About
A watershed is an area of land where all the rainwater or melted snow flows to a common point like a river, lake, or ocean. Watershed management means protecting and restoring important natural resources such as soil, water, plants, and the environment in that area. To manage a watershed well, we first need to identify its problems and then make a plan. This process needs everyone’s involvement, including local people, the government, NGOs, and private organizations. The government has taken several steps for watershed development. One such step is a program under the Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayi Yojana (PMKSY). In its new version, PMKSY 2.0, a special activity called Springshed development was launched to tackle water shortages in hilly areas. There are also other efforts to build rainwater harvesting systems and save water by involving local communities. Examples include the Haryali Watershed Project and Neeru-Meeru in Andhra Pradesh.
Watershed management has helped protect the environment and improve people’s lives. But there are still some problems, like no clear laws and poor teamwork among different groups. These challenges can be solved by encouraging community participation and better governance.
Background
Watershed management in India has its roots in the country’s long tradition of conserving water. In the past, people in India used various traditional methods like stepwells, tanks (reservoirs), and old-style irrigation techniques to collect, store, and use water for farming and daily needs. However, in the 20th century, problems like water shortage, soil erosion, deforestation, and land damage started increasing due to rising population, more farming, and poor land use practices. In the 1950s, India began its first official watershed management programme called the ‘Community Development Program’, which focused on soil and water conservation. Later, in the 1980s, the Indian government started the ‘Watershed Development Project’. Over time, the approach to watershed management in India has shifted from being government-controlled to becoming more community-based and participatory.
Introduction
Watershed management is a complete and balanced method to protect and take care of natural resources like soil, water, plants, and the environment in a specific area called a watershed. It uses a mix of smart strategies to save water and soil, support eco-friendly farming and land use, and encourage community development. The main goals of watershed management are to solve water-related problems, reduce environmental damage, deal with climate change, and improve the lives of people living in that area.
What is a Watershed?
Watershed is a geographical area of land where all the surface water whether coming through rainfall or melting of snow drains to a common outlet point, such as a river, lake, or ocean. It is also known as a drainage basin or catchment area.
Characteristics of a Watershed
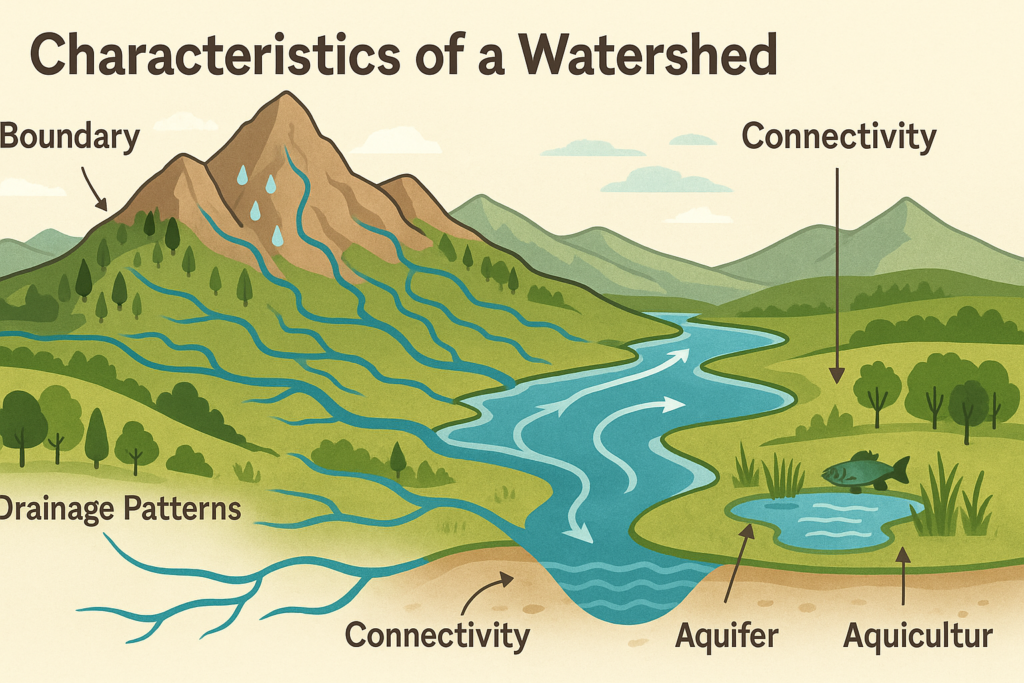
- Boundary:
- The boundary of a watershed is defined by ridgelines, hills, mountains or any other high points, where water flows in different directions.
- Drainage patterns:
- Water follows specific drainage patterns in a watershed with smaller streams and tributaries converging to form larger rivers and eventually flowing into a main water body, such as a lake or sea.
- Connectivity:
- All the water within a watershed is interconnected. Any activity in one part of the watershed impacts the water and land area downstream in other parts of the watershed.
- Role:
- Watersheds play an important role in the hydrological cycle. They regulate the flow of water, recharge the groundwater, and sustain the aquatic ecosystems.
Types of watershed: Watersheds are divided into 5 types based on the size
- Mini watershed:
- Watershed area is 1–100 hectares
- Micro watershed:
- Watershed area is 100–1000 hectares
- Milli-watershed:
- Watershed area is 1000–10,000 hectares
- Sub watershed:
- Watershed area is 10,000–50,000 hectares
- Macro watershed:
- Watershed area is more than 50,000 hectares
Watershed management: Watershed management is a comprehensive approach to manage and protect the natural resources in a specific geographical area of a watershed. It involves integrated planning, conservation of natural resources, and sustainable use of land, water, and vegetation. It works towards both protecting and enhancing the quality of natural resources like land and water.
Objectives of Watershed Management
- Water resource protection:
- Watershed management works towards the conservation of water resources and enhances its quantity, quality, and availability within the watershed.
- Soil conservation:
- It implements measures to prevent soil erosion, sedimentation, and degradation within the watershed. The watershed management works towards increasing the soil fertility and productivity through measures like contour ploughing, terracing, cover cropping, etc.
- Sustainable land use:
- Watershed management involves sustainable land use practices. To realise optimal productivity of land resources, many agriculture techniques like conservation agriculture, agroforestry, rotational grazing, and land-use planning are promoted within the watershed.
- Groundwater recharge:
- Increasing groundwater levels in the water-scarce areas is one of the major goals of the watershed management.
- Ecosystem restoration:
- Watershed management aims to restore and preserve the natural habitats, biodiversity, and ecological functions of watersheds.
- Community engagement:
- The planning in the watershed management involves the participation of local communities. It promotes the collaboration between local communities, government agencies, non-governmental organizations, and private sector entities for fostering local ownership, empowerment, and support for watershed management initiatives.
Principles of Watershed Management
- Holistic approach:
- Watershed management should take a holistic approach considering all aspects of the watershed, including water resources, soil conservation, forest management, and agriculture.
- Single system approach:
- Watershed management should be based on natural boundaries of the area rather than the political boundaries. Watershed should be treated as a single unit.
- Long-term perspective:
- The activities for watershed management should be developed with a long-term perspective to ensure the sustainable use of natural resources.
- Management of available resources:
- Watershed management involves the effective utilisation of available resources. For example, rainwater harvesting and effective irrigation practices.
- Sustainable development:
- Sustainable use of resources is one of the major principles of watershed management which involves the conservation of natural resources like water, soil, etc.
- Flexibility:
- Watershed management should have a flexible approach which means it should be adaptable to changing conditions and new information and able to modify the management practices accordingly.
- Social justice:
- Watershed management should work towards equitable distribution of benefits and resources among all sections of the community.
Procedure of Watershed Management
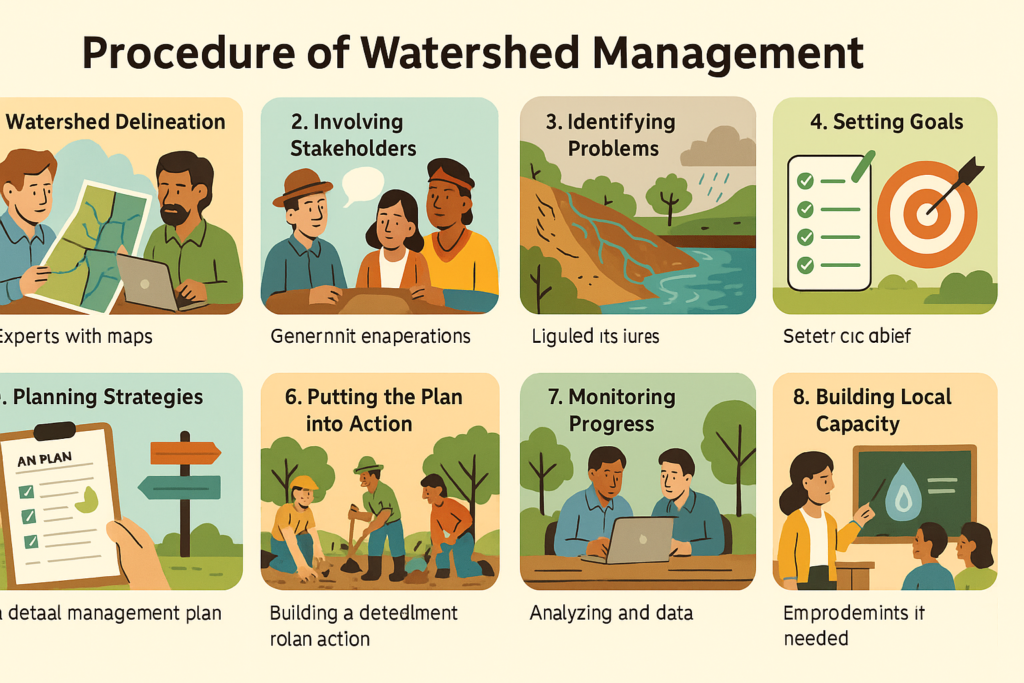
1. Watershed Delineation:
The first step in managing a watershed is to clearly identify and mark its boundaries. This is done using tools like GIS (Geographic Information Systems) and detailed maps. Experts study various features of the area such as land use, soil type, vegetation, water bodies, weather, population, and local activities to understand the watershed better.
2. Involving Stakeholders:
Once the area is understood, the next step is to bring in all the important people and groups — local communities, government departments, NGOs, private organizations, and even indigenous groups. They come together through meetings and discussions to plan and contribute to the management process.
3. Identifying Problems:
With everyone’s input, the real issues in the watershed are identified. These could include things like lack of water, soil erosion, pollution, or deforestation. This joint problem identification helps focus on the most urgent environmental challenges.
4. Setting Goals:
Based on the problems found, clear and realistic goals are set. These goals guide all the future actions and plans for managing the watershed.
5. Planning Strategies:
A detailed management plan is created. It outlines what needs to be done, how it will be done, and who will do it. This plan includes specific actions and solutions to reach the set goals.
6. Putting the Plan into Action:
Once the plan is ready, it’s implemented with the help of available resources, partnerships, and teamwork among all involved groups.
7. Monitoring Progress:
To make sure everything is going according to plan, regular checks and assessments are carried out. This helps track the success of the actions and make improvements if needed.
8. Building Local Capacity:
Training, education, and awareness programs are run to equip local people with the skills and knowledge they need. This enables them to take an active role in managing the watershed and improving the use of natural resources like water and soil.
Government Initiatives for Watershed Management in India
1. Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayi Yojana (PMKSY), 2015
(Earlier known as Integrated Watershed Management Program – IWMP, launched in 2009)

The Government of India started the Integrated Watershed Management Program (IWMP) in 2009 as a Centrally Sponsored Scheme. It was earlier known as the Watershed Development Project, and today, it is part of the larger Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayi Yojana (PMKSY), launched in 2015.
- Who implements it?
The scheme is carried out by the Department of Land Resources under the Ministry of Rural Development. - What is the goal?
The main aim is to protect and restore degraded natural resources like soil, water, and vegetation. This is done by:- Preventing soil erosion
- Collecting rainwater
- Recharging groundwater
- Promoting modern farming techniques
The overall aim is to help rural communities earn a stable livelihood through better resource management.
- Target by 2027:
To cover 55 million hectares of rain-fed land (land that depends on rainfall for irrigation). - Global recognition:
According to a World Bank report (2014), this is the second-largest watershed development program in the world, after China’s. - Funding model:
The cost of the project is shared in a 90:10 ratio between the central government and the state governments. - Program merger:
In 2015, IWMP was merged into PMKSY along with two other schemes:- Accelerated Irrigation Benefit Programme (AIBP)
- On-Farm Water Management (OFWM)
PMKSY 1.0 (Till 2022) – Key Achievements:
- Groundwater level improved by up to 3 meters.
- Cultivated land area increased by 30%.
- Farmers’ income in watershed areas grew by 70%.
- Cropping intensity (growing more than one crop in a year) rose by 18%.
PMKSY 2.0 (From 2021 onwards):
- A new initiative called ‘Springshed development’ was introduced, focusing on the Himalayan states.
- It aims to tackle water scarcity during dry seasons by reviving natural springs.
- It will also help solve problems like landslides and ecological degradation in the fragile Himalayan ecosystem.
2. Micro Watershed Development Projects

Micro watershed development projects are efforts aimed at the sustainable management and conservation of natural resources in small, defined geographic areas, called micro watersheds. These projects are mostly taken up in arid or semi-arid regions of India that are vulnerable to drought and water scarcity.
These projects use various conservation techniques, such as:
- Rainwater harvesting structures
- Contour bunds
- Trenches
- Groundwater recharge structures (like percolation tanks, dug wells, and check dams)
Some important micro watershed development projects in India:
Drought Prone Area Programme (DPAP)
- Started in: 1973
- Purpose: To deal with drought and water scarcity in arid and semi-arid regions of India.
- Activities include:
- Watershed interventions to retain soil moisture
- Recharging groundwater
- Increasing farm productivity in drought-affected areas
Desert Development Programme (DDP)
- Started in: 1995
- Purpose: To address desertification and land degradation in arid/semi-arid regions.
- Targeted Areas:
- Hot desert states like Rajasthan, Gujarat, Haryana
- Cold desert regions like Jammu & Kashmir and Himachal Pradesh
Both DPAP and DDP were later included under the watershed component of PMKSY, specifically the Integrated Watershed Management Programme (IWMP).
Hariyali Watershed Development Project
- Type: Centrally Sponsored Scheme by the Government of India
- Goal: To help rural communities manage water resources for irrigation, afforestation, and drinking water.
- Implementation: Carried out by Gram Panchayats with active participation from local communities.
Neeru-Meeru (Water and You) Program
- Initiated by: Andhra Pradesh Government
- Purpose: Focused on rainwater harvesting through community-driven efforts.
- Structures built:
- Tanks
- Dug-out ponds (called Jihads)
- Check dams, etc.
Tamil Nadu’s Rainwater Harvesting Mandate
- Key Highlight: Tamil Nadu has made rainwater harvesting structures mandatory in all buildings across the state to conserve water.
Significance of Watershed Management
Watershed management is all about taking care of water, soil, and vegetation in a particular area (called a watershed). When done right, it can:
- Improve water quality by reducing pollution.
- Protect natural resources like soil, water, and vegetation.
- Help local communities adopt eco-friendly farming and water practices, which boosts their income.
- Make soil more fertile, which means better crop yields and more food.
- Promote fair and sustainable growth for everyone involved.
Challenges in Watershed Management
Even though watershed management is beneficial, it faces many hurdles:
- Poor Planning and Design
Many projects fail due to bad planning, poor design, or not considering the geography properly. Sometimes there’s also a lack of money or knowledge about how upland and lowland areas interact. - No Clear Law
India doesn’t have a dedicated national law for watershed management. This makes it harder to implement and manage these programs consistently across the country. - Weak Institutions
Local governments and institutions often don’t have enough capacity or resources to implement and monitor watershed projects effectively. Even community-based groups like Self Help Groups (SHGs) are not always included. - Land Conflicts
Watershed areas often face land-use conflicts because they are needed for farming, cities, factories, and roads. This creates competition for land and water resources. - Low Community Involvement
Many people in local areas don’t get involved due to lack of awareness or empowerment. This weakens the effectiveness of watershed planning. - Lack of Monitoring
Without proper tracking and evaluation, it’s hard to know if the projects are working or making a difference.
Conclusion
Watershed management is more than just a conservation effort—it is a lifeline for sustainable development, especially in a country like India where agriculture and rural livelihoods heavily depend on natural resources. By protecting water sources, conserving soil, and restoring degraded land, watershed management ensures long-term environmental balance, improved agricultural productivity, and better living standards for rural communities.
India has a rich history of traditional water conservation practices, and modern programs like PMKSY, Neeru-Meeru, and the Hariyali Project reflect a continued commitment to preserving these vital ecosystems. The integrated and participatory approach of watershed management empowers local communities, promotes eco-friendly land use, and boosts income through sustainable agriculture.
However, persistent challenges like the absence of a unified national law, poor coordination, weak institutional frameworks, and limited community involvement continue to hinder progress. To unlock the full potential of watershed development, India needs to focus on:
- Stronger legal and policy support
- Effective stakeholder collaboration
- Enhanced capacity building at the grassroots
- Robust monitoring and adaptive planning
With the right blend of technology, traditional knowledge, policy reforms, and community participation, watershed management can become a powerful tool to tackle water scarcity, land degradation, and climate vulnerability—paving the way for a greener, more resilient, and prosperous rural India.

















