Why in News?
Iran’s parliament, the Majlis, has reportedly approved the closure of the Strait of Hormuz in response to the attacks by the U.S. on Iranian nuclear facilities, the country’s state-owned media PressTV reported.
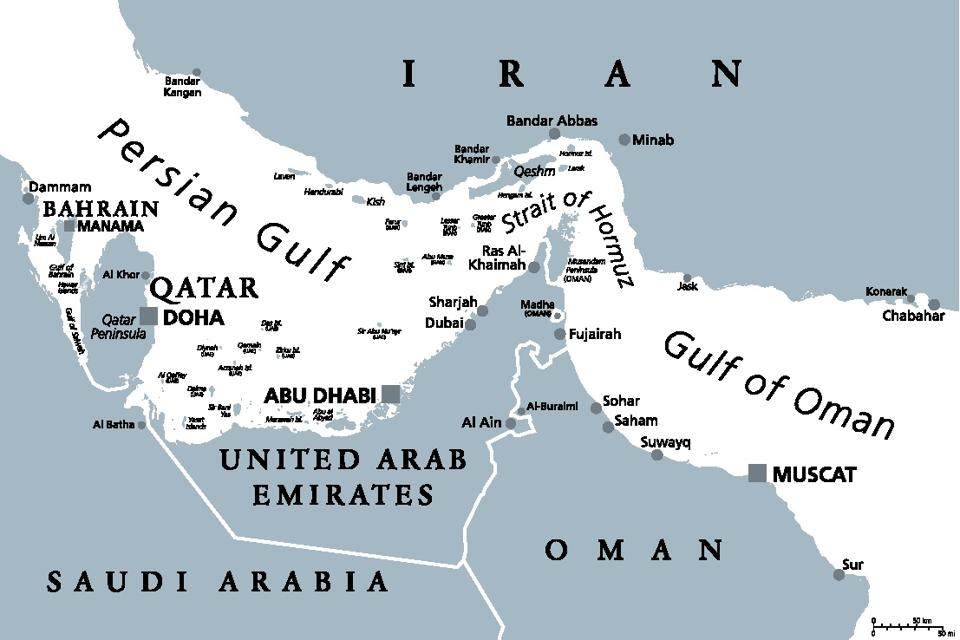
What is the Strait of Hormuz?
The Strait of Hormuz is one of the most strategically important maritime chokepoints in the world. Situated at the mouth of the Persian Gulf, it connects the Persian Gulf to the Gulf of Oman and the Arabian Sea, serving as a vital artery for global energy transport.
Geographical Significance
- Location: Lies between Iran (north) and Oman & the UAE (south).
- Width: Approximately 33 km wide at its narrowest point.
- Shipping Channel: Only 3 km wide in each direction for navigation.
Global Energy Lifeline
- Oil Transport: About 20% of all seaborne crude oil passes through the Strait.
- OPEC Dependence: Major oil exporters like Saudi Arabia, Iran, the UAE, Kuwait, and Iraq rely on this route.
- LNG Transit: Nearly all LNG exports from Qatar—the world’s largest LNG exporter—also pass through the Strait.
Alternate Routes & Strategic Moves
Due to the Strait’s vulnerability to geopolitical tensions:
- Saudi Arabia and the UAE have invested in alternate routes.
- This includes constructing oil pipelines that bypass the Strait of Hormuz, reducing dependency on this chokepoint.
Importance in Global Affairs
Any disruption to navigation in the Strait of Hormuz can:
- Impact global oil prices.
- Trigger military tensions, especially involving Iran and Western powers.
- Affect global energy security, making it a critical focal point in geopolitics.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. Which one of the following straits is nearest to the International Date Line? (2008)
(a) Malacca Strait
(b) Bering Strait
(c) Strait of Florida
(d) Strait of Gibraltar
Ans: (b)
















