Daily Current Affairs Quiz
9 April, 2025
International Affairs
1. China vs. US Trade War
Context:
The US-China trade war intensified as President Trump threatened to raise tariffs on Chinese imports to over 100%. China condemned the move as “blackmail”, vowing to “fight to the end” if the US follows through. Trump stated he’s waiting to hear from China before enacting new duties.
Global Market Impact
- Stock markets, after significant losses, showed signs of recovery.
- US stocks posted gains following a heavy selloff.
- Japan’s Nikkei rose 6%, Chinese blue chips climbed 1%.
- Analysts fear a global recession and further disruption to decades-old trade norms.
EU and Asia Respond Cautiously
- The European Union proposed 25% countertariffs on select US goods including soybeans, nuts, and sausages.
- Bourbon and alcohol tariffs were considered but not included.
- President Trump rejected the EU’s zero-tariff proposal on industrial goods, accusing Europe of unfair trade and military dependence.
- Other Asian economies adopted softer diplomatic tones, contrasting China’s hardline stance.
China’s Six Major Countermeasures
- Ban on US film imports
- Significant tariff hikes on US agriculture (soybeans, sorghum)
- Ban on US poultry
- Suspension of US-China fentanyl cooperation
- Countermeasures in services trade
- IP rights investigations into US firms in China
Economic and Political Fallout
- Citi lowered China’s 2025 GDP forecast to 4.2% from 4.7% citing external risks.
- Euronext CEO said the US now resembles an emerging market, using strategic tariffs.
- China’s manufacturers in sectors like tableware and flooring are now eyeing overseas relocation to escape tariffs.
2. India-Sri Lanka Strategic Relations
Context:
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s 3-day visit to Sri Lanka marks a strategic pivot in India’s Indian Ocean Region (IOR) diplomacy.
- Comes after visits to Mauritius and participation in the BIMSTEC summit in Thailand, signaling a geostrategic balancing act amid China’s expanding influence.
Significance of Modi’s Visit
- First foreign leader to visit Sri Lanka after the election of President Anura Kumara Dissanayake, perceived as China-leaning.
- Builds on India’s $4.5 billion financial assistance extended during Sri Lanka’s economic crisis.
- Aimed at recalibrating bilateral ties and countering China’s growing investments in Sri Lanka.
Key Agreements and Projects
- Seven MoUs signed, covering:
- Power grid interconnection
- Digitisation initiatives
- Security and defense cooperation
- Healthcare services
- Five major development projects:
- Solar energy
- Railway infrastructure
- Defence Cooperation Agreement:
- Training of Sri Lankan military personnel in India
- Technology and intelligence sharing
- Trincomalee Energy Hub Development:
- Joint project with UAE in Sri Lanka’s Tamil-speaking east
- Viewed as a symbol of inclusive development and strategic balancing
Symbolism and Diplomatic Gestures
- 19-gun salute and Mitra Vibhushana (Sri Lanka’s highest civilian honor) conferred on Modi
- Reflects efforts by Sri Lanka to balance ties with both India and China
- Dissanayake reiterated his commitment to not letting Sri Lanka undermine India’s security — an indirect reference to past concerns over Chinese surveillance vessels.
China Factor and Competing Interests
- Colombo signed a $3.7 billion deal with a Chinese state-owned firm for an oil refinery, its largest foreign investment.
- Dissanayake visited India first, then China, reflecting a delicate foreign policy equilibrium.
- China remains Sri Lanka’s largest creditor and investor, yet India’s presence is being revitalized through development-led diplomacy.
Strategic Challenges and Future Outlook
- India’s ability to execute its infrastructure projects in Sri Lanka is under scrutiny.
- Past performance on regional connectivity (e.g., under BIMSTEC) has been slow and ineffective.
- Implementation will be critical to sustaining goodwill and competing with China’s efficiency in delivering large-scale investments.
3. Dubai Crown Prince’s India Visit
Context:
On his first official visit to India, Sheikh Hamdan bin Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum, the Crown Prince of Dubai and UAE Defence Minister, held high-level discussions with Indian leadership to strengthen bilateral cooperation in defence, trade, education, infrastructure, and strategic partnerships.
Top Announcements & Agreements
1. Education
- IIM Ahmedabad campus to open in Dubai.
- First MBA programme to launch in September 2025.
- Indian Institute of Foreign Trade (IIFT) to open its first overseas campus at the India Pavilion, ExpoCity Dubai.
2. Infrastructure & Business
- Construction of Bharat Mart to begin soon; 3D renderings launched.
- Grant of land for UAE-India Friendship Hospital in Dubai.
- Dubai Chamber of Commerce to open India Office.
- Development of ship-repair clusters at Kochi and Vadinar.
3. Defence Cooperation
- Emphasis on training exchanges to enhance mutual understanding.
- Satisfaction expressed over existing cooperation mechanisms and joint military exercises.
- Plans to formalize Coast Guard cooperation through a new MoU.
- Focus on co-production, co-development, and defence innovation.
Strategic Highlights
- PM Modi described Sheikh Hamdan’s visit as symbolizing “generational continuity” in India-UAE relations.
- The visit reaffirmed the India-UAE Comprehensive Strategic Partnership, with shared goals in technology, defence, energy, sports, education, and people-to-people ties.
- Crown Prince’s ceremonial welcome and guard of honour reflected India’s diplomatic priority on ties with the UAE.
- Sheikh Hamdan’s meeting with Piyush Goyal focused on the impact of the Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) on bilateral trade growth.
The visit marked a significant diplomatic milestone, advancing both geostrategic and economic cooperation between India and the UAE. The announcements are expected to catalyze new investments, defence manufacturing, and bilateral trade expansion, reinforcing India’s strategic presence in the Gulf region.
4. UNESCAP 2025 Report
Regional Economic Contribution
- Asia-Pacific accounted for 60% of global economic growth in 2024
Climate Impact Estimates
- At least 6% GDP loss annually projected for one-third of countries in the region
- Average Annual Loss (AAL) of 4.8% of GDP for 30 climate-exposed countries
Most Climate-Vulnerable Nations (11/30)
- Afghanistan
- Cambodia
- Iran
- Kazakhstan
- Laos
- Mongolia
- Myanmar
- Nepal
- Tajikistan
- Uzbekistan
- Vietnam
Root Causes of Climate Vulnerability
- Infrastructure gaps and poor climate resilience
- Agriculture-dependent economies
- Rapid and unregulated urbanisation
- Inadequate disaster risk governance
Major Climate Risks and Exposures
- Frequent floods, droughts, cyclones, and heatwaves
- High exposure in agriculture, energy, and coastal manufacturing
- Poorer countries lack climate finance and resilient public infrastructure
UNESCAP Policy Recommendations
- Proactive Fiscal Strategy: Redirect public investment to green and high-productivity sectors
- Climate-Smart Industrial Upgradation: Develop sustainable production models and green value chains
- Regional Green Transition Framework: Foster collaborative climate action between developing and developed nations
- Advanced Risk Tools: Use the ESCAP Risk and Resilience Portal to monitor climate-induced economic risks
National Affairs
1. Supreme Court Rebukes Tamil Nadu Governor for Unconstitutional Delay on Bills
Context:
In a landmark ruling, the Supreme Court of India strongly criticised Tamil Nadu Governor R.N. Ravi for his prolonged and unjustified inaction on ten legislative Bills. The Court declared his conduct not just inappropriate but “unconstitutional”, underlining the need for timely gubernatorial decisions under Article 200 of the Indian Constitution.
Key Takeaways
Sharp Rebuke from the Supreme Court
- The Court slammed the Governor for acting as a “roadblock” to democratic governance.
- His delay in processing Bills — and eventual referral to the President of India only after they were re-passed — was labelled constitutionally impermissible.
Final Verdict on the 10 Bills
- All 10 re-passed Bills are now considered to have received valid assent.
- The President’s subsequent actions — approval of 1, rejection of 7, and inaction on 2 — were declared null and void.
Mandated Timelines for Governors
- To curb future misuse, the Court has now set strict timelines:
- 1 to 3 months to act on any Bill presented for assent.
Redefining the Governor’s Role
- The Governor’s role must align with that of a “friend, guide, and philosopher”, not an obstructionist.
- Justice Pardiwala noted the current conduct stood in “stark contrast to constitutional expectations.”
Clarification of Article 200
- Under Article 200, a Governor has three clear options:
- Give assent
- Withhold assent
- Refer the Bill to the President
- Importantly, the phrase “as soon as possible” was interpreted to mean “without undue delay”, barring indefinite inaction or a “pocket veto”.
Notable Points
- Assent Must Follow Second Passage:
- If a Bill is reconsidered and passed again by the State Legislature, the Governor must grant assent.
- A maximum time limit of one month applies to the Governor for action after the Bill is reintroduced.
- No Presidential Referral in Second Round:
- The court ruled that referring the Bill to the President in the second instance is not permitted.
- The Governor must either grant assent or act as specified in the first proviso of Article 200.
- Governor’s Discretion Limited by Constitution:
- The phrase “shall not withhold assent” in Article 200 binds the Governor to accept the re-passed Bill.
- The removal of “in his discretion” from the Government of India Act, 1935 in Article 200 implies restricted gubernatorial discretion under the Constitution.
- Governor’s Action Not Bona Fide:
- The Court observed that the Tamil Nadu Governor’s action to reserve the Bill after withholding assent previously was not done in good faith.
Constitutional Interpretation:
- The first proviso to Article 200 explicitly restricts the Governor from acting independently once a Bill is re-passed.
- The ruling reasserts legislative authority in a federal structure, limiting the scope of executive interference.
Implications:
- Sets a precedent for Governor-State legislative relations, especially in politically tense situations.
- Reinforces that Governors are bound by constitutional obligations, not personal or political preferences.
- Prevents executive overreach that may hinder legislative processes in State Assemblies.
UPSC Mains PYQ
Discuss the essential conditions for exercise of the legislative powers by the Governor. Discuss the legality of re-promulgation of ordinances by the Governor without placing them before the Legislature. (UPSC-2022)
2. Police Misuse of Force in India
Context:
Despite India’s constitutional safeguards and procedural codes governing arrests and detentions, a culture of force and fear tactics persists within the police system. A 2025 survey by Lokniti-CSDS and Common Cause, involving 8,276 police personnel, provides revealing insights into police attitudes towards violence, mob justice, and due process.
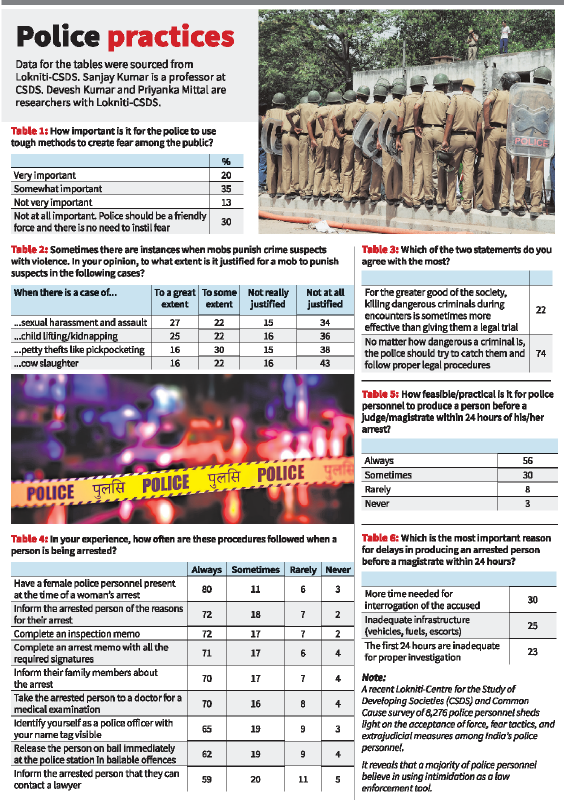
Key Survey Findings:
Endorsement of Intimidation as a Policing Tool
- 55% of police respondents believe instilling fear among citizens is important:
- 20% rated it as very important
- 35% considered it somewhat important
- Only 30% fully rejected the use of fear, supporting a friendly and service-oriented police force.
Alarming Acceptance of Vigilante Justice
- Mob violence justified by a significant portion of the police force:
- Sexual harassment/assault: 27% strongly justified
- Child kidnapping: 25% strongly justified
- Cow slaughter: 16% strongly justified; 22% partially justified
- Pickpocketing/chain-snatching: 16% strongly justified
- State-specific insights:
- Gujarat: 51% endorsed mob violence in cow slaughter cases
- Odisha: 32%
- Rajasthan: 31%
Split Opinions on Encounter Killings
- 74% of personnel prioritised legal procedure over extrajudicial killings
- However, 22% supported encounter killings when they serve the “greater good”, indicating a normalization of extralegal measures.
Gaps in Adherence to Legal Arrest Procedures
- 80% said a female officer was always present during a woman’s arrest
- 72% consistently:
- Informed the accused of arrest reasons
- Completed the inspection memo
- However, only 75% reported complete compliance with all procedures
- 10% admitted they rarely or never follow full procedures
Procedural Challenges: Judicial Presentation and Medical Exams
- Judicial Presentation:
- Only 56% found it always feasible to present arrested persons before a magistrate within 24 hours
- 30% cited a need for extended interrogation time
- 23% felt 24 hours was insufficient for investigations
- Medical Examination:
- 57% said it’s always practical
- About one-third admitted it’s only sometimes feasible
Implications:
- The data points to an institutional mindset that condones violence, undermines legal norms, and tolerates vigilantism under certain circumstances.
- Even when safeguards exist, practical enforcement is inconsistent due to resource constraints, investigative pressures, or cultural acceptance of brutality.
TH
3. Lodhi Garden
Context:
Delhi’s iconic Lodhi Garden celebrates its 89th anniversary this year. Known today as a serene urban oasis for morning walkers, couples, and cultural enthusiasts, its history stretches back centuries—through dynasties, colonial transformations, and post-independence evolution.
Historical Timeline & Transformations
Sultanate Era Origins
- Originally called Bagh-e-Jud, the site functioned as a pleasure garden during the Sayyid Dynasty.
- Its proximity to Hazrat Nizamuddin Auliya’s dargah made it a sacred spot for burials, particularly for those seeking closeness to the Sufi saint.
Burial Grounds of Rulers
- Houses tombs of rulers from both Sayyid and Lodi dynasties:
- Muhammad Shah’s Tomb (Sayyid Dynasty) – Oldest structure in the garden.
- Sikandar Lodi’s Octagonal Tomb, Sheesh Gumbad, and Bada Gumbad Mosque – All from the Lodi era.
- Khairpur Satpula bridge built by a noble in Akbar’s court.
Mughal Decline and Village Settlements
- With the decline of the Mughal Empire, displaced villagers began settling in and around the tombs.
- These settlements evolved into villages, such as Khairpur, with people living in makeshift homes within the heritage structures.
British-Era Redevelopment
- Lady Willingdon, wife of Viceroy Willingdon, envisioned turning the area into a landscaped park.
- Two villages were relocated to create the garden, named Lady Willingdon Park in 1940.
- Captain Young oversaw the resettlement of villagers to present-day Jangpura, originally known as Youngpura.
Post-Independence and Stein’s Vision
- Post-1947, the garden was renamed Lodhi Garden.
- American architect Joseph Allen Stein and his team, credited with transforming Lodhi Estate and building landmarks like the India International Centre, also landscaped the garden’s terrain — creating its now-famous slopes and natural flow.
- The area gained the nickname “Steinabad” due to Stein’s influence.
Present-Day Legacy
- A favorite of locals and tourists, Lodhi Garden remains an architectural, cultural, and ecological treasure in the heart of Delhi.
- With its blend of 14th-century tombs, 20th-century design, and modern-day utility, the garden exemplifies Delhi’s rich, layered history.
4. Amalsad Chikoo Gets GI Tag
Context:
The Amalsad Chikoo, named after the village of Amalsad in Gujarat’s Navsari district, has been granted a Geographical Indication (GI) tag, recognizing its unique identity, superior quality, and cultural connection to the region.
Issuing Authority
The GI tag has been awarded to the Valsad Navsari Jilla Fal Ane Shakbhaji Sahakari Sangh Ltd (Navsari District Fruit and Vegetables Co-operative), supported by:
- Gujarat Council on Science and Technology (GUJCOST)
- Navsari Agricultural University
- Under the guidance of the Department of Science and Technology (DST), Gujarat
Significance of the GI Tag
- Marks legal protection of the Amalsad Chikoo brand
- Enhances global market access for farmers
- Ensures better economic returns and value addition
- Recognizes traditional cultivation practices and superior product attributes
Amalsad Chikoo: Unique Features
- Known for its natural sweetness, smooth texture, and long shelf life
- Cultivated in 87 villages including:
- 51 villages in Gandevi Taluka
- 6 villages in Jalalpore Taluka
- 30 villages in Navsari Taluka
Gujarat’s Chikoo Landscape
- Gujarat contributes 98% of India’s chikoo exports
- Navsari district is the largest chikoo-producing region in the country
- Key export destinations include the UAE, UK, and Bahrain
Other GI-Tagged Fruits from Gujarat
- Gir Kesar Mango
- Kutchhi Kharek (Date)
- Now joined by Amalsad Chikoo as the third GI-tagged fruit from the state
Science & Tech
1. Genome India Project
Context:
The Genome India Project, a national initiative aimed at mapping the genetic diversity of India, has published its preliminary findings in Nature Genetics. This milestone marks a major step toward advancing precision medicine, disease diagnostics, and population-specific healthcare in India.
Key Highlights:
- Scope of Study:
- Genotyped 10,074 healthy and unrelated individuals from 85 populations (32 tribal and 53 non-tribal groups).
- After quality filters, the findings are based on 9,772 individuals (4,696 males and 5,076 females).
- Sample collection included nearly 20,000 individuals across the country.
- Data deposited in the Indian Biological Data Centre, Faridabad.
- Population Representation:
- Tribal Groups: Tibeto-Burman, Indo-European, Dravidian, Austro-Asiatic.
- Non-Tribal Groups: Tibeto-Burman, Indo-European, Dravidian.
- Each non-tribal group had a median of 159 samples, while tribal groups had 75 samples on average.
- Genetic Discoveries:
- 180 million genetic variants identified across the sampled genomes.
- Categories include:
- Disease-associated variants
- Rare and population-specific variants
- Variants unique to India
- Variants exclusive to small ethnic or tribal groups
- Medical & Research Implications:
- Findings pave the way for:
- Low-cost diagnostic tools
- Targeted therapies
- Customized drug response analysis
- Identification of adverse drug reaction genes
- Enables precision medicine in India, leveraging genetic diversity for personalized healthcare solutions.
- Findings pave the way for:
- Next Steps:
- Detailed analyses linking genome data with blood biochemistry and anthropometric information.
- A comprehensive research paper to follow in the coming months.
Significance of GenomeIndia Project:
- First-of-its-kind nationwide effort to capture genomic diversity of Indian populations.
- Essential for improving healthcare equity, addressing regional health disparities, and boosting biomedical research.
- Supports India’s efforts in global genomics and contributes to international datasets with India-specific data.
2. Quantum Supremacy Achieved Using a Simple Odd-Cycle Game
What is Quantum Supremacy?
Quantum supremacy refers to the point at which a quantum computer outperforms the best classical computers at a specific task, highlighting its unique computational advantage.
The Odd-Cycle Game Approach
In a landmark experiment, researchers from the University of Oxford and Universidad de Sevilla demonstrated quantum supremacy using a simple yet elegant task based on the odd-cycle graph colouring problem. Unlike previous approaches using highly complex problems (e.g., Google’s random circuit sampling), this method is intuitive, easily understandable, and verifiable.
Understanding the Problem:
- A circle with an odd number of points (e.g., 3, 5, 7…) must be coloured using two colours (blue and red).
- The rule: adjacent points must not have the same colour.
- Mathematically, this is impossible for an odd number of points.
Game Setup:
- Two players: Alice and Bob, who cannot communicate.
- A referee sends each player a question corresponding to a point on the circle.
- Win conditions:
- If the same point is asked, both must give the same colour.
- If adjacent points are asked, their colours must differ.
- Classical success rate: maxes out at 83.3% for 3-point circles.
Quantum Implementation:
- Two strontium atoms were separated by 2 meters and entangled using lasers.
- Entanglement allowed the players (Alice and Bob) to correlate their answers beyond classical limits.
- They performed angle-specific quantum operations on their respective atoms, depending on the referee’s question.
- Output: A binary measurement (0 or 1), mapped to colours.
Key Results:
- 101,000 games were played for circles ranging from 3 to 27 points.
- Achieved a 97.8% win rate, surpassing the classical ceiling.
- Demonstrated quantum supremacy for up to 19-point circles.
- The remaining 2.2% failure was attributed to noise in entanglement.
- Verified strongest quantum correlations ever recorded between two spatially separated particles.
Significance of the Research:
- Simplifies the demonstration of quantum supremacy, using only two qubits instead of complex multi-qubit systems like Google’s 53-qubit Sycamore.
- Makes verification easier and opens avenues for practical quantum protocols.
- Could be adapted to real-world problems like the rendezvous task, where communication is restricted and coordination is essential.
Quantum vs Classical in Real Scenarios:
- Example: In a search space of 1 million meeting points:
- Classical worst-case steps = 1 million.
- Quantum using Grover’s algorithm = ~1,000 steps.
3. Dire Wolf Reborn!
Context:
In a groundbreaking scientific feat, Colossal Biosciences, a Texas-based biotech startup, has claimed to bring back the legendary dire wolf—albeit not in its original form. The company has successfully engineered three genetically modified wolf pups—Romulus, Remus, and Khaleesi—that embody key traits of the extinct predator, last seen over 12,000 years ago.
De-Extinction Through CRISPR
- Ancient DNA was recovered from dire wolf fossils dating back 13,000–72,000 years.
- Using CRISPR gene-editing, Colossal introduced 20 precise edits across 14 genes in the embryos of modern gray wolves—focusing on traits like size, skull structure, muscle density, and coat texture.
- The embryos were implanted into domestic dog surrogates, leading to the birth of the three pups in early 2025.
What’s “Dire” About the New Wolves?
- The pups display physical traits reminiscent of dire wolves, such as a broader snout and more muscular frame.
- However, scientists note these are not pure dire wolves, but rather genetically altered proxies — gray wolves with carefully selected ancestral DNA.
Scientific and Ethical Crossroads
- Skepticism remains. Experts caution that the dire wolf genome remains only partially mapped, and the current outcome is more “dire-wolf inspired” than a full resurrection.
- No peer-reviewed evidence has yet been published, and the broader implications for ecosystems remain unclear.
- Ethical questions loom: Are we reviving species, or just creating designer animals?
Colossal Biosciences’ Larger Vision
- The company aims to restore lost biodiversity and rebalance ecosystems.
- Upcoming revival targets include the woolly mammoth, dodo, and Tasmanian tiger.
- Investors and public figures—including Tom Brady and Tiger Woods—have thrown support behind this Game of Thrones-esque venture into de-extinction.
Why It Matters
- The success of these dire wolf-like pups may pave the way for a new era in conservation biology.
- If regulated and scientifically validated, such efforts could one day help revive extinct ecosystems or even act as a buffer against biodiversity collapse.
Quick Facts for SEO
- What are dire wolves? Extinct apex predators from the Ice Age, popularized by Game of Thrones.
- Are they back? Not entirely, but scientists have recreated wolf pups that mimic them through gene editing.
- Who’s behind it? Colossal Biosciences, the same team working on mammoth de-extinction.
4. Globalstar Moves to Enter Indian Market with Apple’s Satellite Emergency Services
Context:
Globalstar, Apple’s satellite communication partner for its Emergency SOS feature on iPhones, has officially applied to enter the Indian market. The US-based company has submitted its application to IN-SPACe, India’s nodal space authorization body, marking the first step in a multi-stage regulatory process.
What Globalstar Plans to Offer in India
- Emergency SOS via Satellite: Allows iPhone users to send emergency messages and share GPS locations in areas with no cellular or Wi-Fi coverage.
- Enterprise Satellite Connectivity (Future Scope): May also offer services beyond consumer SOS, targeting businesses and remote industries.
Regulatory Process Underway
- Globalstar has applied to IN-SPACe to authorize its satellite constellation and operations in India.
- The company still needs a GMPCS license from the Department of Telecommunications (DoT) to gain spectrum access and set up earth station gateways.
- It has not yet filed for the GMPCS license.
India’s Growing Satellite Connectivity Market
- India’s satellite communication (satcom) sector is expected to grow from $2.3 billion in 2024 to $20 billion by 2028, per KPMG.
- Trai is finalizing recommendations on satellite spectrum pricing and allocation, which could influence entry timelines for multiple global players.
Market Context and Competitors
- Rivals like Eutelsat OneWeb and Reliance Jio have already received regulatory approvals.
- Applications from Starlink (Elon Musk) and Amazon Kuiper are pending.
- Apple’s limited market share in India may push Globalstar to partner with other smartphone makers and local service providers.
Strategic Importance
- Globalstar’s India entry could boost competition, attract global satellite investments, and accelerate telecom regulatory reforms, according to SatCom Industry Association (SIA-India).
- Their entry also aligns with India’s digital inclusion goals by enabling connectivity in remote and underserved areas.
Banking/Finance
1. Government May Set Up Oversight Panel for CoC Conduct in IBC Process
Context:
The Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) is considering the formation of an oversight committee to ensure stricter enforcement of the Code of Conduct for the Committee of Creditors (CoC) under the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC).
This follows a Supreme Court suggestion made during the Jet Airways liquidation case, where the court highlighted serious lapses in the insolvency resolution process.
Supreme Court Flags Gaps in IBC Framework
- In the Jet Airways judgment, the apex court termed the insolvency proceedings as an “eye-opener” that exposed significant deficiencies in the existing framework. The Court urged better enforcement mechanisms for CoC behavior, beyond self-regulation.
Current IBBI Guidelines and Their Limitations
In August 2024, the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (IBBI) introduced guidelines directing the CoC to:
- Maintain integrity, confidentiality, and objectivity
- Disclose any conflict of interest
- Stay updated on IBC provisions and regulations
However, the Supreme Court noted that these self-regulatory guidelines lacked enforceability and called for an independent enforcement mechanism potentially in the form of an oversight committee.
Background and Regulatory Push
- The Delhi High Court (Feb 2024) had earlier directed IBBI to draft a CoC code of conduct to enhance accountability while preserving the commercial wisdom principle.
- A 2021 discussion paper by IBBI laid the groundwork for these reforms.
Past Concerns About CoC Conduct The Sterling Biotech case highlighted CoC’s questionable actions:
- 90.32% of creditors approved a “one-time settlement” offer by absconding promoters.
- The NCLT criticized the CoC, stating that such conduct undermines commercial wisdom.
Banks Expected to Write Off ₹1.5 Trillion in FY26: ICRA
- Loan Write-Offs for Balance Sheet Cleanup
- According to ICRA, Indian commercial banks are likely to write off ₹1.51 trillion in bad loans during FY26 to improve balance sheet hygiene.
- Upward Revision in Credit Growth Projections
- Credit growth in FY26 is now expected to be 10.8–10.9%, amounting to ₹20.2 trillion.
- This is a revision from previous expectations of 9.7–10.3%.
- Credit expansion is estimated at ₹19–20.5 trillion, compared to ₹18 trillion (10.9%) in FY25.
- Monetary Easing and Impact on NIMs
- ICRA expects a cumulative 75 bps policy repo rate cut starting Feb 2025.
- This may cause Net Interest Margins (NIMs) to drop by 15–17 bps in FY26.
- While profitability may dip slightly, it is expected to stay at comfortable levels.
Key Data Points
| Metric | FY26 Estimate |
|---|---|
| Loan Write-Offs | ₹1.51 trillion |
| Credit Growth | 10.8–10.9% (~₹20.2 trillion) |
| Credit Expansion | ₹19–20.5 trillion |
| Repo Rate Cuts Expected | 75 basis points (from Feb 2025) |
| Drop in Bank NIMs | 15–17 basis points |
2. Shriram Finance Eyes RBI Primary Dealer Licence
Context:
Shriram Finance, one of India’s largest non-banking financial companies (NBFCs), is seeking a standalone Primary Dealer (PD) licence from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). If approved, it would mark a rare entry of an asset finance NBFC into the PD space, which has traditionally been dominated by banks and specialized institutions.
Primary Dealers are authorized to underwrite and support auctions of government securities (G-Secs), T-Bills, and Cash Management Bills.
Strategic Expansion by Shriram Finance
- Shriram Finance is looking to build expertise in trading government securities, leveraging its large investment book.
- The company recently acquired 100% equity in Shriram Overseas Investments (SOIPL) and appointed Umesh Revankar and Parag Sharma to SOIPL’s board.
- According to a source, the PD business is low-margin but carries virtually no risk, aligning well with Shriram’s strategy of diversification.
RBI’s PD Licensing Framework
- RBI has been selective in granting new PD licences.
- The PD system was introduced in 1995 and expanded in 2006–07 to include banks.
- Standalone PDs must be registered as NBFCs for at least one year prior to applying.
- PDs act as market-makers and merchant bankers to the Government of India for G-Sec issuances.
Significance
If successful, Shriram Finance would become one of the first asset finance NBFCs in recent years to secure a PD licence, marking a significant shift in its business strategy and a broader evolution in India’s fixed-income market structure.
3. Finance Ministry Notifies Form ITRB for Disclosure of Undisclosed Income Post Search Operations
Context:
- The Finance Ministry has notified Form ITRB via gazette, to be used by taxpayers for disclosing previously undisclosed income uncovered during income tax search or requisition operations conducted on or after September 1, 2024.
- This form is applicable under the block assessment process.
Key Features of Form ITRB
- Simplified Reporting: Unlike regular ITR forms, Form ITRB requires limited disclosures, focusing strictly on income related to the block assessment period.
- Designed to ease compliance burden while maintaining accuracy in reporting.
Understanding Block Assessment
- Block assessment is a special procedure used primarily during search and seizure operations to assess undisclosed income over a period of years.
- This is triggered when authorities find evidence of concealed or unreported income not declared in regular tax filings.
Tax Credit Provisions
- Form ITRB allows claim of TDS (Tax Deducted at Source) and TCS (Tax Collected at Source) against the disclosed income, offering partial relief to the assessee.
Significance
- The introduction of Form ITRB streamlines tax compliance following search operations and aligns with efforts to tighten enforcement against tax evasion while reducing procedural complexities.
4. Jio Finance Launches Fully Digital Loan Against Securities (LAS) Product
Context:
- Jio Finance, the NBFC arm of Jio Financial Services, has launched a fully digital Loan Against Securities (LAS) product.
- The offering allows customers to avail loans up to ₹1 crore, with interest rates starting at 9.99%, based on individual risk profiles.
Product Features
- Secured Loan Offering: Customers can pledge shares and mutual funds to access funds without liquidating long-term investments.
- Quick Processing: Entire application and disbursal process is digitized and completed in 10 minutes.
- Custom Interest Rates: Rates are tailored to borrower risk profiles, making the offering competitive and personalized.
Significance
- The LAS launch signals Jio Finance’s deepening push into digital lending, leveraging its tech infrastructure to offer fast, paperless, and scalable financial products.
- It positions Jio Finance as a competitive player in the growing fintech lending space, catering to investors seeking liquidity without disrupting their portfolio growth.
5. UPI Outages 2025
Why in News?
- The Unified Payments Interface (UPI) experienced multiple outages between March 26 and April 2, 2025.
- Disruptions impacted both banking apps and third-party UPI platforms, causing widespread transaction failures.
Root Causes Identified
- Telecom network fluctuations (ISP-related) disrupted UPI connectivity on March 26.
- A software-defined wide area network (SDWAN) glitch triggered another outage on April 2.
- Hardware malfunctions and bank-side transaction processing overload added to system instability.
- NPCI’s root-cause analysis led to hardware replacement and infrastructure updates to prevent recurrence.
Transaction Data and Impact
- On March 26, UPI success rates dropped to 50–60%, significantly below normal.
- UPI processed 550 million transactions, down 7% from 581 million the day before.
- March 2025 saw a record ₹24.77 trillion across 19.78 billion transactions, making disruptions more critical.
Infrastructure and Ecosystem Challenges
- UPI relies heavily on ISP-powered NPCI data centers, making it vulnerable to network disruptions.
- Banks’ server-side infrastructure is under strain due to surging transaction volumes.
- Fintech companies reported 50% transaction verification failure rates, affecting customer experience and reliability.
- March 31 outage was attributed to fiscal year-end activities at banks.
UPI’s Exponential Growth (FY25)
- Transaction value up by 30%: ₹260.56 trillion (vs ₹199.96 trillion in FY24)
- Transaction volume up by 42%: 131.14 billion (vs 92.48 billion in FY24)
- Over 80% of India’s digital payments are now processed via UPI, making resilience mission-critical.
6. India Pushes Rupee-Based Trade Settlement Amid US Tariffs
Context:
The Indian government has urged banks to promote rupee-based international trade settlements through the Special Rupee Vostro Account (SRVA) system. The move aims to enhance adoption of INR in global trade, especially in light of recent US tariff increases.
Background: US Tariffs Trigger Strategic Shift
- The United States has imposed a 26% tariff on Indian imports, effective April 9, 2025.
- In response, India is accelerating currency diversification in trade settlements to reduce dependence on the US dollar and cut forex transaction costs.
Infrastructure Enhancement: Infinet for Global Use
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is working to open up the Indian Financial Network (Infinet) — currently used for domestic interbank transfers — to international participants.
- This will enable secure fund transfers under the SRVA mechanism and facilitate faster cross-border settlements in INR.
Bilateral Agreements and Expansion
- India has already signed local currency settlement deals with the UAE, Indonesia, and the Maldives.
- More such bilateral agreements are in the pipeline to bolster rupee-based trade ecosystems.
Strategic Goals
- Boosting local currency use in trade will insulate India from global currency shocks and improve economic resilience during tariff wars.
- The government sees this as an opportunity for banks to leverage ongoing geopolitical shifts toward bilateral and multipolar trade frameworks.
Next Steps
- A stakeholder meeting involving the RBI and major banks is likely to be held later this month to address SRVA adoption hurdles.
- Discussions may focus on technical readiness, global bank integration, and compliance facilitation.
7. SEBI’s Overprotection
The Nanny Regulator’s New Avatar
- The article humorously dubs SEBI as “Mummy-SEBI”, likening the regulator’s approach to overprotective parenting.
- With a wave of new compliance rules, SEBI seems intent on shielding investors from themselves, even if it means sacrificing autonomy.
PAN Card? Not Enough Anymore
- Once, a PAN card was your golden ticket to market participation.
- Now, SEBI’s checklist includes an ECG, blood pressure logs, blood sugar readings, and a medical fitness certificate — all to prove you’re fit enough to trade.
Trading Meets Health Check-Ups
- Thinking of day trading? Better book an appointment with your doctor first.
- The piece jests that SEBI may soon demand pre-market and post-market BP checks, lest volatile markets send investors into a financial coma.
Insurance and Family NOCs: The Final Touches
- SEBI also seemingly wants your life insurance policy on record — because if your portfolio crashes, at least your family is covered.
- And yes, a No Objection Certificate (NOC) from your family is the cherry on top — making sure your “parivar” is fully aligned with your “reckless” decisions.
Tongue-in-Cheek Take on Overregulation
- Through biting satire, the article critiques SEBI’s increasingly interventionist stance, suggesting it strips away personal responsibility in the name of protection.
- The metaphor of SEBI as a Mai-Baap regulator pokes fun at a system that tries to parent adult investors.
TET
8. RBI’s OMO Sees Strong Demand
Context:
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) received ₹70,144 crore worth of bids in its second Open Market Operation (OMO) for FY26, more than 3.5x the notified amount of ₹20,000 crore.
- Investors showed robust interest due to relatively attractive bond pricing, nearing market rates, despite being at a slight discount.
Bond-Wise Demand and Cutoff Insights
- 7.23% 2039 bond (longest maturity):
- ₹6,401 crore accepted, the highest allocation in this round.
- 2034 bond:
- Saw multiple bids at identical cutoffs, leading to partial allotment — only 38.2% of bids were accepted.
- This indicates heightened competition among traders and institutions.
RBI’s Liquidity Management Strategy
- RBI has injected ₹6.6 lakh crore since December 2024 using:
- The April 2025 daily average liquidity is now in surplus mode (~₹1.7 lakh crore), reversing the January 2025 deficit (>₹3 lakh crore).
Forecast & Expected Measures
- Economists expect additional liquidity measures in H2 FY26:
- IDFC First Bank: Predicts ₹3–₹4 lakh crore infusion in FY26.
- Nomura: Anticipates fresh liquidity announcements as early as this week due to the RBI’s proactive approach.
9. ‘One State, One RRB’ Model
Context:
The Department of Financial Services under the Ministry of Finance has notified the merger of 26 Regional Rural Banks (RRBs) to streamline rural banking under the ‘One State, One RRB‘ strategy. This marks the fourth phase of RRB consolidation, aimed at improving efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and scale in rural banking operations.
Key Highlights
- RRBs Merged: 26
- States/UTs Affected: 11 states and 1 Union Territory
- Post-Merger Total RRBs: 28 (down from 43)
- Coverage: Over 22,000 branches across 700 districts
- Rural Focus: Around 92% of branches are in rural or semi-urban areas
- Effective Date: May 1, 2026
- Legal Basis: Section 23A(1) of the Regional Rural Banks Act, 1976
States Undergoing RRB Mergers
- Four RRBs Merged in Andhra Pradesh:
- Chaitanya Godavari Grameena Bank
- Andhra Pragathi Grameena Bank
- Saptagiri Grameena Bank
- Andhra Pradesh Grameena Vikas Bank
→ Merged Entity: Andhra Pradesh Grameena Bank
- Three RRBs Each Merged in:
- Uttar Pradesh
- West Bengal
- Two RRBs Merged in Each of the Following States:
- Bihar
- Gujarat
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Karnataka
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Odisha
- Rajasthan
Historical Context of RRB Consolidation
| Phase | Timeline | RRBs Reduced From | To |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phase 1 | FY06 – FY10 | 196 | 82 |
| Phase 2 | FY13 – FY15 | 82 | 56 |
| Phase 3 | FY19 – FY21 | 56 | 43 |
| Phase 4 | Effective May 1, 2026 | 43 | 28 |
Objectives of the Merger
- Enhance operational efficiency and scalability
- Enable cost rationalization through unified back-end systems
- Strengthen credit delivery in rural areas
- Reduce duplication of services across similar geographies
- Foster faster rollout of government welfare schemes
10. Bank of Baroda Launches ‘Square Drive’ FD Scheme
Context:
Bank of Baroda (BoB) has introduced a new fixed deposit scheme, dubbed the ‘bob Square Drive Deposit Scheme’, offering attractive interest rates up to 7.80% per annum. This move comes as part of BoB’s strategic shift to offer more competitive and flexible investment products in the current economic climate.
Key Highlights of the Square Drive FD Scheme:
- Effective Date: April 7, 2025
- Tenure: 444 days
- Interest Rates:
- General Citizens: 7.15% p.a.
- Senior Citizens (60+ years): 7.65% p.a. (0.50% extra)
- Super Senior Citizens (80+ years): 7.80% p.a. (0.15% extra over senior rate)
This scheme is ideal for conservative investors looking for secure returns over a short-to-mid-term horizon.
Utsav Deposit Scheme Discontinued
Simultaneously, BoB has withdrawn the Utsav Deposit Scheme, a festive-time offering, and made adjustments to existing FD rates across tenures to better reflect market dynamics.
Why it Matters:
- Investor Advantage: Higher returns for super senior citizens stand out among public sector banks.
- Market Relevance: Recalibrated rates align BoB more competitively with peers.
- Focus on Flexibility: A fixed tenure of 444 days offers planning clarity to depositors.
11. Piramal Finance Exits Housing Finance Segment; Transitions to NBFC-ICC Model
Context:
Piramal Finance Ltd. (PFL), formerly known as Piramal Capital & Housing Finance, has officially exited the housing finance business after surrendering its Housing Finance Company (HFC) license. This strategic move follows the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) granting it a new Certificate of Registration (CoR) on April 4, 2025, under Section 45 IA of the RBI Act, 1934.
Key Developments:
- New Certification:
- RBI has registered Piramal Finance as a Non-Banking Financial Company – Investment and Credit Company (NBFC-ICC).
- No Public Deposits:
- As per the new classification, Piramal Finance will not accept public deposits.
- Surrender of HFC License:
- Piramal Finance has voluntarily surrendered its Housing Finance CoR, marking a complete exit from the mortgage and housing loan sector.
Why It Matters
- Strategic Repositioning:
- This shift signals a deeper focus on investment, credit products, and structured lending, rather than retail housing loans.
- Regulatory Clarity:
- With RBI’s approval, PFL is now aligned under NBFC-ICC norms, offering more flexibility in non-housing lending operations.
- Implications for Borrowers & Investors:
Existing home loan customers may be transferred or serviced under different terms, while investors can expect realignment in PFL’s lending portfolio.
13. Niveshak Didi Initiative – Phase 2 (April 2025)
Context:
- Women-led financial literacy initiative for rural and semi-urban populations
- Aims to promote financial empowerment, digital banking, and fraud awareness
- Launched by the Investor Education and Protection Fund Authority (IEPFA) and India Post Payments Bank (IPPB)
Key Details
What is Niveshak Didi?
- A community-based financial education program
- Uses trained women influencers (postal workers) to educate underserved populations
Launch Timeline
- Phase 1: Rolled out in 2023
- Phase 2: Begins in April 2025
Partnering Entities
- IEPFA – Under Ministry of Corporate Affairs
- IPPB – Under Department of Posts, Ministry of Communications
Primary Objectives
- Raise financial literacy among rural women
- Teach safe saving habits, digital banking skills, and fraud protection
- Strengthen inclusive banking through paperless and cashless tools
Phase 2 Highlights
- 40,000+ women postal workers to be trained as “Niveshak Didis”
- 4,000+ new financial literacy camps in rural, semi-urban, and tribal areas
- Curriculum includes:
- Basics of savings and investments
- Digital banking tools via IPPB
- Cybersecurity and financial fraud prevention
Inclusivity and Reach
- Women-centric model: Over 60% of Phase 1 beneficiaries were rural women
- Delivered in 13 Indian languages to enhance vernacular digital inclusion
- Uses community trust and familiarity to drive engagement
Economy
1. Government Launches ₹22,919 Cr Electronics Component Manufacturing Scheme
Context:
Government Launches ₹22,919 Cr Electronics Component Manufacturing Scheme.
Objective and Scope
- Scheme Value: ₹22,919 crore
- Aim: Promote domestic manufacturing of:
- Electronic components
- Display modules
- Camera modules
- Non-surface mount devices
- Multilayer printed circuit boards (PCBs)
- Lithium-ion cells for digital applications
Operational Timeline
- Scheme to be operationalised within 2–3 weeks
- The Ministry of Electronics and IT will start accepting applications post notification
- Operational guidelines will be finalized after consultation with industry players
Key Features of the Scheme
- Duration: 6 years with an optional 1-year gestation period
- Application types: Both greenfield and brownfield projects eligible
- Segment-wise application: Companies must apply separately for each product category
Incentive Structure
- Turnover-based incentives:
- Based on net incremental sales over the base year for goods manufactured in India
- Capex-based incentives:
- Subject to investment thresholds and commercial production start
- Hybrid incentives: Combination of turnover and capex models available
Governance and Oversight
- Governing Council chaired by the IT Secretary
- Members from:
- Department of Expenditure
- Department of Economic Affairs
- DPIIT (Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade)
- Department of Telecommunications
- Ministry of Heavy Industries
- The Project Management Agency (PMA) will submit reports for application approval
Complementing India’s Electronics Manufacturing Vision
- This scheme is part of a three-tier strategy:
- Semiconductor manufacturing
- Component manufacturing
- Final product assembly (e.g., mobile phones, laptops)
- India has now moved from final goods to component manufacturing phase, as noted by Union Minister Ashwini Vaishnaw
Growth Statistics & Milestones
- Electronics production CAGR: 17%
- Electronics exports CAGR: 20%
- FY25 smartphone exports crossed ₹2 trillion, with ₹1.5 trillion from Apple’s iPhone exports
- Electronics exports rose 54% YoY, becoming one of India’s top export categories
BS
2. Rupee Falls Below 86 as Yuan Weakens and Dollar Demand Surges
Context:
The Indian rupee continued its decline on Tuesday, falling by 0.5% to close at ₹86.26 per US dollar, compared to Monday’s ₹85.86. The fall was largely attributed to:
- Weakness in the Chinese Yuan
- Strong demand for dollars by importers and oil companies
- Renewed foreign portfolio investor (FPI) outflows from Indian equities
On Monday, the rupee had already declined by 0.7%, reversing its year-to-date gains.
Yuan at 19-Month Low Amid US-China Trade Tensions
The Chinese Yuan dropped to 7.35 per USD, its lowest since September 2023, after signals emerged that the People’s Bank of China may allow further depreciation to offset the economic impact of U.S. tariffs.
- U.S. President Donald Trump’s threat of a 50% tariff on Chinese imports has reignited trade tensions.
- Investors are seeking safe-haven assets, further strengthening the US dollar.
Strength in US Dollar and Treasury Yields
The dollar index rose to 103.27 on Tuesday from 102.75 the previous day, supported by:
- Rising U.S. Treasury yields: 2-year and 10-year yields increased by 22–24 basis points
- Safe-haven demand amid global uncertainty
Oil Price Crash Fuels Importer Dollar Demand
Global oil prices have fallen to a four-year low, prompting Indian oil companies to ramp up dollar purchases to lock in cheaper prices, adding pressure on the rupee.
RBI Policy Decision Looms
- The rupee has depreciated by 0.8% so far in calendar year 2025.
- It is expected to stabilize around ₹85.50/$, though risks remain tilted to the downside.
Markets are closely watching the RBI Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) meeting. The central bank is expected to cut the repo rate by 25 bps to 6.00%, which could weigh further on the rupee.
Key Indicators
| Metric | Value/Change |
|---|---|
| Rupee Close (Tuesday) | ₹86.26/$ |
| Dollar Index | 103.27 (vs 102.75 Monday) |
| Yuan Level | 7.35/$ |
| Oil Prices | Four-year low |
| Rupee YTD Depreciation | 0.8% |
| Expected RBI Repo Cut | 25 bps (to 6.00%) |
Agriculture
1. Agri Founders Retreat 2025
Context:
The fourth edition of the Agri Founders Retreat was recently held at Chilika, Odisha, with 57 agricultural entrepreneurs from across India participating in the event. This edition followed earlier retreats in Nashik, Bengaluru, and Jaipur.
A Different Kind of Agri-Tech Meet
Unlike conventional conferences, the retreat deliberately excluded pitch decks, panel discussions, and networking rituals like business card exchanges. Instead, it offered a safe space for vulnerability, honesty, and collaboration, focusing on:
- Embracing failures and learning from struggles
- Co-creating solutions through peer-led discussions
- Building authentic connections in the agri-startup ecosystem
Diverse Participants The retreat saw a dynamic mix of entrepreneurs including:
- Bio-input innovators
- Aquaculture pioneers
- Climate-tech disruptors
- Goat farmers
- Soil health scientists This diversity of expertise brought rich perspectives to the dialogues.
Key Themes & Conversations Participants engaged in deep, sincere conversations around:
- Scaling challenges and startup pivots
- Funding barriers in agri-tech
- Climate-resilient agriculture
- Soil health management
- Chemical-free food systems
Significance
This retreat format is gaining traction as a transformative model for founder wellness, cross-disciplinary collaboration, and community-driven innovation in agriculture. It marks a shift away from competitive, investment-centric models to a human-first, ecosystem-centric approach.
Facts To Remember
1. Suruchi Singh wins air pistol gold
Suruchi Singh asserted her undisputed class as she defeated three Chinese, with a 2.4 point margin for the women’s air pistol gold, in the shooting World Cup in Buenos Aires.
2. India gets its first Grade-1 karting circuit as MIKA receives CIK-FIA certification
The Madras International Karting Arena (MIKA) in Sriperumbudur, near here, received the highly coveted CIK-FIA Grade-1 certification, thus placing the facility among elite karting circuits in the World.
3. ´One State, One RRB´ to be effective from May 1 2025
The Union government releaseda gazetted notification announcing the amalgamation of several Regional Rural Banks (RRBs) effective from May 1. In line with the powers granted under Section 23A(1) of the Regional Rural Banks Act, 1976, the notification stipulates that these RRBs will merge intoa single entity, inheriting their respective properties, powers, rights, obligations, and duties.
4. India´s first climate change station launched in J&K
Union Minister Dr Jitendra Singh launched India´s first highaltitude climate research station in Jammu and Kashmir´s Udhampur district on Tuesday and said that India is now at the forefront of climate forecasting and research in the Himalayas.
5. India, Slovakia sign two MoUs to cooperate in MSMEs & Foreign service
President Droupadi Murmu today discussed various aspects of bilateral relations and issues of shared global and regional interests with President Peter Pellegrini of the Slovak Republic during one-to-one meeting and delegation-level talks in Bratislava.
6. RBI cuts repo rate by 25 basis points, switches to accommodative stance to spur growth
Slashing policy rates for the second time in a row, the Monetary Policy Committee of the Reserve Bank of India today unanimously announced a reduction of 25 basis points in the policy repo rate, bringing it down to 6 percent.
7. RBI lowers GDP growth forecast to 6.5% for 2025-26
RBI has projected GDP growth for 2025-26 at 6.5 percent. RBI has said that this downward revision of its earlier assessment of 6.7 percent essentially reflects the impact of global trade and policy uncertainties.
8. CBDT notifies April 30 as last date to submit tax arrears declaration under Vivad se Vishwas Scheme
The Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT) has notified that the last date to submit a tax arrears declaration under the Direct Tax Vivad se Vishwas Scheme is the end of this month.
9. BIMSTEC Agriculture Ministers meet to discuss status, challenges, collaboration
The Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC) Agriculture Ministers-level meeting is taking place in Kathmandu today.

















