Daily Current Affairs Quiz
1 October, 2025
National Affairs
1. India–EFTA Trade and Economic Partnership Agreement (TEPA)
Source: News on Air
Context:
The India–European Free Trade Association (EFTA) Trade and Economic Partnership Agreement (TEPA) came into effect on 1st October 2025. It is India’s first FTA with four developed European countries, promising $100 billion investments and 1 million jobs in the next 15 years.
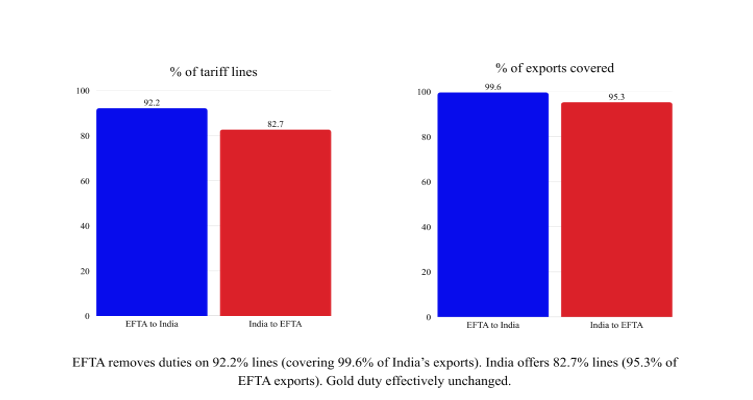
About TEPA
- What it is?
- A comprehensive Free Trade Agreement (FTA) between India and the European Free Trade Association (EFTA).
- First Indian FTA linking trade, investment, and job creation.
- Signed on:
- 10th March 2024 in New Delhi
- EFTA Members:
- Switzerland (India’s largest EFTA trade partner)
- Norway
- Iceland
- Liechtenstein
Key Features
| Key Area | Provisions / Highlights |
|---|---|
| 1. Investment & Employment | • $100 billion FDI commitment over 15 years • 1 million direct jobs in manufacturing & services |
| 2. Market Access for Goods | • EFTA offers zero-duty access on 92.2% tariff lines • Covers 99.6% of India’s exports |
| 3. Services & Mobility | • Commitments in 100+ sub-sectors (IT, education, audiovisual, business services) • Mutual Recognition Agreements (MRAs) in nursing, architecture, chartered accountancy • Facilitates: Mode 1 (Digital delivery), Mode 3 (Commercial presence), Mode 4 (Personnel mobility) |
| 4. Intellectual Property Rights (IPR) | • TRIPS+ standard with safeguards for generic medicines • Prevents patent evergreening while protecting innovation |
| 5. Sustainable Development | • Focus on green growth, social inclusion, and environmental protection • Encourages technology collaboration in renewable energy, precision engineering, and health sciences |
2. Dugong Conservation in India
Source: IE
Context:
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) has recognised Tamil Nadu’s Dugong Conservation Reserve in Palk Bay as a global model for marine biodiversity conservation during the IUCN World Conservation Congress 2025.
Key Highlights:
- First Dugong Reserve of India: Declared in September 2022 under the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972.
- Location & Size: Spread over 448.34 sq. km in northern Palk Bay, Tamil Nadu; includes 12,250 hectares of seagrass meadows.
- IUCN Recognition: Motion proposed by Omcar Foundation, supported by 98% of countries/agencies and 94.8% NGOs/research bodies.
- Species Focus: Dugongs (Dugong dugon), listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List.
- Ecological Role: Seagrass meadows provide feeding grounds, support biodiversity, and act as carbon sinks.
3. Female Labour Force Participation in India
Context:
The Female Labour Force Participation Rate (FLFPR) measures the share of women who are employed or actively seeking work. While India’s FLFPR fell from 31.2% in 2011-12 to 23.3% in 2017-18, it rose sharply to 41.7% in 2023-24, driven mainly by rural women.
Female Labour Force Participation Rate (FLFPR)
- Female Labour Force Participation Rate (FLFPR) is the proportion of women (aged 15 years and above) who are either employed (working) or actively seeking employment.
- It is a key indicator of gender equality, economic inclusion, and social progress.
Key Highlights:
| Dimension | Key Findings (2017-18 / 2018-19 vs 2023-24) |
|---|---|
| Earnings vs Participation | • Female Labour Force Participation Rate (FLFPR) rose, but real earnings declined for most women (except casual workers). • Increased participation ≠ better-paid or secure jobs. |
| Sectoral Composition | • Share of rural women in agriculture increased: 71.1% (2018-19) → 76.9% (2023-24). • Decline in women’s employment in secondary (industry) and tertiary (services) sectors. |
| Shift from Domestic Duties | • Women reporting domestic duties fell: 57.8% (2017-18) → 35.7% (2023-24). • Helpers in household enterprises: 9.1% → 19.6%. • Own account workers/employers: 4.5% → 14.6%. • Indicates shift mainly to self-employment, not wage employment. |
| Vulnerabilities | • Helpers in household enterprises often unpaid/low-paid, blurring line between employment & domestic labour. • Even among self-employed women, real earnings declined, showing persistent income insecurity. |
Banking/Finance
1. FPI Outflows from Indian Equities
Context:
Foreign Portfolio Investors (FPIs) withdrew ₹23,885 crore from Indian stocks in September 2025, marking the third consecutive month of net outflows, according to NSDL data.
What are Foreign Portfolio Investors (FPIs)?
- FPIs are investors (institutions, hedge funds, individuals) registered with SEBI who invest in Indian financial assets like:
- Stocks
- Bonds
- Mutual funds
- Investments are made in secondary markets and can be withdrawn quickly.
Characteristics
- Short-term & liquid investments.
- Highly sensitive to global interest rates, currency, and risk sentiment.
- Governed by SEBI FPI Regulations, 2019.
Impact of FPI Flows on Indian Market
- Outflows → Stock market correction, rupee depreciation, higher volatility.
- Inflows → Boost to equity valuations, liquidity, and investor confidence.
- FPIs hold ~16–18% of Indian market capitalization, making their flows crucial for market sentiment.
FPI vs FDI
| Feature | Foreign Portfolio Investment (FPI) | Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) |
|---|---|---|
| Nature | Investment in financial assets (stocks, bonds, etc.) | Investment in physical assets/companies (factories, infrastructure, JV) |
| Duration | Short-term, liquid | Long-term, stable |
| Control | No control over management | Provides management control/ownership |
| Volatility | Highly volatile (quick entry & exit) | Stable and less volatile |
| Regulation | SEBI (Securities market regulator) | DPIIT + RBI (FEMA guidelines) |
2. ADB Downgrades India’s Growth Outlook for FY26
Source: TH
Context:
The Asian Development Bank (ADB) has lowered India’s economic growth forecast for the current financial year (2025-26) to 6.5% from the earlier 6.7%, mainly due to the impact of 50% U.S. tariffs on imports from India. The growth outlook for 2026-27 has also been revised downward to 6.5% from 6.8%.
Key Highlights:
| Dimension | Key Highlights |
|---|---|
| Growth Forecast | • Developing Asia’s growth for 2025 revised: 4.9% → 4.8%. • 2026 forecast cut: 4.7% → 4.5%. • Downgrades due to global uncertainty, especially in India & Southeast Asia. |
| Impact of U.S. Tariffs | • Elevated tariffs cover ~60% of exports to the U.S. • Key affected sectors: textiles, garments, jewellery, shrimp, chemicals. • Likely to weigh on growth in H2 2025-26 and 2026-27. • Merchandise export growth modest, but services exports remain strong. • Investment growth subdued amid trade uncertainty. |
| Domestic Demand & Consumption | • Consumption demand expected to grow faster, aided by lower food prices and tax cuts. • Public investment continues to support growth momentum. |
| Inflation Outlook | • FY26 inflation revised down to 3.1% due to low oil & falling food prices. • FY27 inflation projected at 4.2% as food prices normalize. |
3. India’s Fiscal Deficit
Context:
The Centre’s fiscal deficit for April–August 2025 stood at 38.1% of the full-year Budget Estimate (BE), as per data released by the Controller General of Accounts (CGA).
What is Fiscal Deficit?
- The shortfall between the government’s total expenditure and total revenue (excluding borrowings).
- Formula:
Fiscal Deficit = Total Expenditure – (Revenue Receipts + Non-debt Capital Receipts) - It shows how much the government needs to borrow to finance its expenditure.
What to Do When Fiscal Deficit Occurs?
Governments adopt a mix of short-term financing measures and long-term structural reforms:
Short-term Financing (Bridging the Gap)
- Borrowings: From domestic market (bonds, securities) or foreign sources.
- Disinvestment: Selling govt stake in PSUs to raise capital.
- Use of Reserves: Dividend transfers from RBI/PSUs.
- External Aid/Loans: From multilateral institutions (World Bank, ADB, AIIB).
Long-term Structural Measures
- Boost Revenue:
- Widen tax base (GST, direct tax compliance).
- Improve non-tax revenues (dividends, fees, spectrum auctions).
- Rationalise Expenditure:
- Cut down subsidies/leakages.
- Better targeting via DBT (Direct Benefit Transfer).
- Prioritise productive capex over revenue expenditure.
- Reforms for Growth:
- Encourage FDI, FPI, private investment.
- Infrastructure push to boost GDP and tax collection.
Last Resort
- Monetisation of Deficit (RBI printing money) – Inflationary, avoided in normal times.
Types of Deficit
| Type of Deficit | Formula | Meaning | Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fiscal Deficit | Total Expenditure – (Revenue Receipts + Non-debt Capital Receipts) | Borrowing requirement of govt. | Indicates debt burden. |
| Revenue Deficit | Revenue Expenditure – Revenue Receipts | Govt borrowing to meet daily expenses. | Fiscal imprudence. |
| Primary Deficit | Fiscal Deficit – Interest Payments | Borrowings excluding past debt interest. | Shows fresh burden of current policies. |
| Effective Revenue Deficit | Revenue Deficit – Grants for capital creation | Refines revenue deficit by excluding productive transfers. | Used in Budget targets. |
| Monetised Deficit | Part of Fiscal Deficit financed by RBI printing new money | Direct monetisation of deficit. | Highly inflationary, rarely used now. |
4. RBI Launches Scheme to Activate Inoperative Accounts and Settle Unclaimed Deposits
Source: News on Air
Context:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has launched a one-year incentive scheme (October 2025 – September 2026) to encourage banks to reactivate inoperative accounts and repay unclaimed deposits to rightful claimants.
What is an Inoperative Account?
- A bank savings/current account that has had no customer-initiated transactions for 2 years (as per RBI guidelines).
- Balance remains but account is inactive until reactivated by the customer.
Key Highlights:
- Incentives for Banks:
- Banks will receive 5%–7.5% of amounts (up to ₹25,000) for:
- Reactivating inoperative accounts.
- Settling unclaimed deposits with legitimate owners.
- Payouts are linked to:
- Account age – older inoperative accounts may attract higher incentives.
- Deposit size – larger unclaimed amounts may receive proportionate rewards.
- Banks will receive 5%–7.5% of amounts (up to ₹25,000) for:
- Objective:
- Reduce the stock of dormant/inoperative accounts in the banking system.
- Ensure depositors receive their rightful funds, improving customer trust in banks.
5. SEBI Seeks Disclosures on Promoters’ In-Laws and Related Entities
Source: TOI
Context:
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has clarified that listed companies must disclose information about the relatives of promoters, including:
- Spouse’s parents
- Married children’s spouses and their parents
- Entities where these relatives hold over 20% shareholding, even if they do not own shares in the listed company
What is the New Proposal?
- Promoter-related disclosures to be expanded.
- Now, listed companies must also disclose relationships with:
- Promoters’ in-laws (beyond immediate family).
- Entities where such relatives hold beneficial interest or control.
Why is SEBI Doing This?
- Current loophole: Some promoters route money through relatives (like in-laws) or associated entities to avoid RPT scrutiny.
- SEBI wants to plug gaps and ensure all such transactions are reported to exchanges.
- Strengthens protection for minority shareholders.
Related-Party Transactions (RPTs)
- Any deal between a company and its related entities/individuals.
- Includes promoters, directors, relatives, and entities under their control.
- Must be disclosed and, in some cases, approved by shareholders.
6. RBI Governor to Chair New Payments Regulatory Board (PRB)
Source: IE
Context:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has constituted a six-member Payments Regulatory Board (PRB) to regulate payment systems in India. The board replaces the existing Board for Regulation and Supervision of Payment and Settlement Systems (BPSS).
Composition of PRB:
- Chair: RBI Governor Sanjay Malhotra
- RBI Members (3):
- Deputy Governor
- Executive Director in charge of Payment and Settlement Systems
- Governor
- Government Nominees (2):
- Secretary, Department of Financial Services (DFS)
- Secretary, Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY)
- Additional Member: Aruna Sundararajan, former MeitY secretary
- Permanent Invitee: RBI’s Principal Legal Adviser
Functions and Meetings:
- Regulates payment systems in India
- Will ordinarily meet at least twice a year
- Replaces BPSS, which had no government representatives and was a five-member body
Background:
- The move follows recommendations from an inter-ministerial committee headed by the Economic Affairs Secretary.
- The committee suggested amendments to the Payment and Settlement Systems Act, 2007 and proposed an independent regulatory board to handle payment-related issues.
7. RBI Raises Overseas Perpetual Debt Limit for Banks
Source: BS
Context:
The Indian central bank has raised the limit for perpetual debt that banks can raise overseas and use as part of their core capital, according to a circular
Key Highlights:
- Regulator: Reserve Bank of India (RBI) issued a circular allowing banks to raise perpetual debt overseas and include it in their core capital.
- Perpetual Debt: A type of debt without a fixed maturity date, often used by banks to strengthen capital buffers.
- Purpose: Eligible for inclusion in Additional Tier-1 (AT1) capital, which forms part of a bank’s core capital under Basel III norms.
- Additional Tier-1 (AT1) Capital: Additional Tier-1 (AT1) capital is a component of a bank’s regulatory capital that is perpetual in nature (no fixed maturity) and absorbs losses to help banks remain solvent during financial stress.
- It is part of the Tier-1 capital, which is considered core capital, along with Common Equity Tier-1 (CET1).
Updated Guidelines
- Limit for AT1 Inclusion: Banks can now include up to 1.5% of Risk-Weighted Assets (RWA) through perpetual debt.
- Risk-Weighted Assets (RWA): Risk-Weighted Assets (RWA) are a bank’s assets weighted by credit risk. They represent the total assets of a bank adjusted for the riskiness of each asset, rather than just the raw book value.
- Foreign Issuance: Debt issued in foreign currency or in Indian rupees overseas can now be fully counted towards the 1.5% AT1 limit.
- Earlier Norms: Previously, only less than half of the 1.5% AT1 limit could be raised overseas, the rest had to be domestic.
Significance
- Strengthens Bank Capital: Helps banks bolster their core capital to meet regulatory requirements.
- Flexibility: Provides banks with more leeway to raise funds globally, improving capital adequacy and liquidity.
- Cost Advantage: Overseas debt may offer competitive interest rates and access to a broader investor base.
8. PhonePe and Mastercard Launch Tap-and-Pay Feature
Source: BS
Context:
Fintech giant PhonePe and Mastercard have introduced a new feature allowing Mastercard cardholders to make in-store transactions via tap-and-pay using NFC-enabled smartphones.
Key Details:
- Mastercard users can tap their smartphones at NFC-enabled payment terminals to complete purchases.
- The feature also supports tokenised e-commerce transactions on NFC-capable Android smartphones.
- Cardholders can save their Mastercard credit, debit, and prepaid cards on their smartphones for seamless payments.
9. Major Rule Changes Effective from October 1, 2025
Source: ET
Context:
From October 1, 2025, several important regulatory and policy changes across banking, pensions, ticketing, and postal services will take effect. These changes aim to improve efficiency, enhance transparency, and provide greater flexibility to consumers.
Banking – Cheque Clearing
- What’s new? Cheque clearing moves from batch clearing to continuous clearing.
- Phased implementation:
- Phase 1: October 4, 2025 – January 2, 2026.
- Phase 2: Full roll-out after January 2, 2026.
- Impact: Faster settlement and reduced delay in fund transfers.
IRCTC Ticket Reservation
- New rules for general category online bookings.
- Aadhaar-based authentication mandatory in certain cases to prevent misuse.
- Impact: Reduces fraudulent and bulk ticket bookings.
NPS (National Pension System)
- 100% equity option allowed for non-government subscribers.
- Investors can maintain multiple schemes under one PRAN across different Central Recordkeeping Agencies (CRAs).
- Deadline: Government employees cannot switch from Unified Pension Scheme (UPS) to NPS after September 30, 2025.
- Impact: More flexibility, potentially higher returns for investors.
Banking Service Charges
- PNB, YES Bank, and others revising service charges.
- Affects locker rent, stop payment, nomination services, and standing instruction failure fees.
- Impact: Customers may face higher costs, need to check bank notifications.
Postal Services
- Speed Post tariff revision and new features.
- OTP-based delivery authentication and GST split shown separately in invoices.
- Impact: Better transparency and customer trust in India Post services.
10. RBI Raises Limit for Perpetual Debt in Banks’ Core Capital
Source: BS
Context:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has revised rules on perpetual debt inclusion in banks’ capital structure, allowing a higher share of such debt raised overseas to count towards Additional Tier-1 (AT1) capital.
What is Perpetual Debt?
- A type of debt instrument that has no maturity date.
- Banks pay interest (coupon) on it indefinitely, but principal is not repaid.
- Treated as quasi-equity in regulatory terms.
RBI’s New Guidelines
- Earlier Rule: Perpetual debt up to 1.5% of Risk-Weighted Assets (RWA) could be counted in AT1 capital, but less than half was allowed from foreign currency or rupee-denominated bonds issued overseas.
- New Rule (Sept 2025): Entire 1.5% of RWA can now be raised overseas, either in foreign currency or in rupees issued abroad.
- Impact: Gives banks more flexibility to access cheaper global funds.
Why It Matters
- Strengthens Core Capital: AT1 capital is part of banks’ Basel-III capital framework, critical for absorbing financial shocks.
- Diversified Funding: Reduces over-reliance on domestic markets, allowing banks to tap global investors.
- Boosts Lending Capacity: Higher capital adequacy means more room to expand credit.
Related Concepts
- Risk-Weighted Assets (RWA): Bank assets (like loans, investments) adjusted for risk levels; used to calculate minimum capital requirements.
- Additional Tier-1 (AT1) Capital: The core capital of banks, consisting of equity and perpetual instruments, used to absorb losses while the bank is still a going concern.
Agriculture
1. Farmer Suicides in India – NCRB 2023 Data
Source: TH
Context:
The National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) reported that 10,786 farmers and agricultural workers committed suicide in 2023. This continues a trend of over 10,000 farm sector suicides annually, highlighting ongoing distress in agriculture.
Key Highlights:
- State-wise Distribution:
- Maharashtra: 38.5% of cases (highest), especially Marathwada and Vidarbha cotton/soybean belts.
- Karnataka: 22.5%
- Andhra Pradesh: 8.6%
- Madhya Pradesh: 7.2%
- Tamil Nadu: 5.9%
- Several states reported no farm suicides: West Bengal, Bihar, Odisha, Jharkhand, Himachal Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh, Goa, Manipur, Mizoram, Nagaland, Tripura, Chandigarh, Delhi, Lakshadweep.
- Farmer vs Agricultural Worker Suicides:
- Farmers/Cultivators: 4,690 (4,553 male; 137 female)
- Agricultural Workers: 6,096 (5,433 male; 663 female)
- Farm sector suicides accounted for 6.3% of total suicides (1,71,418) in India in 2023.
- Causes & Concerns:
- Farmer organisations blame government policies, including the waiver of import duty on cotton, which could impact domestic cotton farmers.
- Marathwada and Vidarbha regions are particularly affected.
- Critics argue that trade agreements and imports from the U.S. threaten the livelihoods of smallholders.
2. AVPL Launches Tech Park to Indigenize Drone Components
Source: BL
Context:
AVPL Ltd (AITMC Ventures Limited International), an integrated agri-drone company, is looking at indigenizing the drone ecosystem in the country in league with component manufacturers, said Preet Sandhu, co-founder and Chairperson, AVPL Ltd.
Objective: To reduce dependence on imported drone parts, enhance supply chain resilience, and foster innovation in the agricultural drone industry.
Key Features of the Tech Park
- Location: Situated in a strategic area to facilitate research, development, and production activities.
- Facilities: Equipped with state-of-the-art laboratories, testing zones, and assembly lines for drone components.
- Focus Areas:
- Development of autonomous navigation systems.
- Creation of lightweight drone frames.
- Integration of AI-powered sensors for precision agriculture.
- Manufacturing of high-capacity batteries tailored for agricultural drones.
Potential Impact on Agriculture
- Enhanced Productivity: Drones equipped with advanced sensors can monitor crop health, optimize pesticide use, and improve irrigation efficiency.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Real-time data collection enables farmers to make informed decisions, leading to better yield and resource management.
- Sustainability: Precision agriculture practices promoted by drone technology contribute to sustainable farming by minimizing chemical usage and conserving water.
Facts To Remember
1. BJP leader V.K. Malhotra passes away at 93
Veteran Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) leader Vijay Kumar Malhotra, a five-time Lok Sabha member from Delhi, passed away on Tuesday morning after a brief illness. He was 93.
2. Sumit completes a hat-trick of titles with meet record
Sumit completes a hat-trick of titles with meet record with a season’s best of 72.35m, almost 25 metres more than the personal best of his closest competitor in the F64 javelin throw category, the two-time Paralympic champion and world record holder had only himself to beat on day four of the World Para Athletics.
3. Vinay wins trap bronze; Indian pairs make it a 1-2 in mixed air rifle
Vinay Pratap Chandrawat fought his way to the trap bronze, even as the Indian mixed air rifle teams clinched the gold and silver, in the Junior World Cup.
4. Srihari wins his fifth medal, Rohit claims silver in 50m butterfly
Star Indian swimmer Srihari Nataraj once again stood tall, bagging a bronze in the 100m freestyle to extend his personal haul to five medals at the 11th Asian aquatics championships.
5. Isha & Himanshu clinch 10m rifle gold
Indian shooters continued their winning run at the ISSF Junior World Cup by winning gold and silver at the Dr Karni Singh Shooting Range.
6. Nehra breaches 80m to claim javelin gold
Rishabh Nehra became India’s newest member of the 80m club as he grabbed the javelin gold at the National Open Athletics Championships in Ranchi.
7. Indian Railways to Launch First Container Service with Assured Transit Time
Indian Railways, in partnership with Container Corporation of India (CONCOR), will launch its first container train service with assured transit time on a pilot basis from October 1, 2025.
















