Context:
India’s literacy rate has reached 80.9% for individuals aged seven years and above, as reported in the Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) 2023–24. Despite this progress, significant disparities persist across gender and urban-rural lines.
National Overview
- Overall literacy rate (7+ years): 80.9%
- Overall literacy rate (5+ years): 79.7%
- Male literacy (7+ years): 87.2%
- Female literacy (7+ years): 74.6%
- Gender gap (7+ years): 12.6 percentage points
- Source: Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) 2023–24, released by NSSO, Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation.
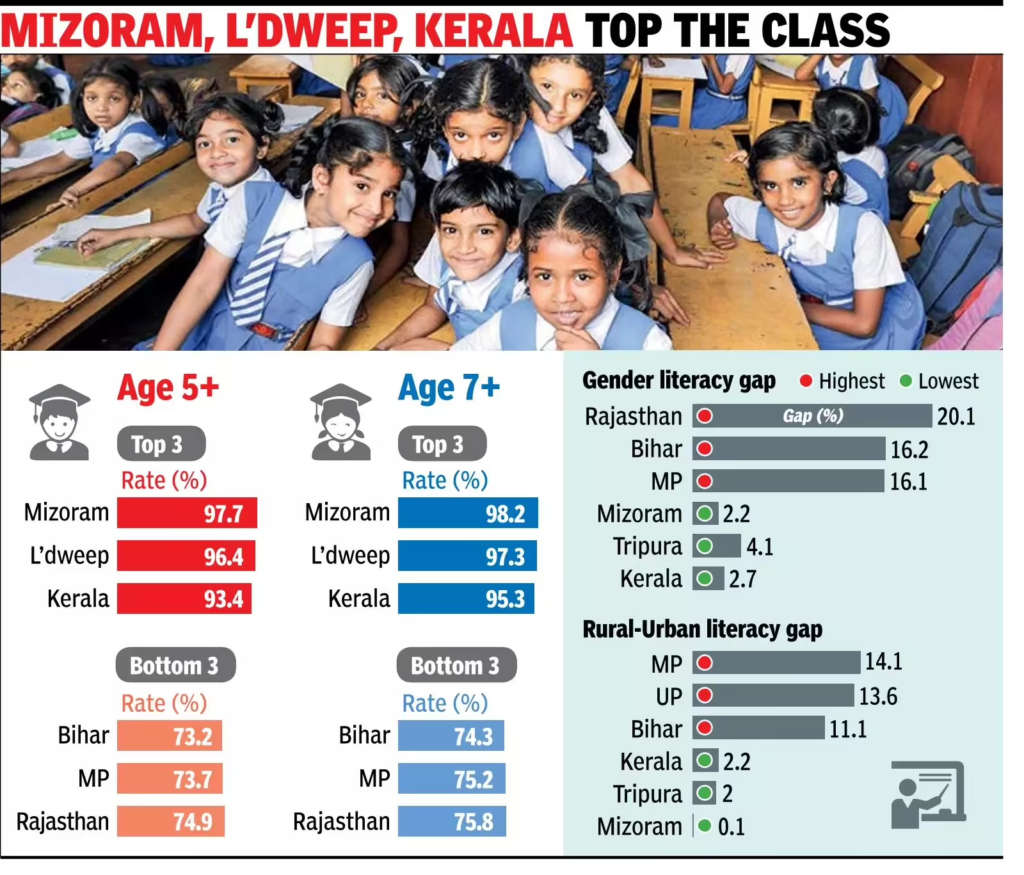
Top 5 States/UTs with Highest Literacy (7+ years)
| Rank | State/UT | Literacy Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Mizoram | 98.2 |
| 2 | Lakshadweep | 97.3 |
| 3 | Kerala | 95.3 |
| 4 | Tripura | 93.7 |
| 5 | Goa | 93.6 |
States with Lowest Literacy Rates (7+ years)
| Rank | State | Literacy Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Bihar | 74.3 |
| 2 | Madhya Pradesh | 75.2 |
| 3 | Rajasthan | 75.8 |
Urban-Rural Literacy Divide
- Urban literacy rate (7+ years): 88.9%
- Rural literacy rate (7+ years): 77.5%
- Significant urban-rural gaps:
- Madhya Pradesh: Rural 71.6%, Urban 85.7%
- Bihar: Rural 72.1%, Urban 83.2%
- Rajasthan: Rural 72.5%, Urban 84.7%
Gender Gap
- Highest gender gaps (7+ years):
- Rajasthan: 20.1% (M: 85.9%, F: 65.8%)
- Bihar: 16.2% (M: 82.3%, F: 66.1%)
- Madhya Pradesh: 16.1% (M: 83.1%, F: 67.0%)
- Rural gender gap examples:
- Rajasthan: M: 83.6%, F: 61.8%
- Bihar: M: 81.5%, F: 65.0%
- MP: M: 80.0%, F: 62.6%
- Best performers in gender parity:
- Mizoram: M: 99.2%, F: 97.0%
- Kerala: M: 96.7%, F: 94.0%
Key Observations
- Literacy rates are improving but disparities remain stark across regions, especially:
- In northern and central states
- Among tribal and rural populations
- Between genders
- States with higher educational infrastructure and outreach, such as Kerala and Mizoram, report minimal gaps.
















