
Introduction
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is the most advanced space observatory ever built, launched by NASA in collaboration with ESA (European Space Agency) and CSA (Canadian Space Agency). Often referred to as the successor to the Hubble Space Telescope, JWST aims to explore the universe’s earliest galaxies, star formation, exoplanets, and even alien atmospheres.
Key Facts at a Glance
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Name | James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) |
| Agencies | NASA, ESA, CSA |
| Launch Date | 25 December 2021 |
| Launch Vehicle | Ariane 5 rocket (from French Guiana) |
| Cost | Approx. $10 billion |
| Orbit | Halo orbit around Sun-Earth Lagrange Point 2 (L2) |
| Wavelength Range | Infrared (0.6 to 28.3 microns) |
| Successor to | Hubble Space Telescope |
| Main Mirror Diameter | 6.5 meters (compared to Hubble’s 2.4 meters) |
| Mission Duration (Expected) | Minimum 10 years |
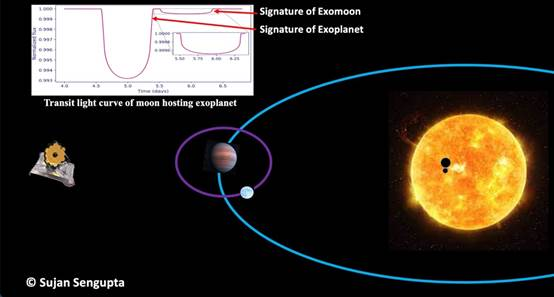
light curve.
The co-alignment or non-coalignment of the orbits of the planet and the moon are used as parameters (using two angular parameters), and they can be used to model all the possible orbital alignments for a star-planet-moon system. Using these generic models and the analysis of photometric transit light curves of exoplanets that is being obtained by JWST, a large number of exomoons can be detected in near future. According to the researchers, an exo-moon around a gas giant planet like Jupiter in the habitable zone of the host star where temperature is appropriate for water to exist in liquid state may harbour life. Under favourable alignment of moon-planet-star, such exomoon may also be detected by JWST. The research has been accepted for publication in The Astrophysical Journal, which is published by the American Astronomical Society (AAS).
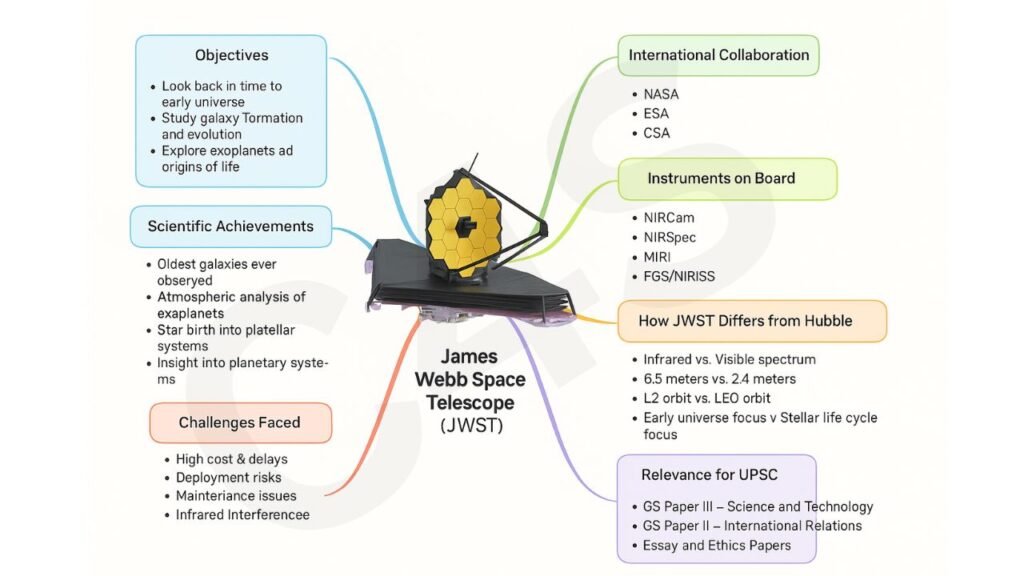
Objectives of JWST
JWST was designed with four major scientific goals:
- Look back in time to the early universe:
- Detect the first galaxies formed after the Big Bang.
- Study the Epoch of Reionization.
- Study galaxy formation and evolution:
- Understand the birth and growth of galaxies.
- Explore the life cycle of stars:
- Observe star formation and planetary systems.
- Investigate stellar nurseries obscured in visible light.
- Study exoplanets and origins of life:
- Analyze atmospheres of Earth-like exoplanets.
- Look for biosignatures and potential habitability.
Instruments on Board
JWST carries four main scientific instruments:
| Instrument | Full Form | Function |
|---|---|---|
| NIRCam | Near Infrared Camera | Captures high-resolution images in near-infrared. |
| NIRSpec | Near Infrared Spectrograph | Performs spectroscopy on up to 100 objects at once. |
| MIRI | Mid-Infrared Instrument | Observes colder, dustier objects and distant galaxies. |
| FGS/NIRISS | Fine Guidance Sensor/Near InfraRed Imager and Slitless Spectrograph | Ensures precise pointing and studies exoplanets. |
Scientific Achievements (as of 2025)
- Oldest galaxies ever observed:
- JWST detected galaxies that formed just 300 million years after the Big Bang, pushing back the observable timeline.
- Atmospheric analysis of exoplanets:
- Detected water vapor, carbon dioxide, and methane in exoplanet atmospheres.
- Star birth and stellar nurseries:
- Revealed breathtaking visuals of stellar nurseries like the Pillars of Creation in new light.
- Insight into planetary systems:
- Uncovered protoplanetary disks, aiding in understanding solar system formation.
International Collaboration
| Agency | Contribution |
|---|---|
| NASA | Lead developer and manager; provided spacecraft and launch services. |
| ESA | Provided launch vehicle (Ariane 5) and science instruments. |
| CSA | Provided Fine Guidance Sensor and scientific support. |
How JWST Differs from Hubble ?
| Parameter | Hubble Space Telescope | James Webb Space Telescope |
|---|---|---|
| Wavelength Range | Visible and ultraviolet | Infrared |
| Mirror Size | 2.4 meters | 6.5 meters |
| Orbit | Low Earth Orbit (LEO) | L2 (1.5 million km from Earth) |
| Main Focus | Stellar life cycle, galaxies | Early universe, exoplanets |
| Launch Year | 1990 | 2021 |
India’s Relevance
While India is not a direct participant, JWST:
- Inspires India’s own missions like Astrosat and upcoming XPoSat.
- Encourages global science partnerships.
- Offers learning for ISRO’s future infrared astronomy missions.
India’s Strategic Opportunity
While not a partner in JWST, India can:
| Opportunity | Description |
|---|---|
| ISRO Missions | Build upon JWST data to design better missions like Astrosat-2. |
| Scientific Diplomacy | Increase participation in global missions via policy dialogues and contributions. |
| Capacity Building | Train next-gen Indian astronomers and astrophysicists using JWST data. |
| Private Sector Role | Promote Indian space-tech firms in global value chains of instrumentation and data services. |
Application in Education, Research, and Policy
Academic and Research Potential
- Universities worldwide are integrating JWST findings into curricula.
- Encourages interdisciplinary research across astronomy, physics, chemistry, and data science.
- Promotes innovations in machine learning algorithms for interpreting cosmic data.
Policy and Global Space Governance
- Sparks discussions on:
- Sustainable space exploration
- Intellectual property in global missions
- Data sharing and open access in scientific missions
- Emphasizes the need for:
- Space treaties update
- International space traffic management
Challenges Faced
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| High Cost & Delays | Originally budgeted for $1 billion, ballooned to $10 billion with over a decade of delays. |
| Deployment Risks | Involved 300+ single-point failures; unfolded a tennis court-sized sunshield in space. |
| Maintenance Issues | Not serviceable due to its distant location at L2. |
| Infrared Interference | Requires extremely low temperatures (below 50K) to avoid interference. |
Conclusion
The James Webb Space Telescope represents the pinnacle of human innovation, scientific ambition, and international cooperation. By peering into the farthest corners of the universe, it not only rewrites cosmic history but also opens new chapters for philosophical and ethical debates on our place in the cosmos.
















