Daily Current Affairs Quiz
1 December, 2025
National Affairs
1. NITI Aayog’s Fiscal Health Index (FHI), 2025
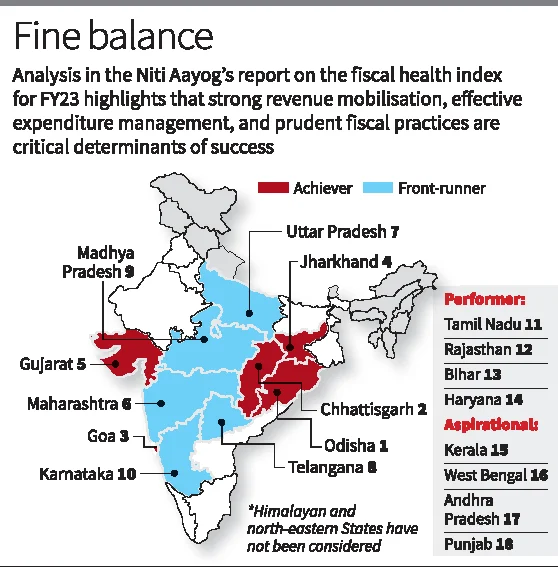
Purpose of the Report
The Fiscal Health Index (FHI) evaluates the fiscal performance of 18 major Indian states.
It focuses on key indicators such as contribution to GDP, public expenditure, revenues and fiscal stability to assess statelevel fiscal health.
Top Performing States Achievers
- States
- Odisha, Chhattisgarh, Goa and Jharkhand.
- Success Factors
- Strong capital investment up to 4% of Gross State Domestic Product or GSDP.
- Successful mobilization of non-tax revenue.
- Revenue surplus with low interest payment up to 7% of revenue receipts.
- Highest overall index score 678 for Odisha with a lead in debt index 990 and in debt sustainability at 640.
Front Runners
- States
- Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh ,Telangana, Madhya Pradesh and Karnataka.
- Strengths
- Developmental expenditure very high up to 73 percent.
- Own tax revenues growth has been consistent.
- Improved fiscal management and the debt to GSDP ratio 24 per cent.
Moderate Performers
- States
- Tamil Nadu, Bihar, Rajasthan and Haryana.
- These States have performed moderately but have areas of improvement in the parameter of debt and also on expenditure management.
Aspirational States
- States
- Punjab, Andhra Pradesh, West Bengal and Kerala.
- Challenges
- Low revenue mobilization and the fiscal deficits are high.
- Increasing debt burdens and bad debt sustainability.
- Quality of Expenditure and Debt management
- Quality of expenditure and debt management is a concern for the States of Kerala and Punjab. West Bengal has problems with revenue mobilization and debt index issues.
- Andhra Pradesh is plagued with a very high fiscal deficit.
- The debt profile of Haryana is bad.
Fiscal Health Index (FHI) 2025 – Methodology & Key Indicators
Data Sources & Scope
- Source: Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG)
- Period Covered:
- 2022-23 (for index calculation and analysis)
- 2014-15 to 2021-22 (historical trends provided in the report appendix)
Five Major Sub-Indices & Their Minor Sub-Indices
| Major Sub-Index | Minor Sub-Indices | Purpose & Insights |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Quality of Expenditure | 1.1 Total Developmental Expenditure / Total Expenditure | Measures proportion of budget spent on long-term economic growth & social services |
| 1.2 Total Capital Outlay / GSDP | Assesses how much of the state’s economic output is invested in infrastructure & long-term assets | |
| 2. Revenue Mobilisation | 2.1 State Own Revenue / GSDP | Indicates financial independence by measuring state-generated revenue vs. economic output |
| 2.2 State Own Revenue / Total Expenditure | Shows the extent to which the state’s expenditures are funded by its own revenue sources | |
| 3. Fiscal Prudence | 3.1 Gross Fiscal Deficit / GSDP | Evaluates borrowing levels relative to economic size, signaling potential debt sustainability concerns |
| 3.2 Revenue Deficit / GSDP | Highlights if the state is generating sufficient revenue to cover its operational costs | |
| 4. Debt Index | 4.1 Interest Payments / Revenue Receipts | Measures percentage of revenue receipts used for interest payments, assessing debt servicing capability |
| 4.2 Outstanding Liabilities / GSDP | Reflects overall debt burden in proportion to the state’s economic output | |
| 5. Debt Sustainability | 5.1 Growth Rate of GSDP – Growth Rate of Interest Payments | A positive gap suggests debt is manageable; a negative gap indicates fiscal stress |
Detailed Explanation of Key Indicators
1. Quality of Expenditure
- Developmental Expenditure: Spending on long-term economic growth & infrastructure (schools, hospitals, roads, etc.)
- Non-Developmental Expenditure: Routine government expenses like salaries and operational costs
- Key Ratios:
- Developmental Expenditure/Total Expenditure → Shows government’s spending priorities
- Capital Outlay/GSDP → Measures investment in infrastructure & long-term assets
2. Revenue Mobilisation
- State Own Revenue: Income from state taxes & non-tax revenue sources
- Key Ratios:
- State Own Revenue/GSDP → Reflects state’s financial self-sufficiency
- State Own Revenue/Total Expenditure → Measures the extent to which a state funds its own expenses
3. Fiscal Prudence
- Gross Fiscal Deficit: Gap between total expenditure & total revenue, indicating borrowing needs
- Revenue Deficit: When government income is insufficient to cover operational costs
- Key Ratios:
- Gross Fiscal Deficit/GSDP → High ratio signals unsustainable borrowing
- Revenue Deficit/GSDP → High ratio shows reliance on borrowing to fund basic expenses
4. Debt Index
- Key Ratios:
- Interest Payments/Revenue Receipts → High ratio means more revenue is spent on debt servicing, reducing funds for development
- Outstanding Liabilities/GSDP → Measures overall debt burden relative to state’s economy
5. Debt Sustainability
- Key Indicator:
- Growth Rate of GSDP – Growth Rate of Interest Payments → Positive gap shows healthy economic management; negative gap signals financial distress
Key Takeaways
- Higher rankings in FHI indicate strong fiscal health, sustainable debt, and efficient resource allocation.
- Lower rankings highlight high deficits, excessive borrowing, and poor revenue generation.
- Interstate disparities in expenditure quality, debt management, and revenue mobilisation underline the need for targeted fiscal reforms.
Importance of the Report
- For better understandings of state level fiscal policy and practice.
- Proves necessity in revamping revenue mobilization and debt management issues in states.
- It encourages achievers and frontrunners to continue and build upon fiscal discipline and developmental spending.
This report provides a guide for states to enhance the stability of their finances and efficiently use their resources to achieve sustainable economic growth.
2. World Social Protection Report (WSPR) 2024-26: ILO
Source: PIB
Context:
According to the International Labour Organization’s (ILO) World Social Protection Report 2024–26, India’s social protection coverage has increased from 24.4% in 2021 to 48.8% in 2024, marking a significant expansion in welfare reach. The report credits key government initiatives for extending benefits such as health insurance, pensions, employment support, and food security to millions of citizens.
As per the Ministry of Labour and Employment, nearly 920 million people (65% of the population) are now covered by at least one form of social protection through central government schemes. India’s progress has also contributed to a 5-percentage point rise in global social protection coverage, highlighting its international significance.
Overview of the ILO Report
- The World Social Protection Report is published periodically by the ILO, a UN agency focused on labour rights and social justice.
- The 2024–26 edition emphasizes universal social protection for climate action and a just transition.
- For the first time, it incorporates trend data and offers regional companion reports, including Asia-Pacific, detailing unique socio-economic and environmental conditions.
Key Government Initiatives Expanding Social Security
1. Ayushman Bharat (AB-PMJAY)
- As of March 26, 2025: 39.94 crore Ayushman Cards issued.
- Offers health coverage up to ₹5 lakh per family.
- Accessible at 24,810 empanelled hospitals nationwide.
2. Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana (PMGKAY)
- Provides free food grains to vulnerable populations.
- As of December 2024: 80.67 crore beneficiaries, close to the intended 81.35 crore.
3. eShram Portal
- Launched August 26, 2021 to create National Database of Unorganised Workers (NDUW).
- Offers Universal Account Number (UAN) for social security access.
- As of March 3, 2025: 30.68 crore unorganised workers registered, 53.68% women.
4. Atal Pension Yojana (APY)
- Launched May 9, 2015, targeting unorganised sector workers.
- Along with PMJJBY and PMSBY, strengthens social security.
- As of December 31, 2024: 7.25 crore enrolled with total corpus ₹43,369.98 crore.
5. Poverty Reduction Impact
- Over the past decade, 24.8 crore people have escaped multi-dimensional poverty due to social security measures.
Social Protection Data Pooling Exercise
- Launched March 19, 2025 by the Ministry of Labour & Employment.
- Aims to consolidate data across major central schemes to provide a holistic assessment of welfare coverage.
- Phase 1: Ten states targeted, including Uttar Pradesh, Rajasthan, Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Odisha, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Karnataka, Gujarat.
- Over 200 crore records processed using encrypted Aadhaar IDs across schemes like MGNREGA, EPFO, ESIC, APY, PM POSHAN.
- Collaboration with ILO ensures that housing, food security, and other in-kind benefits are incorporated in future evaluations.
Quick Takeaways
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Social protection coverage 2021 | 24.4% |
| Social protection coverage 2024 | 48.8% |
| People covered (2024) | 920 million (65% of population) |
| Key schemes | Ayushman Bharat, PMGKAY, eShram, APY, PMJJBY, PMSBY |
| Impact on poverty | 24.8 crore people escaped multi-dimensional poverty |
| Data pooling initiative | Phase 1 covering 10 states; 200 crore records processed |
| Global contribution | +5 percentage points in worldwide social protection coverage |
3. Asia Power Index 2025
Source: News on Air
Context:
In the 2025 Asia Power Index (API) published by the Australia-based Lowy Institute, India has been elevated from a “middle power” to a “major power”, ranking 3rd overall behind the United States and China. This milestone reflects India’s growing economic strength, military capability, and regional influence.
Key Highlights:
- Ranking & Major Power Status: India crosses the API-defined threshold for “major power” in 2025.
- Power Growth: Both India and China have improved across multiple metrics, but a significant gap remains between them.
- Scope of Assessment: The 7th edition of API evaluates 27 Asian countries/territories across 131 indicators in 8 thematic measures:
- Military Capability & Defence Networks
- Economic Capability & Relationships
- Diplomatic Influence
- Cultural Influence
- Resilience
- Future Resources
7–8. Other indicators assessing technology, governance, and soft power contributions
Strategic Implications
- India’s rise to a major power reflects growing economic clout, military strength, and diplomatic influence.
- The ranking enhances India’s geopolitical leverage in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Despite improvements, India still faces the challenge of converting capability into sustained influence at regional and global levels.
Banking/Finance
1. Crisil & AMFI Develop Market-Making Framework for AA–BBB Corporate Bonds
Source: FE
Context:
India’s corporate bond market is heavily skewed toward AAA-rated securities, leaving AA–BBB segments illiquid and unattractive despite their higher yields. To address this structural gap, Crisil and the Association of Mutual Funds in India (AMFI) are preparing a detailed proposal for a market-making framework for sub-AAA corporate bonds. The initiative aligns with consultations launched by the Department of Economic Affairs (DEA) under the Ministry of Finance.
Why a Market-Making Framework Is Needed
- About 66–67% of bond market trading is in AAA-rated securities.
- Nearly 33–34% involves AA-rated papers.
- BBB and other lower-rated segments see negligible trading, leading to low liquidity and high exit risk.
- MSMEs, mid-tier companies, NBFCs, HFCs, and startups—most of which do not enjoy AAA ratings—struggle to raise debt capital.
- A liquid market for AA–BBB bonds can unlock funding, reduce borrowing costs, and improve credit transmission.
DEA’s Proposed Models
The Department of Economic Affairs is reviewing two possible market-making structures:
1. Government-Backed Market Maker
- A government-sponsored entity will provide continuous two-way quotes (buy & sell).
- Ensures stability and market confidence.
- Useful for kick-starting liquidity in the AA–BBB space.
2. Private Entities as Market Makers
- Large institutions with high capital and net worth may act as market makers.
- Could be supported by a government backstop facility to mitigate risk.
- Encourages private sector innovation and competitive spreads.
What the Framework Will Cover
- Spread management for lower-rated papers
- Inventory handling rules for market makers
- Transparency and reporting norms
- Risk-mitigation safeguards to avoid concentration of exposure
- Mechanisms for price discovery in illiquid segments
Why This Matters?
According to industry participants:
For Investors
- Offers greater liquidity and better exit options.
- Encourages participation in higher-yielding sub-AAA bonds.
- Standardisation ensures better rate transmission and transparency.
For Issuers
- Expands access to debt financing, especially for:
- MSMEs
- NBFCs
- Housing finance companies
- Startups
- Reduces overdependence on AAA-dominated markets.
- Supports economic resilience by giving mid-tier companies new funding pathways.
Agriculture
1. Puducherry Launches NABARD-Supported Smart Farmer ID Cards
Source: PIB
Context:
On 27 November 2025, the Puducherry Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare Minister, Thiru K. Djeacoumar, launched Smart Farmer Identification Cards (SFIC) at the State Level Bankers’ Committee (SLBC) meeting. Supported by NABARD under its Farm Sector Promotion Fund, the initiative aims to digitize farmers’ records, streamline access to government schemes, and enhance transparency in agricultural financing.
Key Highlights:
- Launched By: Thiru K. Djeacoumar, Agriculture & Farmers’ Welfare Minister
- Supporting Agency: NABARD (Grant: ₹9.50 lakh)
- Program: AgriStack — part of India’s digital agriculture framework
- Attendance: Finance Secretary, Agriculture Secretary, NABARD GM, RBI GM, Indian Bank ED, senior officials, and farmers
About Smart Farmer ID Cards (SFIC)
- Format: QR code-enabled, replacing traditional booklet-style ID cards
- Purpose: Provides single digital identity for farmers
- Key Benefits:
- Availing crop loans, subsidies, and government schemes
- Authorized as valid alternative to traditional land documents
- Real-time verification and paperless transactions
- Prevents duplication and enhances transparency
- Enables future services like digital Kisan Credit Cards (KCC), crop insurance, and online benefit delivery
Significance
- Digital Agriculture: Supports India’s move towards paperless, transparent, and secure agricultural financing
- Farmer Empowerment: Simplifies access to loans, subsidies, and schemes
- Financial Inclusion: Reduces delays, ensures real-time verification, and prevents fraud
- Replication Potential: Serves as a model for other states
2. Saras Food Festival 2025
Source: News on Air
Context:
Union Minister for Rural Development and Panchayati Raj, Shivraj Singh Chouhan, will inaugurate the Saras Food Festival 2025 in Delhi. The festival showcases India’s diverse rural cuisine, women-led enterprises, and traditional food culture under the DAY-NRLM (Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana – National Rural Livelihoods Mission).
Key Objectives
- Promote rural entrepreneurship and women-led SHGs.
- Provide urban consumers access to authentic regional cuisines.
- Enable market linkages for SHG food businesses.
- Boost the visibility of traditional Indian foods and local ingredients.
Key Highlights:
- The Saras Food Festival brings together Self-Help Groups (SHGs) from various states to present regional dishes.
- Organised by the Ministry of Rural Development under DAY-NRLM.
- Venue: Delhi (specific location to be announced or covered in the event schedule).
- Participants: Women SHGs representing multiple states and UTs.
- Focus: Traditional recipes, local ingredients, millet-based dishes, tribal foods, and state-specific culinary varieties.
- The festival is expected to attract strong footfall from Delhi NCR, supporting rural livelihoods.
Facts To Remember
1. Indira Gandhi International Airport becomes first in India to achieve “water-positive” status
Indira Gandhi International Airport (IGIA) has become the first airport to achieve water positive status in the country with a capacity of more than 40 million passengers per annum.
2. India–ADB Sign Over $800 Million in Loans for Key Infrastructure & Skills Projects
The Government of India and the Asian Development Bank (ADB) signed three major loan agreements worth over $800 million, along with a $1 million Technical Assistance grant, to support infrastructure, renewable energy, metro rail development, and skills enhancement across Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, and Assam.
3. Government Sanctions ₹17 Crore Under PM Janjatiya Unnat Gram Abhiyan for Tribal Homestays and Development
Over 17 crore rupees have been approved under Pradhan Mantri Janjatiya Unnat Gram Abhiyan to provide funding support for development and renovation of Tribal Homestays and village community requirements.
4. 14th edition of India-Maldives bilateral exercise EKUVERIN to take place tomorrow in Kerala
The 14th edition of the annual India-Maldives bilateral exercise EKUVERIN is set to take place from tomorrow till the 15th of this month in Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala.
5. World AIDS Day
Health and Family Welfare Minister Jagat Prakash Nadda highlighted the need for greater understanding of HIV and AIDS on the occasion of World AIDS Day today.
6. India finishes strong at World Skills Asia Competition 2025, Secures 8th Rank in first-ever participation
India marked a significant milestone on the global skills stage by securing 8th rank in its first-ever participation at the World Skills Asia Competition 2025, competing against 29 nations.
7. Union Minister Piyush Goyal Inaugurates MP Krida Mahotsav for Divyang Children in Mumbai
Union Commerce and Industry Minister Piyush Goyal today inaugurated the MP Krida Mahotsav for divyang children at Borivali in North Mumbai.



















