Daily Current Affairs Quiz
11&12 January, 2026
National Affairs
1. Aditya-L1 Solar Mission ISRO
Context:
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) announced that its Aditya-L1 solar mission has provided crucial insights into how intense solar storms affect Earth’s magnetosphere, especially during extreme space-weather events.
Key findings of the study
- The most severe impacts occurred when the turbulent region of a solar storm struck Earth.
- This turbulence strongly compressed Earth’s magnetic field, pushing it unusually close to the planet.
- As a result, some geostationary orbit satellites were briefly exposed to harsh space conditions, a phenomenon seen only during severe space-weather events.
About the Mission
- Mission Type: India’s first dedicated solar observatory
- Launch Vehicle: PSLV-XL (Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle – XL configuration)
- Launched by: Indian Space Research Organisation
- Launch Date: September 2023
- Orbit: Halo orbit around L1 (Lagrange Point-1), ~1.5 million km from Earth towards the Sun
- Objective: Continuous observation of the Sun without Earth’s shadow
2. Regional Cooperation Agreement on Combating Piracy and Armed Robbery against Ships in Asia (ReCAAP)
Source: BS
Context:
India is set to deepen maritime security engagement in Asia through closer cooperation with Regional Cooperation Agreement on Combating Piracy and Armed Robbery against Ships in Asia (ReCAAP). The move aims to promote safe and secure seas amid evolving maritime security threats.
Key Developments
- India will enhance coordination with the ReCAAP Information Sharing Centre (ISC), based in Singapore.
- Greater cooperation is expected with India’s Maritime Rescue Coordination Centre (MRCC), which serves as the Indian Focal Point for ReCAAP.
About ReCAAP
- Established: 2006
- Members: 21 countries
- Headquarters: Singapore
- Nature: Government-to-government regional framework
- Objective:
- Combat piracy and armed robbery against ships
- Enhance maritime security and safety
- India is a founding member.
3. PSLV-C62 / EOS-N1 Mission
Source: ET
Context:
The 22.5-hour countdown has begun for the launch of PSLV-C62 / EOS-N1 mission from Sriharikota. Launch scheduled at 10:17 a.m. from the first launch pad.
Launch Details
- Launch vehicle: Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV)
- Mission name: PSLV-C62 / EOS-N1
- Variant: PSLV-DL
- PSLV flight number: 64th
- Total launches from Sriharikota: 105th
- Launch site: Satish Dhawan Space Centre
- Executing agency: Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)
Mission Nature
- Commercial mission executed through NewSpace India Limited (NSIL)
- Payloads:
- EOS-N1 (primary satellite): Injected into Sun Synchronous Orbit (SSO)
- 15 co-passenger satellites
- EOS-N1:
- Earth Observation Satellite
- Built for strategic purposes
4. Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS): India’s Space Station
Source: TOI
Context:
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has taken a formal step towards establishing India’s own space station by inviting Indian industry to develop the first module of the proposed Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS).
BAS-01 Module
- First operational module of India’s future space station
- To be placed in Low Earth Orbit (LEO)
- Scheduled for deployment by 2028
- Forms the first step towards a five-module space station by 2035
Key Features of Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS)
- Planned mass: ~20 tonnes
- Designed to host three astronauts
- Envisioned as a modular space station
- Intended to ensure sustained human presence in space
- Successor programme to Gaganyaan
5. Govt May Mandate Source Code Access for Smartphone Security
Source: TH
Context:
The Union government is considering mandating smartphone manufacturers to share source code and comply with new software security requirements. The proposal has triggered concerns from global tech firms such as Apple and Samsung, according to a Reuters report.
What is Proposed?
- Under the proposed Indian Telecom Security Assurance Requirements (ITSAR):
- Smartphone makers may be required to:
- Provide access to source code for security analysis
- Notify the government of major software updates
- Comply with a set of 83 security standards
- Smartphone makers may be required to:
- Objective:
- Enhance user data security
- Prevent online fraud, cyber breaches, and malware threats
6. AyulSat
Source: ET
Context:
India is a step closer to becoming the second country in the world to demonstrate on-orbit satellite refuelling, with the launch of AyulSat aboard PSLV-C62. The mission is led by Indian space start-up OrbitAid, in collaboration with Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).
What is AyulSat?
- Launched by: Indian Space Research Organisation
- Launch Vehicle: PSLV
- Mission Type: Technology Demonstration
- Satellite Mass: ~25 kg
- Developer: OrbitAid Aerospace
- Launch Date: January 2026
Mission Objective
- To demonstrate technologies critical for on-orbit servicing, including:
- Fuel transfer mechanisms in micro-gravity
- Satellite refuelling interfaces
- Propellant management in space
- Acts as a precursor mission for future in-orbit refuelling and satellite life-extension systems
7. TERI Report on India’s PV Manufacturing
Context:
The The Energy and Resources Institute (TERI) released the report “India’s PV Manufacturing & Its Strategic Inflection Points” at the Bharat Climate Forum 2026, alongside the launch of the National Cleantech Manufacturing Implementation Plan.
The report examines how India can capture higher domestic value from its rapidly expanding solar deployment by strengthening upstream and midstream manufacturing.
What the TERI Report Is About
It is a strategic policy-and-industry assessment of India’s solar photovoltaic (PV) manufacturing value chain, covering:
- Polysilicon
- Ingots and wafers
- Solar cells
- Solar modules
The report identifies “strategic inflection points” where targeted interventions in policy, finance, R&D, and skilling can make India globally competitive, resilient, and less import-dependent.
Key Trends Highlighted
| Theme | Key Highlights |
|---|---|
| Global Solar PV Scale (2024–25) | • Global cumulative PV capacity: ~2.2 TW (end-2024) • Global module manufacturing capacity: ~1.8 TW (projected end-2025) |
| Global Manufacturing Concentration | • ~80% of PV manufacturing capacity concentrated in China across the value chain |
| China’s Upstream Dominance | • Wafers: ~98% • Polysilicon: ~92% • Cells: ~91.8% • Modules: ~84.6% |
| Systemic Risks | • High geographic concentration creates supply-chain vulnerabilities • Energy-importing countries face risks from price shocks, export controls, and geopolitical disruptions |
| India’s Current Manufacturing Profile | • Manufacturing base is downstream-heavy • Dominated by module assembly, limited upstream integration |
| India’s Installed Capacity (FY2025) | • Module manufacturing capacity: ~120 GW per year |
| Policy Drivers of Scale-Up in India | • Production Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes • High import duties on finished solar panels • ALMM (Approved List of Models and Manufacturers) creating domestic demand-pull |
| India’s 2030 Manufacturing Ambition | • Module capacity: >280 GW/year • Cell capacity: ~171 GW/year (from ~30 GW currently) |
| Key Bottleneck: Finance | • Upstream segments are capital-intensive and high-risk • Limited access to low-cost, long-tenure finance |
| Proposed Financial Innovation (TERI) | • Issuance of sovereign Green PV Bonds • Objective: Lower borrowing costs and de-risk upstream investments |
| Need for a Full Manufacturing Ecosystem | • Solar Manufacturing Technology Parks • Dedicated PV–Semiconductor Skill Council • Structured recycling and circular economy frameworks |
| Stakeholder Involvement Required | • Central & State Governments • OEMs and developers • MSMEs • Financial institutions and long-term investors |
8. Indian Army Launches DIME Platform
Source: ET
Context:
On 8 January 2026, the Indian Army launched Depot Integration Management Edition (DIME), a new digital platform aimed at modernising and digitising military logistics management.
What is DIME?
DIME is a comprehensive digital logistics platform designed to provide commanders with real-time, data-driven visibility of spares, equipment, and inventory across the Army’s logistics chain.
Development Details
- Developed by: Indian Army and Bhaskaracharya National Institute for Space Applications and Geo-Informatics (BISAG-N)
- Ministry Involved: Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY)
Purpose of DIME
- Integrate inventory control, maintenance planning, and demand forecasting
- Enable faster and more informed decision-making by commanders
- Replace fragmented, manual logistics processes with a unified digital system
9. Indian Army Procures Solar-Powered MAPSS UAV
Context:
In January 2026, the Indian Army placed a Rs 168 crore order with NewSpace Research & Technologies (NRT) for the Medium Altitude Persistent Surveillance System (MAPSS) UAV. This marks the first deployment of solar-powered UAVs by the Indian Army, beyond battery-powered and tethered drones.
About MAPSS UAV
Indigenous Development
- Developed under the iDEX framework
- Reflects India’s push for Atmanirbhar defence technologies
Long Endurance Capability
- Solar-powered recharging enables persistent, long-duration flights
- Suitable for continuous Intelligence, Surveillance and Reconnaissance (ISR) missions
Operational Roles
- Border and area surveillance
- Electronic Intelligence (ELINT)
- Communications relay
- Artillery spotting and network extension
Advanced Mission Autonomy
- Capable of operating in GNSS-denied environments
- Reduces logistical dependence and enhances survivability in contested zones
Low Detectability
- Quiet electric propulsion
- Low thermal signature
- Minimises enemy detection risks
Banking/Finance
1. Bank of Baroda Gets RBI Approval to Set Up SPD Subsidiary
Source: BL
Context:
In January 2026, Bank of Baroda (BoB) received in-principle approval from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to switch from its existing Bank Primary Dealer (PD) business to a wholly-owned subsidiary for undertaking Standalone Primary Dealer (SPD) business.
This marks a key step in the strategic restructuring of Public Sector Banks (PSBs).
What Does the Approval Mean?
- BoB will hive off its PD activities from the bank’s balance sheet
- The new entity will operate as a Standalone Primary Dealer (SPD)
- Final setup is subject to other regulatory approvals
Regulatory Background and Policy Context
- The RBI introduced the Primary Dealer (PD) system in 1995 to deepen the Government Securities (G-Sec) market
- In 2006–07, banks were allowed to undertake PD business departmentally
- RBI has now encouraged clearer separation of risks by strengthening the SPD framework
RBI Liquidity Support to SPD
- RBI increased the aggregate Standing Liquidity Facility (SLF) limit for SPDs
- From Rs 10,000 crore to Rs 15,000 crore
- Effective from April 2, 2025
- Liquidity available at the prevailing repo rate
About Primary Dealers (PDs)
Primary Dealers are RBI-registered NBFCs that act as intermediaries in the Government Securities market, ensuring liquidity and smooth debt issuance.
Functions
- Buy government securities directly from RBI
- Underwrite and distribute G-Secs
- Provide liquidity through secondary market trading
Types of PDs in India
Bank PDs
- PD business conducted as a department within a commercial bank
Standalone Primary Dealers (SPDs)
- Either:
- Wholly-owned subsidiaries of banks, or
- NBFCs incorporated under the Companies Act
About Bank of Baroda
- MD & CEO: Dr. Debadatta Chand
- Headquarters: Vadodara, Gujarat
- Tagline: India’s International Bank
- Established: 1908
2. Skydo Gets RBI Authorization as PA-CB
Source: BL
Context:
On 9 January 2026, Skydo, a cross-border payments platform, received final authorization from the RBI to operate as a Payment Aggregator – Cross Border (PA-CB) entity.
What does a Payment Aggregator – Cross Border (PA-CB)?
- Aggregates and processes international inbound and outbound payments
- Enables Indian exporters, importers, MSMEs, freelancers, and platforms to receive or make foreign payments
- Acts as an intermediary between merchants and overseas buyers/payers
Why did RBI introduce PA-CB?
- To bring cross-border payment fintechs under a clear regulatory framework
- To enhance consumer protection, AML/CFT compliance, and transparency
- To ensure secure, traceable, and regulated forex transactions
What is a PA-CB License?
A PA-CB license allows an entity to:
- Collect payments from foreign customers
- Remit funds to Indian businesses
- Operate under full RBI regulatory oversight
About Skydo
- Founded: 2022
- Headquarters: Bengaluru, Karnataka
- Received in-principle RBI approval in 2025
- Focus: Building cross-border payment infrastructure for Indian businesses
3. Stricter KYC Norms for Crypto Exchanges in India
Source: ET
Context:
India has tightened Know Your Customer (KYC) and anti-money laundering (AML) norms for cryptocurrency exchanges. The move follows updated guidelines issued on January 8 by the Financial Intelligence Unit (FIU).
What has been mandated?
New KYC Requirements
Crypto exchanges must now mandatorily collect:
- PAN of the customer
- Selfie with liveness detection
- Geographical coordinates (latitude & longitude) of onboarding location
- Date & timestamp of onboarding
- IP address of the user
- Bank account verification using ‘penny-drop’ method
These form part of enhanced Client Due Diligence (CDD) norms.
Reporting & Compliance
- All crypto exchanges must:
- Register with FIU as “reporting entities”
- Submit regular reports on suspicious transactions
- Maintain customer transaction records
- The FIU functions under the Ministry of Finance.
Activities Restricted
The guidelines:
- Discourage Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) and Initial Token Offerings (ITOs)
- Prohibit facilitation of:
- Tumblers and mixers
- Anonymity-enhancing tokens
- Aim to curb:
- Money laundering
- Terrorist financing
- Proliferation financing
Legal Framework
- Crypto exchanges are regulated under the:
- Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA)
- Cryptocurrencies:
- Not legal tender in India
- Taxed under the Income-Tax Act
Background
- FIU first issued AML-CFT guidelines for crypto service providers in March 2023.
- The 2025 update strengthens surveillance and traceability amid rising crypto adoption.
4. MoRTH Proposes Amendments to the Motor Vehicles Act (MV Act)
Source: TNIE
Context:
The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH) has proposed amendments to the Motor Vehicles Act (MV Act) to:
- Curb uninsured vehicles
- Tighten driving licence (DL) norms
- Link insurance premiums with driver behaviour
Key Proposal: Behaviour-Based Insurance
Linking Premiums to Challan History
- Proposed amendment to Section 147 of the MV Act
- Empowers Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) to:
- Fix base insurance premiums and liabilities based on:
- Vehicle age
- Traffic violation (challan) history
- Fix base insurance premiums and liabilities based on:
Expanding Mandatory Third-Party Insurance
- Proposal to extend mandatory third-party insurance coverage to:
- Owner
- Driver
- Occupants of personal vehicles
- Currently mandatory only for:
- Commercial vehicles
- Aim:
- Increase insurance penetration
- Protect road users financially
- Issue highlighted:
- Large number of vehicles, especially two-wheelers, remain uninsured
Driving Licence (DL) Reforms Proposed
1. Renewal & Driving Test
- Amendment to Section 9 (Issuance & Renewal of DL)
- Proposal:
- Remove exemption from driving test during renewal if:
- Applicant has a poor challan history
- Remove exemption from driving test during renewal if:
- Current rule:
- No driving test required if renewal is sought within one year before licence expiry
2. Bar on Fresh Licence
- Proposal:
- No fresh DL for applicants whose licence was revoked in the last 3 years
- Objective:
- Improve road safety
- Deter habitual offenders
3. Graded Licence System
- Proposal to:
- Introduce graded eligibility for heavier/larger vehicles
- Based on:
- Driving experience
- Skill progression
- Similar to international best practices
4. Medical Fitness Norms
- Mandatory medical certificate age proposed to be raised:
- From 40 years → 60 years
- Applicable for:
- New DL issuance
- DL renewal
5. Regulatory Review Cell (RRC)
Context:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is preparing for wide-ranging regulatory reforms to modernise India’s financial architecture in line with Viksit Bharat 2047. These changes build on recent initiatives to simplify regulation, strengthen governance, and align credit flow with economic priorities.
Regulatory Review Cell (RRC)
The Regulatory Review Cell (RRC) is an institutional mechanism set up under the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH) to review, streamline, and rationalise regulations in the road transport and highways sector.
- Set up by RBI and housed in the Department of Regulation
- Operational from October 1, 2025
- Mandate:
- Comprehensive review of regulations every 5–7 years
- Remove obsolete rules (“regulatory spring-cleaning”)
Background
- Builds on Regulatory Review Authority (RRA 2.0)
- Over 400 circulars withdrawn
- Inspired by:
- Global central bank best practices
- Law Commission of India (96th Report, 1984) advocating periodic repeal of outdated laws
6. Integrated Ombudsman Scheme (IOS)
Source: BS
Context:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has launched a nationwide special campaign (Jan 1–Feb 28) to clear all pending customer grievances under the Integrated Ombudsman Scheme (IOS). The move signals a regulatory shift from rule-based compliance to consumer-centric governance.
Integrated Ombudsman Scheme (IOS)
The Integrated Ombudsman Scheme (IOS) is a single, unified grievance redressal mechanism introduced by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to resolve customer complaints against regulated financial entities.
What is IOS?
Launched in November 2021, the IOS merged and replaced multiple earlier ombudsman schemes into one common framework to simplify complaint filing and resolution.
Schemes merged under IOS
- Banking Ombudsman Scheme
- Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFC) Ombudsman Scheme
- Digital Transactions Ombudsman Scheme
Now governed by one authority, one process, and one portal
Who is covered?
Complaints can be filed against:
- Banks (public, private, foreign)
- NBFCs
- Payment system operators
- Digital payment service providers
- Credit institutions regulated by RBI
7. Small Finance Banks (SFBs)
Context:
A decade after the licensing of Small Finance Banks (SFBs), their performance is being reassessed in terms of financial inclusion, innovation, and differentiation from microfinance institutions (MFIs). The experience of SFBs is contrasted with the mixed outcomes of universal banks, local area banks (LABs), and payments banks.
Small Finance Banks (SFBs)
Small Finance Banks (SFBs) are specialised banks licensed by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to promote financial inclusion by providing basic banking services to unserved and underserved sections of society.
Key features
- Can accept deposits (savings, current, fixed)
- Can provide loans, especially small-ticket credit
- Required to focus at least 75% of Adjusted Net Bank Credit (ANBC) on priority sector lending
- Minimum 50% of loans must be of ₹25 lakh or less
- Subject to CRR, SLR, and prudential norms like other banks
Ownership & governance
- Promoter’s minimum initial stake: 40%
- Mandatory listing within 6 years of commencement
- Regulated fully by RBI under the Banking Regulation Act, 1949
Background: Why SFBs Were Introduced
RBI’s Original Vision (2014)
- Create small, locally rooted banks with:
- Strong regional focus
- Deep financial inclusion
- Technology-led, low-cost operations
- Target:
- Unserved and underserved populations
- Savings mobilisation + credit delivery
Key Regulatory Requirements
- 75% of Adjusted Net Bank Credit (ANBC) to priority sector
- 50% of loan book to consist of loans below ₹25 lakh
- Preference (not mandate) for operations in:
- North-East
- Eastern & Central India
Agriculture
1. Digital Agriculture Mission with AI
Source: Mint
Context:
- The Centre is considering a major expansion of the Digital Agriculture Mission (DAM) in the upcoming Union Budget.
- The proposed outlay is ₹7,500 crore for FY27–FY30, marking a 166% increase over the earlier allocation of ₹2,817 crore for FY22–FY26.
What is the Digital Agriculture Mission (DAM)?
- Launched in FY22 as a five-year mission
- Nodal ministry: Department of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare
- Objective:
- Build Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) for agriculture
- Enable AI-driven, real-time decision-making at farm and policy levels
Key Components of DAM
- AgriStack
- Unified digital database of farmers, land records and crops
- Krishi Decision Support System (KDSS)
- AI-enabled analytics for:
- Weather
- Crop stress
- Pest outbreaks
- Yield forecasting
- AI-enabled analytics for:
- Soil Fertility & Profile Maps
- Integrated soil health and nutrient datasets
- Remote Sensing & AI Tools
- Crop monitoring
- Early warning systems
2. Parasitic Weed Threatens India’s Mustard Crop
Source: IE
Context:
India’s mustard crop — the backbone of indigenous edible oil production — is facing a growing biotic threat from a parasitic weed, Orobanche aegyptiaca, prompting concerns over farm incomes, oilseed self-reliance and crop sustainability.
Why Mustard Matters
- Largest indigenous oilseed crop of India
- Cultivated on ~9 million hectares
- Key contributor to:
- Edible oil availability
- Import substitution
- Crop diversification in rabi season
- Central to India’s National Mission on Edible Oils–Oilseeds
The Weed: Orobanche aegyptiaca
Nature
- A root-parasitic weed
- Lacks chlorophyll → depends entirely on host plant
- Attaches to mustard roots underground
Why It Is Dangerous
- Damage begins before visible emergence
- Extracts:
- Water
- Nutrients
- Photosynthates
- Yield loss becomes irreversible by the time detection is possible
Persistence
- One plant produces 40,000–45,000 seeds
- Seeds remain viable in soil for up to 20 years
- Creates long-term soil infestation
Emerging Solutions
1. Herbicide-Tolerant Mustard Hybrids
- Enable selective weed control
- Allow use of specific herbicides without harming crop
- Being trialled by farmers in affected areas
2. Biotechnological Approaches
- Development of:
- Multi-herbicide resistant mustard lines
- Potential for:
- Precision weed control
- Reduced yield loss
3. Digitalisation of India’s Dairy Sector
Source: PIB
Context:
The National Dairy Development Board (NDDB) has achieved a major milestone by generating over 35.68 crore Pashu Aadhaar IDs, strengthening the digital backbone of India’s dairy ecosystem. This transformation is often described as the Second White Revolution, shifting focus from volume expansion to traceability, efficiency, quality assurance, and value addition.
What is Digitalising India’s Dairy Sector?
Digitalisation refers to the use of digital databases, automation, analytics, and IT platforms across the dairy value chain—from animal identification and breeding to milk procurement, payments, logistics, and exports. India, accounting for 25% of global milk production, is using digital tools to convert scale into sustainable farmer income and global competitiveness.
Importance of the Dairy Sector in India
- Rural Livelihood Security
Provides regular income to over 80 million rural households, especially in rain-fed regions.
Example: Dairying stabilises incomes in Vidarbha and Marathwada during crop failures. - Nutritional Security
Key source of protein, calcium, and micronutrients for a largely vegetarian population.
Example: Fortified milk under Mid-Day Meal and ICDS addresses Vitamin A and D deficiencies. - Economic Contribution
Contributes more to agricultural GDP than rice and wheat combined.
Example: Amul model showcases commercial scale and export potential. - Women Empowerment
Women manage most household dairy activities, strengthening financial independence.
Example: Women-led SHGs running milk collection centres in Odisha and Andhra Pradesh. - Inclusive Growth
Livestock ownership is widely distributed, unlike land.
Key Fact: About 75% of rural households with 2–4 animals drive India’s global dairy leadership.
Initiatives for Digitalisation
- National Digital Livestock Mission (NDLM):
Creation of the Bharat Pashudhan database covering breeding, health, and vaccination records. - Pashu Aadhaar:
12-digit unique identification for animals enabling traceability, disease surveillance, insurance, and credit linkage. - Automatic Milk Collection System (AMCS):
Digital fat/SNF testing with instant, transparent payments to farmers. - NDDB Dairy ERP (NDERP):
Open-source ERP (ERPNext) to manage the supply chain from procurement to consumer. - GIS-based Route Optimisation:
Reduces fuel costs, procurement time, and milk spoilage.
National Dairy Development Board (NDDB)
The National Dairy Development Board (NDDB) is a statutory body set up to promote, finance, and support the development of India’s dairy sector, with the objective of increasing milk production and improving rural livelihoods.
Background
- Established in 1965
- Headquarters: Anand, Gujarat
- Created under the National Dairy Development Board Act, 1987
4. Government Boosts Fertilizer Security
Source: PIB
Context:
India has achieved an all-time high fertilizer production of 524.62 lakh tonnes in 2025, meeting nearly 73% of its total fertilizer demand through domestic supply. This marks a major step towards strengthening fertilizer security and reducing vulnerability to global disruptions.
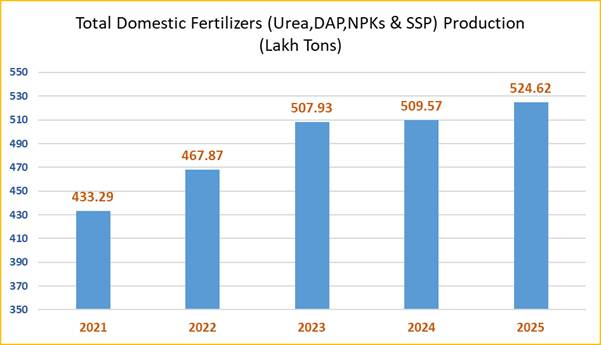
What is Fertilizer Security?
Fertilizer security refers to ensuring the timely, affordable, and uninterrupted availability of key fertilizers—Urea, DAP, NPKs, and SSP—to Indian farmers by:
- Reducing import dependence
- Expanding domestic production
- Securing raw material supply chains
It is a critical component of food security, farm productivity, and macroeconomic stability.
Facts To Remember
1. Women’s Hockey India League Final
In the Women’s Hockey India League (HIL) final held at the Marang Gomke Jaipal Singh Stadium Jharkhand, the title clash between Pipers and Shrachi Bengal Tigers went down to a third sudden-death encounter of the season.
2. Tarique Rahman named BNP chairperson
Tarique Rahman has been appointed chairperson of the Bangladesh Nationalist Party (BNP), days after the demise of his mother and former party chairperson Khaleda Zia.
3. Govt. launches drive to reduce road accident deaths
The Union Ministry of Road Transport and Highways, in collaboration with the NGO Save Life Foundation, has identified 100 districts with the highest number of road crashes to launch a data-driven zero-fatalities programme, in line with the government’s pledge to reduce road deaths by 50% by 2030.
4. Kerala women spikers retain title; Railways men triumph
It was mixed luck for Kerala in the 72nd senior National volleyball championships in Varanasi on Sunday. Defending champion Kerala women retained the title with a 22-25, 25-20, 25-15, 22-25, 15-8 win over Railways.
5. Third time lucky for Poland in United Cup
Poland battled past Switzerland 2-1 in the United Cup final on Sunday to banish the pain of title-round defeats in the previous two editions and secure a long-awaited maiden triumph in the season-opening mixed-team competition.
6. Indian Railways reigns supreme with twin titles
It was double delight for the Indian Railways at the 75th senior National basketball championship at the Nehru Indoor Stadium on Sunday.
7. Govt to Open ASI Monument Conservation to Private Sector
Context:
The Union government has decided to open the conservation of centrally protected ASI monuments to private sector participation under a revamped framework of the National Cultural Fund (NCF). The move introduces a public–private partnership (PPP) model aimed at strengthening heritage conservation capacity and reducing delays.
8. India’s rice exports surge in 2025 after lifting curbs
India’s rice exports rose 19.4% in 2025 to 21.55 million metric tonnes, the second-highest level on record, after the government lifted all export restrictions imposed earlier, according to officials cited by Reuters. Exports are now close to the 2022 record of 22.3 million tonnes, underscoring India’s dominance as the world’s largest rice exporter.
9. Nation pays homage to Swami Vivekananda on National Youth Day
The nation pays homage to Swami Vivekananda on National Youth Day today.
10. India to host 28th Conference of Speakers and Presiding Officers of Commonwealth
India will host the 28th Conference of Speakers and Presiding Officers of the Commonwealth (CSPOC) in New Delhi.
11. Union Minister Bhupender Yadav says PACS network gives India resilience against global economic crisis
Union Minister for Environment, Forest and Climate Change Bhupender Yadav today said that India’s strong network of Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS), comprising 32 crore people, provides the country with resilience against any global economic crisis.
12. India-Germany sign MoUs; defence, trade & technology, marking new chapter in bilateral relations
India and Germany have announced a wide range of initiatives spanning defence, trade, and technology, marking a new chapter in bilateral relations following a high-level meeting between Prime Minister Narendra Modi and German Chancellor Friedrich Merz in Gandhinagar.
13. Union Home Minister Amit Shah pays tribute to Rajmata Jijabai on her birth anniversary
Union Home Minister Amit Shah today paid tribute to Rajmata Jijabai on her birth anniversary.
14. Govt says fish production in country increased to 198 lakh tonnes in 2024-25 from 95 lakh tonnes in 2013-14
The government has said that the fish production in the country has increased to around 198 lakh tonnes in 2024-25 from 95 lakh tonnes of fish production in 2013-14.
15. Union Minister Ashwini Vaishnaw to participate in G7 Critical Minerals Ministerial Meeting today in Washington
Union Minister for Electronics and Information Technology Ashwini Vaishnaw will participate in the G7 Critical Minerals Ministerial Meeting today in Washington DC, United States.
16. PRAGATI platform marks 50th meeting, boosting pro-active governance since launch by PM Modi in 2015
The Prime Minister’s flagship platform for Pro-Active Governance and Timely Implementation, PRAGATI, has marked a significant milestone with the successful conduct of its 50th meeting.
17. Udyan Utsav: Celebration of Indian heritage, agriculture, sustainability & citizen engagement
Over a lakh people visited the second edition of the Udyan Utsav, hosted at Rashtrapati Nilayam, Bolarum, during the past 9 days.
18. Tunisian filmmaker Zoubeir Jlassi win world’s largest AI Film Award for his film Lily & receives one-million-dollar prize
Tunisian filmmaker Zoubeir Jlassi has won the world’s largest AI Film Award for his film Lily, receiving a one-million-dollar prize from Sheikha Latifa bint Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum during the 1 Billion Followers Summit in Dubai.
19. NHAI creates four Guinness World Records on Bengaluru–Kadapa–Vijayawada Economic Corridor
The National Highway Authority of India (NHAI) has successfully created four Guinness World Records on the under-implementation Bengaluru-Kadapa-Vijayawada Economic Corridor of NH-544G.
20. PM Modi Praises Shrimad Vijayaratna Sunder Surishwarji Maharaj on 500th Book Release
Prime Minister Narendra Modi has said that Shrimad Vijayaratna Sunder Surishwarji Maharaj has not confined knowledge to books alone.
















