Context:
Israel and Hamas agreed to a ceasefire deal to pause the devastating war in the Gaza Strip, raising the possibility of winding down the deadliest and most destructive fighting between the bitter enemies.
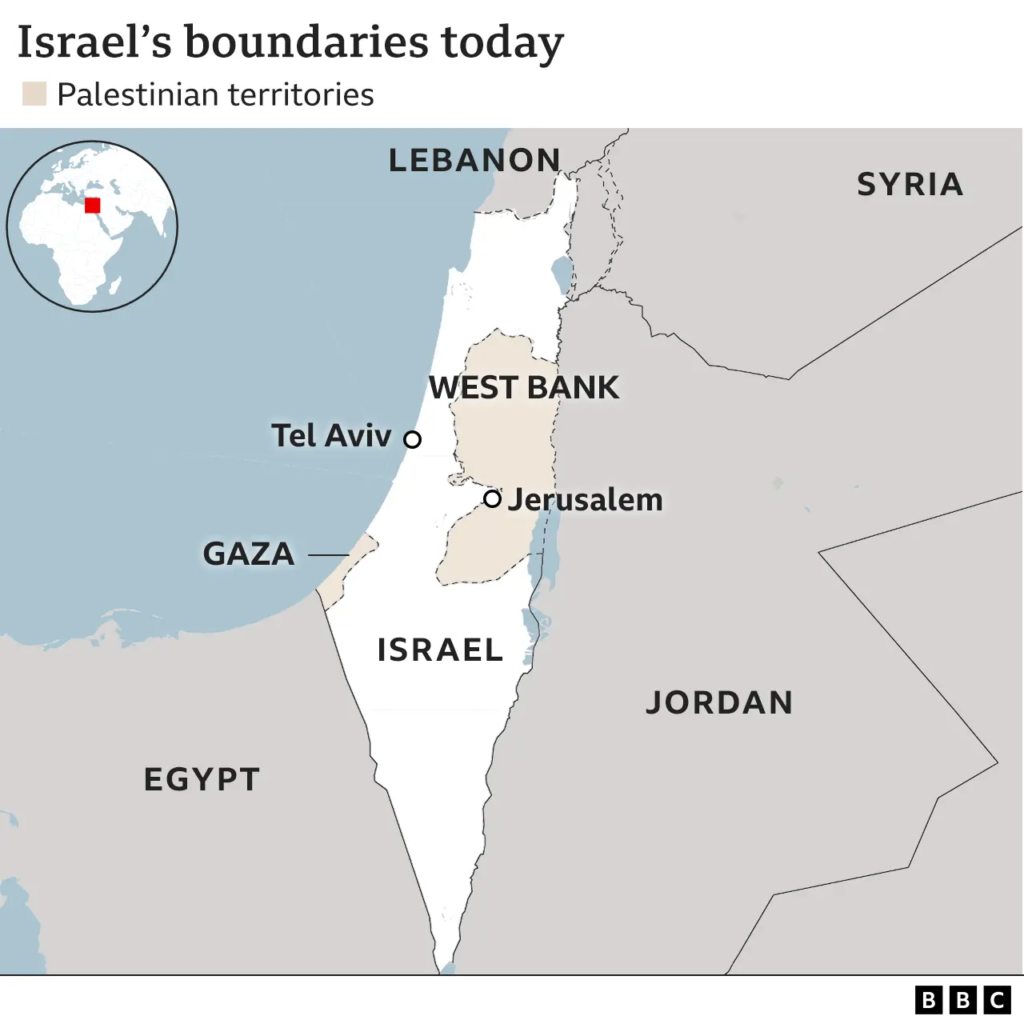
Background
- The conflict, started because of an attack by Hamas, claimed the lives of 1,200 Israelis while the capture of 250 others caused economic havoc on the Israeli side.
Role of Countries in Mediation
- U.S., Egypt, and Qatar facilitated talks between Israel and Hamas.
Course of the War
The Israel-Palestine conflict is a deeply rooted conflict in historical, religious, and political factors. The modern conflict began in the early 20th century, although the region’s significance dates back to ancient times, with Jerusalem being sacred to Jews, Christians, and Muslims.
Historical Context
- Ancient History
- The region of Israel has been long a place of religious significance, especially to Jews, Christians, and Muslims.
- The region’s ancient history deeply relates with the lives of Abraham, King David, and Solomon. Over the years, the region was conquered and ruled by the Romans and later the Byzantines.
- Modern History
- The Zionism movement, initiated in the late 19th century by prominent thinkers such as Theodor Herzl, advocated for a Jewish state in Palestine under Ottoman rule.
- After the defeat of the Ottomans during World War I, Britain was granted the League of Nations mandate over Palestine and, due to the high rates of immigration into the country, tensions between the Arab majority and Jewish population increased.
Declarations
- Balfour Declaration (1917)
- This declaration by Britain supported the establishment of a homeland for Jews in Palestine, scaring the Arabs.
- The United Nations Partition Plan (1947)
- The UN then proposed partition of Palestine into one Jewish and an equal Arab state and accepted by Jews but rejected by Arabs. So, soon violence broke out that eventually led to the declaration of Israeli as an independent country in 1948.
- Arab-Israeli War (1948)
- Following the declaration of Israel’s independence, neighboring Arab states attacked, displacing hundreds of thousands of Palestinians. Palestinians refer to this event as the Nakba, or “catastrophe.”
Ongoing Conflicts

- Wars and Conflicts
- Key issues were: Israeli-Palestinian conflict is a dispute over land—specifically, who has the right to live in the territory between the Jordan River and the Mediterranean Sea, and under what conditions they can do so.
- Israel’s occupation of Palestinian territories in the West Bank and Gaza Strip, and the status of Jerusalem.
- Key issues were: Israeli-Palestinian conflict is a dispute over land—specifically, who has the right to live in the territory between the Jordan River and the Mediterranean Sea, and under what conditions they can do so.
- Hamas
- Hamas is a militant organization that runs the Gaza strip. This organization was formed in 1987 and has been engaged in frequent wars with Israel. Holds beliefs with no compromise on cession of Palestinian territory.
- Israel views it as a terrorist group.
- Jerusalem
- Jerusalem is a very crucial and disputed city in the conflict, which both Israelis and Palestinians claim as their capital. The city contains religious sites sacred to Jews (such as the Western Wall), Muslims (Al-Aqsa Mosque), and Christians (Church of the Holy Sepulchre).
Postwar Gaza: Primary Uncertainties and Challenges
Uncertainty in Return of the Palestinians
- Displaced Palestinians
- Uncertainty about when, and how many, of the displaced Palestinians will return to their homes.
- Demand of Hamas
- Among the top demands of Hamas were the total withdrawal of Israel troops and an end to the war.
- Government
- Uncertainty over who will now govern Gaza after the conflict.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q 1. Which one of the following countries of South-West Asia does not open out to the Mediterranean Sea? (2015)
(a) Syria
(b) Jordan
(c) Lebanon
(d) Israel
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q1. ‘Too little cash, too much politics, leaves UNESCO fighting for life.’ Discuss the statement in the light of US’ withdrawal and its accusation of the cultural body as being ‘anti-Israel bias’. (2019)
Q2 . “India’s relations with Israel have, of late, acquired a depth and diversity, which cannot be rolled back.” Discuss. (2018)















