steadiness
- it is possible for India to start a clean-energy source
- Technology Transfer
- India will have access to civilian nuclear technology and fuel in the US
- Nuclear Trade
- India may emerge as a reliable partner for nuclear trade
- International Cooperation
- India will engage in cooperation with the US as well as other countries on civil nuclear energy
- Key provisions of the agreement
- India agreed that inspectors from IAEA will have access to its civilian nuclear program.
- India agreed to follow international guidelines for exports of nuclear and missiles.
- India agreed to continue its self imposed moratorium on nuclear testing.
- India agreed to use civil nuclear trade only for peaceful purposes.
It is the 3rd India-U.S. Civil Nuclear Agreement. In the year 2008, an agreement was passed that would enable the U.S. civilian nuclear technology to be shared with India. The deal marks a great milestone, but such regulatory ban upon Indian institutions resulted in the signing after more than ten years of delays.
Indira Gandhi Centre for Atomic Research (IGCAR)
Indira Gandhi Centre for Atomic Research (IGCAR) is one of India’s premier nuclear research centres. It was established in 1971 and is situated in Tamil Nadu. It was an exclusive centre dedicated to the pursuit of fast reactor science and technology, due to the vision of Vikram Sarabhai. Originally, it was called Reactor Research Centre (RRC). It was renamed to Indira Gandhi Centre for Atomic Research (IGCAR) by the then Prime Minister of India Rajiv Gandhi in December 1985.
The Bhabha Atomic Research Centre
The Bhabha Atomic Research Centre, also known as BARC, is India’s leading nuclear research center, located at Trombay, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India. It was established by Homi Jehangir Bhabha as the Atomic Energy Establishment, Trombay (AEET) in January 1954 as a multidisciplinary research program essential for India’s nuclear program.
IREL (India) Limited
IREL (India) Limited is an Indian Public Sector Undertaking based in Mumbai, Maharashtra. It specializes in mining and refining rare earth metals. Founded in 18 August 1950.
3. India-China Border Dispute
China’s Provocative Actions
- Dam on Brahmaputra River
- Construction of a dam on the Yarlung Zangbo River(Brahmaputra River), with an aim to generate 300 billion kWh of electricity annually.
- Downstream impact
- Lesser water and silt flow, harming India and Bangladesh’s agriculture, fisheries, and biodiversity.
- India’s Plan on Brahmaputra River:
- Expedited plans for 12 hydropower stations in Arunachal Pradesh for a $1 billion investment.
- Govt Plans India’s Second-Largest Dam On Brahmaputra at Yingkiong In Arunachal Pradesh, To Counter China’s River Diversion Plans
- Budget Estimate
- Estimated to cost Rs 50,000 crore
Geographical Dispute
India and China have argued over the sovereignty of many areas along their border, including Aksai Chin and Arunachal Pradesh.

- Aksai Chin
- Situated in the extreme northeast of Ladakh, Aksai Chin is a salt flat desert about the size of Switzerland
- China seized Aksai Chin during the 1962 war with India
- The region is sparsely populated, except for ancient trade routes crossing through it
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Situated in the extreme northeast of India, Arunachal Pradesh borders China in the north
- China claims nearly all of Arunachal Pradesh, calling it “South Tibet”
- The northern border of Arunachal Pradesh was drawn by the McMahon Line during the 1914 Simla Convention
- Line of Actual Control (LAC)
- A vague, 2,100-mile-long de facto border that lies along the Himalayas
- The LAC is a point of conflict between India and China
- The LAC may vary in different areas because of rivers, lakes, and snowcaps
- 1962 war
- India lost the 1962 war to China and lost territory in Aksai Chin
- Over 7,000 Indian soldiers were killed in the war
India’s Strategic Challenges
- Border Disputes
- Ladakh standoffs continue unabated and Arunachal Pradesh claims remain unrelenting.
- Strategic Vulnerabilities
- Weak surveillance and infrastructure in border areas enable China to exploit weaknesses.
- South Asia’s Fragmented Approach
- Bilateral engagement with China, power asymmetry, need for a unified South Asian strategy, and diplomatic engagement.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q.‘Hand-in-Hand 2007’ a joint anti-terrorism military training was held by the officers of the Indian Army and officers of the Army of which one of the following countries? (2008)
(a) China
(b) Japan
(c) Russia
(d) USA
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. The China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) is viewed as a cardinal subset of China’s larger ‘One Belt One Road’ initiative. Give a brief description of CPEC and enumerate the reasons why India has distanced itself from the same. (2018)
National Affairs
1. Madurai-Thoothukudi New Line Project
Context:
Railways Minister Ashwini Vaishnaw clarified that the Madurai-Thoothukudi new line project had not been shelved, and there were no issues pertaining to land acquisition for it.
Madurai-Thoothukudi New Line Project
- The railway infrastructure initiative seeks to connect the southern parts of Tamil Nadu for economic growth.
- Connectivity
- It will create a new railway line from Madurai to Thoothukudi.
- The proposed railway line is about 143 km long.
- Features
- Direct and faster rail connectivity between the two cities.
- Facilitating freight transport from Thoothukudi port.
Importance of the Project
- Economic Development
- Enhances movement of goods, thereby fostering industrial growth and exports.
- Regional Development
- Improves accessibility to smaller towns and villages along the route.
Project Challenges
- Rehabilitation
- Major Concern regarding the rehabilitation of the people in the area whom lands are to be acquire.
- Other challenges involved are disputes and negotiations, environmental clearances, and funding.
2. Calcutta Illumination Project
Context:
Kolkata-based social activist Mudar Patherya wants to light up 125 heritage buildings in the city by the end of 2025. The project has been called the Calcutta Illumination Project.
- How it Started?
- Started in November 2023, and so far, 62 structures have been illuminated in 14 months.
- How it works?
- It is a one-man initiative undertaken by Patherya, and he funds it through crowdfunding.
- The project uses LED lights to illuminate the buildings.
- The aim is to make history visible at night in the city.
- Why it’s important?
- It beautifies the city and highlights the historic importance of the buildings.
- It can help create pride and identity among the community.
- It may redefine the neighborhoods of the buildings.
- Landmark structures
- Raj Bhavan, St. Paul’s Cathedral, General Post Office, St. James Church, Standard Assurance Building.
3. Roman Script for Kokborok in Textbooks
Context:
About 12 members of the Twipra Students Federation (TSF) were detained for staging a protest at the entrance of the Tripura Assembly to press for their demand for the use of the Roman script for Kokborok in textbooks and for official work.
A majority of the tribes in the State speak Kokborok, which has been recognised as the second State language after Bengali.
The Roman Script
The Roman script, also known as Latin script, is a writing system that uses the letters of the Latin alphabet. It is used to write many languages in Europe, Africa, America, and Oceania.
- How it originated?
- The Roman script originated from the Greek alphabet, which was modified by the Etruscans and then the Romans.
- Letters
- The early Roman alphabet had 23 letters, but the alphabet changed over time as the language developed.
- For example, the letter “I” was split into “I” and “J”, and the letter “V” was split into “U”, “V”, and “W”.
- How it is used?
- Roman script is used in many languages, including English.
- It is also used in bilingual volumes, such as Sanskrit literature, where the original text is in Roman script and the translation is in another language.
- Gravestones & Monumental Capitals
- Roman script is used in gravestones, where the letters are chiseled or sandblasted.
- Roman script is used in monumental capitals, which are large capital letters inscribed on stone, such as on monuments.
Why Roman script for Kokborok?
- Accessibility
- The Roman script is compatible with the modern technology and digital platforms.
- Educational Opportunity
- Students may find writing easier in the Roman script, which will help them in widening their educational opportunities.
- Preservation
- Use the Roman script could preserve the language in a familiar form widely utilized.
- Cultural resources
- Spread indigenous literature as well as indigenous cultural resources would be promoted.
Kokborok
Kokborok is a language that appears in textbooks in Tripura, India, and neighboring areas of Bangladesh. It is a Sino-Tibetan language that is spoken by the Borok people, also known as Tripuris.
- What is Kokborok in textbooks?
- Kokborok textbooks may include lessons on vocabulary, grammar, and language learning.
- Kokborok textbooks may also include literature, such as prose and poetry.
- What is the origin of Kokborok?
- The word “Kokborok” is the combination of words “Kok” and “Borok”. “Kok” means “verbal” and “Borok” means “people” or “human”.
- The first written form of Kokborok was the Kokboroma Ang Tripura-Vyakaran Grammar, which was made in 1897 by a Muslim scholar known by the name Doulot Ahammad.
4. The Assam Coal Mining Tragedy
Context:
The Assam coal mining tragedy occurred when a sudden influx of water flooded an illegal rat-hole mine in Dima Hasao district, Assam on January 6, 2025. The mine was abandoned by the state’s Mines and Minerals Department 12 years ago.
Definition and Hazards of Rat-Hole Mining
Rat-hole mining, a method of manually digging narrow holes in North East India for coal extraction, is banned by the National Green Tribunal but still used by artisanal mining operations in Meghalaya.
Techniques
- Side Cutting Method
- Coal seams traverse along hill slopes.
Seams are visible at the outer edge of rocks.
- Coal seams traverse along hill slopes.
- Box Cutting Method
- A pit is dug which has a width of 5 square meters and a depth of 400 feet in order to collect the coal.
- Dangerous Conditions
- The employees face extreme dangers due to the narrow, dangerous tunnels.
- Eco-Negative Impact
- Serious damages to local ecosystems and landscapes.
- Inrequent Mine Accidents
- Many deaths and injuries take place in these mines.
- Hazards
- The risk of flood, health, environmental hazard, and the inability to gain the economic feasibility.
Ban and Continued Practice
- It was banned by the NGT in 2014. Because it’s a dangerous operation which causes hazardous environment.
- Supreme Court Observation (2019) questioned the “connivance” of officials in the continuation of illegal mining.
- Regulation is still lax, allowing the illegal business to thrive.
Dima Hasao Tragedy
- Administrative Failure
- Assam Chief Minister said that it was probably an illegal mine abandoned.
- These mines continue despite the ban on account of lapses in administration and unscrupulous exploitation.
Coal and Coal Mining in India
5. Maharishi Agastya
Context:
“With Maharishi Agasthyar as the central theme and Mahakumbh and Shri Ayodhya Dham as the backdrop, Kashi Tamil Sangamam 3.0 will offer a divine experience and bring Tamil Nadu and Kashi – the two timeless centres of our civilisation and culture, more closer than ever” Said Union Education Minister Dharmendra Pradhan.
Maharishi Agastya
Agastya was a revered Indian sage of Hinduism.. In the Indian tradition, he is a known ascetic and a great scholar of various Indian subcontinent languages. In some traditions, he is considered a Chiranjivi. He and his wife Lopamudra are the famous authors of the Sanskrit text Rigveda hymns 1.165 to 1.191 and other Vedic literature.
Agastya is the father of Siddha medicine. He is one of the Tamil Siddhar in the Shaivism tradition and is revered as such. He invented the grammar of the early Tamil language called Agattiyam and took the pioneering steps in the development of Tampraparniyan medicine and spirituality.
6. The Indian National Science Academy (INSA)
Context:
The annual list of Fellows announced by the 90-year-old Indian National Science Academy, among the country’s most prestigious assembly of scientists, sticks out this year for its deviation from the academy’s traditional practice. The list features a phalanx of famous Indians who are not professional scientists.
The Indian National Science Academy (INSA)
The Indian National Science Academy (INSA) is the New Delhi-based national academy for Indian scientists of all disciplines. In 2015, it founded the Indian National Young Academy of Sciences (INYAS), a junior wing for young scientists. INYAS is affiliated with Global Young Academy and has signed the declaration on Core Values of Young Academies. The current president of INYAS is Prof. Ashutosh Sharma.
- Founder
- Lewis Leigh Fermor
History and Growth
- INSA is an autonomous institution of the Department of Science & Technology, Govt. of India. It was established in 1935 to promote, nurture, and safeguard the interests of sciences and scientists.
- INSA is an accredited Premier National Scientific Society by the Government of India. It moved to its present premises in Delhi in 1951.
- INSA was requested in 1968 to represent India in all International Science Fora.
- In 1970, NISI was renamed as Indian National Science Academy (INSA).
- The main INSA-building, the Golden Jubilee Building, was completed in 1996.
7. PM-WANI Scheme
Context:
The draft Telecommunication Tariff (Seventy First Amendment) Order, 2025 proposes that the “broadband tariff (fiber to the home [FTTH]) for Public Data Office (PDO) under the PM-WANI scheme shall not exceed twice the tariff applicable for retail broadband FTTH services for the corresponding capacity offered by the respective service provider.”
PM-WANI Scheme
The Prime Minister’s Wi-Fi Access Network Interface (PM-WANI) was launched in December 2020 by the Department of Telecommunications (DoT)
- About
- A prominent scheme to promote public WiFi hotspot penetration and achieve the robust development of a digital communication infrastructure for the nation is PM-WANI.
- This has been introduced by the DoT since December 2020.
- Framework
- It is a framework that enables any entity, be it a shopkeeper, a tea stall owner, or a Kirana store owner, to set up a public Wi-Fi hotspot and provide internet service to customers.
- This framework builds forward the objectives of the National Digital Communications Policy, 2018 (NDCP) by creating a strong digital communications infrastructure.
PM-WANI Ecosystem
- Public Data Office (PDO)
- PDO is the entity that establishes, maintains, and operates the Wi-Fi hotspot and provides last-mile connectivity to the users by procuring internet bandwidth from telecom service providers or internet service providers.
- Public Data Office Aggregator (PDOA)
- PDOA is the entity that provides aggregation services, such as authorization and accounting, to PDOs, and facilitates them in providing services to the end users.
- App Provider
- This is the party that creates an application to sign up users and find and display PM-WANI compliant Wi-Fi hotspots in proximity for accessing the internet service and also authenticate the potential users.
- Central Registry
- This is the organization that keeps information about App Providers, PDOAs, and PDOs. Presently, this is maintained by the Centre for Development of Telematics (C-DoT).
Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI)
- About
- DPI means digital platforms like digital identification, payment infrastructure, and data exchange solutions.
- DPIs act as intermediaries for the flow of people, money, and information.
- India developed all three foundational DPIs through India Stack
- Digital identity (Aadhar), Real-time fast payment (UPI), and Account Aggregator.
- DPI consists of three layers
- Market, Governance, and Technology Standards.
- Advantage
- The advantages of DPI are lower development costs, versatile application, and the democratic yet non-monopolistic nature.
- Programs of DPI
- The successful DPI programs undertaken in India include Aadhaar, UPI, CoWin, among others like Unified Health Interface (UHI), Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM), and Open Network for Digital Commerce.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year’s Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following statements: (2018)
- Aadhaar card can be used as a proof of citizenship or domicile.
- Once issued, Aadhaar number cannot be deactivated or omitted by the Issuing Authority.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)
8. Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)
Context:
The outgoing Joe Biden administration in the United States (US) is proposing a framework restricting the export of advanced computer chips (mainly GPUs or graphics processing units) used to develop artificial intelligence (AI).
Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)
Banking/Finance
1. Variable Rate Repo (VRR)
Context:
the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has announced that it will conduct daily variable rate repo (VRR) auctions on all working days in Mumbai, until further notice. The daily auctions, aimed at easing the current liquidity tightness in the banking system.
The Variable Rate Repo (VRR)
The Variable Rate Repo (VRR) is that tool with the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) can fine-tune liquidity in the banking system. The VRR is a lending rate which might change as and when required to the economy.
- How does the VRR work?
- The RBI uses the VRR to reduce the amount of cash in the system.
- The RBI undertakes VRR operations to keep the system sufficiently liquid.
- The VRR impacts the rates of interest on loans that the banks charge.
- Why is the VRR significant?
- What is the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC)?
- A six-member committee heads the MPC under the RBI Governor.
- The MPC determines the repo rate in terms of the existing and changing macroeconomic scenario.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. If the RBI decides to adopt an expansionist monetary policy, which of the following would it not do (2020)
- Cut and optimize the Statutory Liquidity Ratio
- Increase the Marginal Standing Facility Rate
- Cut the Bank Rate and Repo Rate
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Q. With reference to Indian economy, consider the following: (2015)
- Bank rate
- Open market operations
- Public debt
- Public revenue
Which of the above is/are component/ components of Monetary Policy?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4
(c) 1 and 2
(d) 1, 3 and 4
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. Do you agree with the view that steady GDP growth and low inflation have left the Indian economy in good shape? Give reasons in support of your arguments. (2019)
2. RBI’s Exchange Rate Policy
Context:
The RBI has discontinued its flexible exchange rate regime in 2022 and is maintaining a de facto peg against the U.S. dollar.
Exchange Rate Policy
A flexible exchange rate is a monetary system where the exchange rate of a currency is determined by supply and demand in the foreign exchange market. It’s also known as a floating exchange rate.
- How it works
- The value of a currency changes based on supply and demand.
- When demand is low, the value of the currency goes down.
- When the demand for the currency is high, the value of the currency becomes more.
- At times, the central banks interfere to avoid steep fluctuations.
- Advantages
- It gives the currency a real value, brings about control of inflation, and one does not need large reserves.
- Examples
- United States, Japan, Australia, and The United Kingdom.
- Compare to fixed exchange rate
- In the case of fixed exchange rate, the government fixes the exchange rate.
- The government does not interfere with the exchange rate system of the currency under a flexible rate system.
Key Assumptions:
- Accidental Event:
- The change could have been accidental, which may have been a consequence of an effort to rebuild India’s foreign exchange reserves after the outflow of capital in 2022.
- Inflation Curb:
- The RBI had tried to contain inflation by arresting rupee depreciation that would have aggravated inflationary trends.
- Political Factors:
- Some analysts believe that political forces for a more strengthened rupee may have acted to enhance the economic sentiment and reduce import cost.
- Role of External Commercial Borrowings (ECBs)
- ECBs had surged in early 2023 due to U.S. interest rates.
- Had the exchange rate been pegged, the threat of depreciation may have been lowered, and therefore, ECBs may have soared.
Unintended Consequences of the Peg
- Increased Currency Risk:
- The increase in ECBs raised exposure to currency risks, especially for firms with dollar-denominated debt.
- Erosion of Competitiveness:
- Defending the peg led to a decline in India’s competitiveness, particularly affecting exports.
- Capital Outflows:
- Resulted in a $70 billion decrease in reserves over several months.
External Commercial Borrowing
- An ECB is a type of funding that is not equity-based.
- ECBs can include commercial bank loans, credit from export credit agencies, and credit from multilateral financial institutions.
- ECBs can be beneficial because they offer lower interest rates, large amounts of funds, and relatively long terms.
- All entities, except for Limited Liability Partnerships, are eligible for ECBs.
Currency peg
A currency peg is a policy that ties a country’s currency to another country’s currency, or a basket of currencies. The goal is to keep a country’s currency stable so that it can compete in international trade.
Price-to-earnings-to-growth (PEG) ratio
A PEG ratio is a financial metric that investors use to evaluate a stock’s value. It compares a stock’s price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio to its earnings growth rate.
Economy
1. Merchandise Trade Deficit
Context:
India´s merchandise trade narrowed to $21.94 in December, down from a record $31.86 billion in November, as gold imports halved to $4.7 billion, according to commerce department released.
Merchandise Trade Deficit
A merchandise trade deficit is when a country imports more than it exports. This simply means that the country is spending more on foreign goods than it is earning from exports.
- Explanation
- The balance of trade (BOT) is the total value of a country’s exports minus its total value of imports.
- A negative BOT indicates a trade deficit.
- A positive BOT indicates a trade surplus.
- Factors that can contribute to a trade deficit
- If it is rich with a high level of demand in that country, it may import more goods than exporting.
- Over dependence on the use of imported foreign goods may force the country to import more than export.
- Over reliance on foreign goods due to other factors and which influence the view of public perception may import more goods than it exports.
- Effects of having a trade deficit
- A trade deficit can become a political matter that affects decisions on policy.
- A trade deficit may suggest that the country is excessively dependent on imports.
2. Foreign Borrowings
Context:
Indian companies´ foreign borrowings plunged 20.2 per cent to $23.33 billion in 2024, down from $29.22 billion a year earlier.
Foreign Borrowings
Foreign borrowings, also referred to as external debt, is borrowed money by a government, corporation, or household from another country. Foreign borrowings can either be short-term or long-term liabilities.
- Benefits of foreign borrowings
- Access to capital
- Foreign borrowings can be a cheap source of capital for investments.
- Financing
- Foreign borrowings can finance gross domestic investment.
- Access to capital
- Risks of foreign borrowings
- Debt crisis
- Foreign borrowings can cause debt crises, especially in developing economies.
- Economic growth
- Foreign borrowings can slow economic growth, especially in low-income countries.
- Financial market turmoil
- Foreign borrowings can lead to financial market turmoil.
- Exchange rate risk
- A local currency depreciation can increase the default probability of a firm that borrows in foreign currency.
- Debt crisis
- Examples of foreign borrowings
- Foreign currency borrowing
- If a firm has borrowed money from elsewhere other than domestic currency.
- Obligations to international organizations
- If the government borrows from the World Bank, Asian Development Bank, International Monetary Fund among others
- Foreign currency borrowing
India Inc’s Foreign Borrowings Down in 2024
- Slump in Foreign Borrowings
- 20.2% slide to $23.33 billion in 2024 from $29.22 billion in 2023.
- Effect of Currency Devaluation
- Falling rupee value against the US dollar increases the cost of foreign loans for Indian corporations.
- Rising Cost of Borrowing
- Repayment costs are high, and forward cover prices are rising with depreciation, forcing Indian companies to avoid foreign debt.
- Change in Strategy of Borrowing
- Many Indian companies will reduce foreign borrowings owing to a high cost of overseas debt.
- Preference for Local Debt
- Many Indian companies have been preferring to raise debt from local banks owing to the cost difference.
- Expert Opinion
- Rabal Banerjee sees foreign loan outtakes to slow in 2025.
Agriculture
1. Permaculture Farming vs Conventional Farming
Permaculture farming is a sustainable farming method that is nature-based and productive for future generations. Conventional farming, also referred to as chemical farming, is based on chemical inputs to control pests and increase growth.
Differences between Permaculture and Conventional farming
- Monoculture
- Monoculture is the growing of a single crop in a particular area.
- Permaculture does not support monoculture, while conventional farming utilizes monoculture.
- Soil Health
- Permaculture uses organic fertilizers, while conventional farming uses chemical fertilizers that can make soil less fertile.
- Mulching
- Mulching is the process of covering the soil with a protective layer of organic or inorganic material. It can help with weed control, water conservation, and soil protection.
- Permaculture uses mulching, while conventional farming doesn’t always.
- Suitability to semi-arid regions
- Conventional farming is more suitable for semi-arid regions, while permaculture is not.
- System Design
- Permaculture is an integrated design system that considers local conditions, while conventional farming is more suited to monoculture cropping.
- Ethics
- Permaculture is based on ethics of caring for the earth, people, and fair share.
Permaculture Farming
- Principles
- Earth care, people care, and reciprocal means of sharing fairly
- Practices
- Organic fertilizers, mulching, and the integration of farming systems
- Goals
- Achieves self-reliance and long-term sustainability
- Benefits
- More resistant to chemicals, less pollution, and helps maintain soil health
Conventional Farming
- Practices
- Chemical fertilizers, pesticides, herbicides, and other chemicals used to control pests and promote growth
- Objectives
- Increase crop yields, often through GMOs and chemical application
- Challenges
- Results in soil salination, imbalance in the soil, and poor bioavailability of minerals
UPSC PYQ Prelims Question
Q. How is permaculture farming different from conventional chemical farming? (2021)
- Permaculture farming discourages monocultural practices but in conventional chemical farming, monoculture practices are predominant.
- Conventional chemical farming can cause an increase in soil salinity but the occurrence of such phenomenon is not observed in permaculture farming.
- Conventional chemical farming is easily possible in semi-arid regions but permaculture farming is not so easily possible in such regions.
- Practice of mulching is very important in permaculture farming but not necessarily so in conventional chemical farming.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 3
(b) 1, 2 and 4
(c) 4 only
(d) 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Q. With references to organic farming in India, consider the following statements: (2018)
- ‘The National Programme for Organic Production’ (NPOP) is operated under the guidelines and directions of the Union Ministry of Rural Development.
- ‘The Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority’ (APEDA) functions as the Secretariat for the implementation of NPOP.
- Sikkim has become India’s first fully organic State.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: B
2. Initiative for Nutritional Security through Intensive Millets Promotion (INSIMP)
The INSIMP is a programme to promote intensive millet cultivation and consumption in India. It was launched in 2011-12 under Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY).
- Ministry
- Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
- Goals
- Increase the production of millet, Generate the demand for the product based on millets, Show improved production and post-harvesting technologies.
- Popularize millets as “Nutri-cereals, and Motivate the farmers to opt for millet crops.
- How it works
- Provides financial help to states on seed production, processing units and awareness camps
- Advantages of millets
- They are free from gluten content and have lower glycemic indices
- They act as good magnesia and can prevent failure of heart, because of having low glycemic index
- Cells are protected through tannins, phytates, and phenols from getting damaged
UPSC Prelims PYQ
Q. With reference to ‘Initiative for Nutritional Security through Intensive Millets Promotion’, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2016)
- This initiative aims to demonstrate the improved production and post-harvest technologies, and to demonstrate value addition techniques, in an integrated manner, with a cluster approach.
- Poor, small, marginal and tribal farmers have a larger stake in this scheme.
- An important objective of the scheme is to encourage farmers of commercial crops to shift to millet cultivation by offering them free kits of critical inputs of nutrients and micro irrigation equipment.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 2 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Exp:
- ‘Initiative for Nutritional Security through Intensive Millets Promotion’ Scheme aims to demonstrate the improved production and post-harvest technologies in an integrated manner with visible impact to catalyse increased production of millets in the country. Besides increasing production of millets, the Scheme, through processing and value addition techniques, is expected to generate consumer demand for millet-based food products. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- Technology demonstrations in compact blocks would be organized in selected districts for four categories of millets – sorghum, pearl millet, finger millet and small millets. Poor, small, marginal and tribal farmers have a larger stake in this scheme. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- There is no such provision to encourage farmers of commercial crops to shift to millet cultivation. Hence, statement 3 is not correct.
- Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
Facts To Remember
1. GRAP III, IV back in Delhi
- As the city’s air deteriorated (AQI 401 at 8 p.m.), the Centre reintroduced a ban on construction and demolition activities, plying of BS-III petrol and BS-IV diesel four-wheelers, and mandatory shifting of classes to ‘hybrid mode’ for students, except for those in grades 10 and 12, in Delhi-NCR.
- The actions are part of stage III and IV of the Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP), a set of short-term emergency measures to reduce air pollution.
2. Easy access to clean toilets essential for human dignity: SC
- The Supreme Court on Wednesday declared that easy access to clean public toilets for all — including men, women, persons with disabilities, and transgender people — is not just a matter of convenience but a basic right and an essential part of human dignity.
3. Indra Bhavan
- Congress Parliamentary Party Chairperson Sonia Gandhi on Wednesday inaugurated the new Congress headquarters, Indira Bhavan, at 9-A Kotla Marg, named after former Prime Minister Indira Gandhi, marking a new chapter in the party’s history.
4. Thailand eases long-term visa rules to attract foreign talent, investment
- Thailand eases long-term visa rules to attract foreign talent and investment. It has also removed the five-year minimum work experience requirement for professionals to increase the global talent pool in the country.
5. Punjab launches SHE COHORT 3.0 to empower women-led startups
- SHE COHORT 3.0 (Startups Handholding & Empowerment – Cohort 3.0) was launched at Mohali yesterday. The initiative empowers aspiring female startups and students to build and scale technology-based ventures with support from business incubators and ecosystem enablers.
6. Indonesian President to be Chief Guest of RD celebration this year
- President of Indonesia, Prabowo Subianto, will be the Chief Guest at the 76th Republic Day celebrations this year. At the invitation of Prime Minister Narendra Modi, President Subianto will pay a state visit to India on the 25th and 26th of January.
7. India to set up 60 smart classrooms in Sri Lanka
- India and Sri Lanka have signed an agreement to set up 60 smart classrooms in plantation regions on the island. The project is funded by a grant of 508 million Sri Lankan rupees from the Indian government.
8. Maha Kumbh at Prayagraj
- The Maha Kumbh, held once every 12 years in Prayagraj, is anticipated to attract 400 million devotees over 45 days.
9. VP calls upon agro & agri based industries to help farmers under CSR
- Vice President Jagdeep Dhankhar has urged the active participation of ICAR and Agricultural Universities across the country to support the farming sector.
10. 8th Pay Commission for Central govt employees & Pensioners
- The government today announced the setting up of the 8th Pay Commission for the Central government employees and pensioners. An announcement in this regard was made by Union Information and Broadcasting Minister Ashwini Vaishnaw in New Delhi. He was briefing the media about Cabinet’s decision.
11. Protest in Bangladesh over removal of a particular graffiti from textbooks
- In Bangladesh, protesting ethnic minority students were attacked by other student groups and local people in the capital Dhaka on Wednesday night. More than a dozen, mostly students belonging to different ethnic minority communities, were injured in an attack in the presence of the police.
12. ITPO showcases India’s growing prominence in global security & safety sector.
- Intersec 2025, the world’s leading trade fair for security, safety, and fire protection, concludes today at the Dubai World Trade Centre, marking another milestone in its 25-year legacy of advancing industry innovation.
















