Daily Current Affairs Quiz
15 January, 2025
International Affairs
1. Indo-Pacific Region
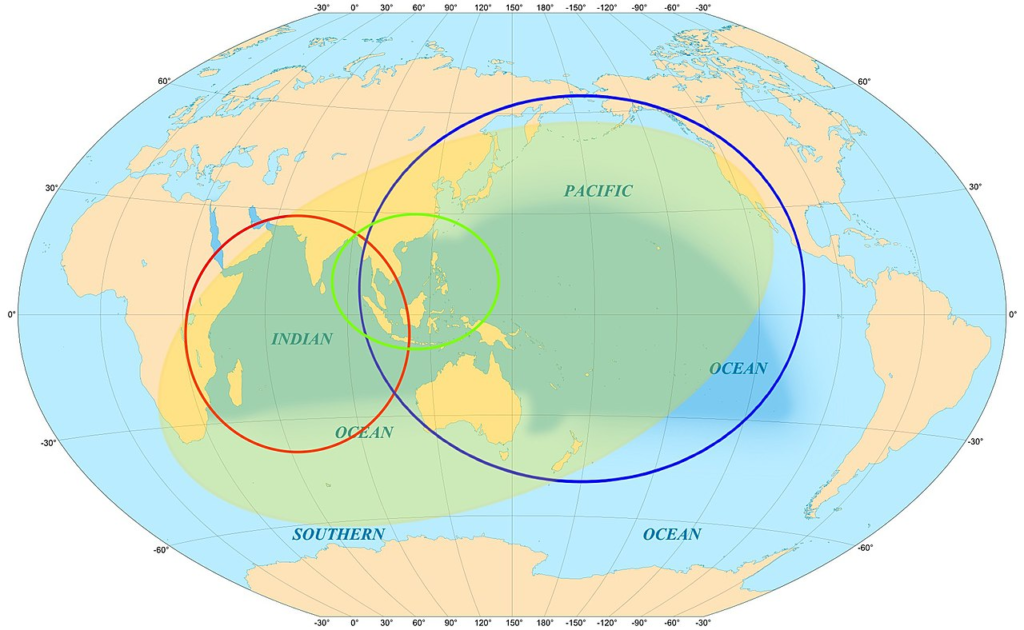
The Indo-Pacific region is a maritime area that includes the Indian and Pacific Oceans, as well as the countries and islands that border them. It comprises the tropical waters of the Indian Ocean, the western and central Pacific Ocean, and the seas connecting the two. It’s a major area of geopolitical interest and economic activity.
- Current Scenario
- The Indo-pacific region constitutes Asia, Africa, Australia, and America, known as a global economic hub, hosting 60% of the world’s population and producing 2/3rd share of global economic output.
- From India, its perspective involves cooperation towards security architecture, equal shares in trade and investments, and a united ASEAN.
- Increased Geopolitical Competition
- Rising geopolitical tensions are sweeping over the Indo-Pacific region, as Chinese power rises and falls.
- All countries are beginning to take sides, some directly with China, others hedging, and yet many trying to counter China.
- India’s Perspective of the Indo-Pacific
- Co-operate with Others for Security Architecture: Many of India’s special partners, such as the US, Australia, Japan and Indonesia want India’s presence in the South China Sea, and East China Sea, basically to counter China.
- India, on the other hand, wishes to cooperate for an architecture of peace and security in the region. The common prosperity and security demand that the countries evolve, through dialogue, a common rules-based order for the region.
- Equal Share in Trade and Investment: India supports a rule-based, open, balanced, and stable trade environment in the Indo-Pacific Region, which lifts up all nations on the tide of trade and investment.
- Importance of Indo-Pacific for ASEAN Nations
- India desires a united ASEAN, not a fractured one and likes to engage with China.
- Importance of Indo-Pacific
- Indo-Pacific is a free, open, and an inclusive region for America.
- Indo-Pacific would be democratized for Vietnam and not a play of one hegemony actor.
- Geopolitical Significance
- The region comprises the world’s most populous and economically vibrant countries, hence the importance of the region within the broad contours of global geopolitics.
- Economic Significance
- The Indo-Pacific region serves as an influential driver for the global economy because it harbors key maritime trade routes, which are many of the busiest ports in the world.
- Security and Strategic Concerns
- The Indo-Pacific is a region of increasing strategic competition among major powers, including the United States, China, India, and Russia.
- Balancing China’s Rise
- There are several countries in the region that have an interest to balance the influence of China and guarantee their security through alliances and partnerships.
- Maritime Security
- There is a large concern among the Indo-Pacific countries about ensuring the security of maritime trade routes.
- Regional Organizations and Forums
- Regional organizations that take an active interest in regional issues are ASEAN, QUAD, and the Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA).
- Connectivity and Infrastructure Development
- Economic and political shape of the region is to be molded by China’s Belt and Road Initiative and the U.S. “Free and Open Indo-Pacific” strategy.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Questions (PYQ)
Prelims
Q.With reference to “Look East Policy” of India, consider the following statements: (2011)
- India wants to establish itself as an important regional player in East Asian affairs.
- India wants to plug the vacuum created by the termination of the Cold War.
- India wants to restore the historical and cultural ties with its neighbors in Southeast and East Asia.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q1. The new tri-nation partnership AUKUS is aimed at countering China’s ambitions in the Indo-Pacific region. Is it going to supersede the existing partnerships in the region? Discuss the strength and impact of AUKUS in the present scenario. (2021)
2. The Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN)
ASEAN is a political and economic union of 10 Southeast Asian states, with a population of more than 600 million and a land area of over 4.5 million km2. Established to promote political and social stability in post-colonial Asia.
- Headquarter
- Jakarta, Indonesia
- Seceratery-General
- Kao Kim Hourn
- Chairmanship of ASEAN
- Malaysia
ASEAN’s Objectives
- Promote economic growth, social progress, and cultural development.
- Justice, the rule of law, and UN Charter principles as the foundation to ensure regional peace and stability.
- Aims have broadened beyond economic and social realms in recent times.
- Motto: “One Vision, One Identity, One Community.”
- ASEAN Day is observed on 8th August.
Recent Developments
- 24th ASEAN-India Senior Official’s Meeting on 15 June 2022 in Delhi.
- 30th anniversary of Dialogue Relations celebrated.
- India-ASEAN Digital work plan finalized in 2nd ADGMIN Meeting.
Member Nations
- Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Brunei, Vietnam, Laos, Myanmar, Cambodia.
India-ASEAN Cooperation
- Act East Policy
- India’s relationship with ASEAN is an integral part of its foreign policy and Act East Policy.
- India has a separate Mission to ASEAN and the EAS in Jakarta.
- Fourth Largest Trading Partner
- ASEAN is India’s fourth largest trading partner, with India’s trade with ASEAN accounting for approximately 10.6% of India’s overall trade.
- ASEAN India-Business Council (AIBC)
- In 2003, the ASEAN India-Business Council (AIBC) was instituted with the purpose of bringing key private sector players from India and the ASEAN countries together.
- Programmes that seek to increase people-to-people interaction with ASEAN have been instituted.
3. India-ASEAN Relations
Historical Context and Elevation of Partnership
- India was a Sectoral Dialogue Partner of ASEAN in 1992.
- In 1995, the relationship became that of a Dialogue Partner. Consequently, both began to have more frequent interactions up to the Foreign Minister level.
- The relationship further entered Strategic Partnership in 2012 and, in 2018, concentrated on cooperation in the maritime domain.
Economic Powerhouse-Gateway to Southeast Asian Markets
- ASEAN is an important economic bloc for India, providing an access to the market of over 650 million people with a collective GDP of USD 3.2 trillion.
- India is among the topmost trade partners of ASEAN accounting for 11% of India’s global trade.
Strategic Counterbalance:
- ASEAN is a very important strategic partner for India at a time of increasing tensions in the international political landscape, particularly with China.
- ASEAN provides an avenue for India to exercise its role as a net provider of security in the region through participation in summits like the East Asia Summit and ASEAN Regional Forum.
Connectivity Catalyst
- ASEAN plays a significant role in the Indian vision for enhanced regional connectivity.
- The India-Myanmar-Thailand Trilateral Highway and the Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit Transport Project are examples of India’s efforts to integrate physically with Southeast Asia.
Cultural Confluence
- The historical and cultural bonds between India and Southeast Asia are deep-rooted and provide a unique foundation for soft power diplomacy.
- The establishment of the ASEAN-India Network of Universities in 2022 further strengthens academic and cultural exchanges.
Technological Synergy
- ASEAN’s fast digitalizing economies offer tremendous opportunities for India’s IT sector and start-up ecosystem.
- ASEAN-India Science and Technology Development Fund facilitates joint research in cutting-edge areas.
Maritime Security Cooperation
- ASEAN is an important partner in India’s maritime security strategy, especially in the context of the Indo-Pacific region.
Energy Security and Sustainability
- ASEAN’s energy-rich members open up opportunities for India to diversify its sources of energy, which is crucial for its fast-growing economy.
Important Issues of India-ASEAN Relations
- Trade Imbalance
- India’s trade deficit with ASEAN has witnessed a sharp growth, more than doubling since FTA was enforced in 2010.
- Infrastructure Connectivity
- Even though India and ASEAN have strengthened their digital and cultural connectivity, physical infrastructure connectivity is still developing.
- Geopolitical Balancing
- India’s attempts to become a counterbalance to China have received mixed responses from ASEAN countries.
- Regulatory Hurdles
- Non-tariff barriers to trade and investment exist between India and ASEAN countries in the form of differences in regulatory standards and procedures.
India-ASEAN Trade Inequality and Measures to Improve Relations
Major Issues
- Manufacturing Competitiveness
- The productivity levels of Vietnam and Thailand are higher than that of India, which affects exports and imports.
- The imbalance in trade arising from India’s involvement in the ASEAN-centric regional value chains is increased.
- Services Trade Restrictions
- Language among other factors impede India to balance the trade deficit in the goods sector.
- Rules of Origin Abuse
- Weak rules of origin in AIFTA create an opportunity for non-ASEAN countries such as China, to route its exports to India through ASEAN, thereby augmenting the deficit.
Steps toward Strengthening Relations
- Rebalancing the ASEAN-India Free Trade Agreement
- India should also seek a critical review and rebalancing of AIFTA for redressing this trade imbalance.
- Infrastructure Connectivity
- India has to speed up the completion of the key connectivity projects such as the India-Myanmar-Thailand Trilateral Highway and must extend it to the rest of its neighbors, Cambodia, Laos, and Vietnam.
- Manufacturing Competitiveness
- It should focus sector-specific interventions in addition to joining manufacturing initiatives undertaken with ASEAN countries.
- Enhancing Energy Cooperation
- India should propose a comprehensive “ASEAN-India Energy Partnership” focusing on energy security, clean energy transition, and technology cooperation.
- Enhancing Strategic and Defense Cooperation
- India should deepen its strategic engagement with ASEAN, particularly in maritime security.
- Aligning on Climate Change and Sustainability
- India should propose an “ASEAN-India Green Partnership” focusing on climate change mitigation, renewable energy, and sustainable development.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q1. India is a member of which among the following? (2015)
- Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation
- Association of South-East Asian Nations
- East Asia Summit
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) India is a member of none of them
Ans: (b)
Q2. Consider the following countries: (2018)
- Australia
- Canada
- China
- India
- Japan
- USA
Which of the above are among the ‘free-trade partners’ of ASEAN?
(a) 1, 2, 4 and 5
(b) 3, 4, 5 and 6
(c) 1, 3, 4 and 5
(d) 2, 3, 4 and 6
Ans: (c)
Q3. The term ‘Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership’ often appears in the news in the context of the affairs of a group of countries known as (2016)
(a) G20
(b) ASEAN
(c) SCO
(d) SAARC
Ans: (b)
Q4. In the Mekong-Ganga Cooperation, an initiative of six countries, which of the following is/are not a participant/ participants? (2015)
- Bangladesh
- Cambodia
- China
- Myanmar
- Thailand
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 1, 2 and 5
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. Evaluate the economic and strategic dimensions of India’s Look East Policy in the context of the post-Cold War international scenario. (2016)
National Affairs
1. Prime Ministers Museum and Library (PMML)
Context:
The govt has reconstituted the executive council of the Prime Ministers Museum and Library (PMML) with former principal secretary to the PM Modi, Nripendra Mishra, getting another five-year term as its chairperson.
Prime Ministers Museum and Library (PMML)
The Prime Ministers’ Museum and Library Society previously known as the Nehru Museum and Library Society is a museum and library in New Delhi, India, which aims to preserve and reconstruct the history of the Indian independence movement.
Background
The Nehru Memorial Library was established in the year 1964 as an autonomous institution under the Indian Ministry of Culture. It was made the world resource center on India’s first prime minister, which contained Mahatma Gandhi’s writings and private papers of many leaders. Noted among its published works are Selected Works of Jawaharlal Nehru, Man of Destiny by Ruskin Bond, and Nehru Anthology (1980).
2. INS Surat, INS Nilgiri and INS Vaghsheer
Why in News?
PM Narendra Modi will dedicate 3 frontline naval combatants — INS Surat, INS Nilgiri and INS Vaghsheer , to the nation on their commissioning at the Naval Dockyard in Mumbai.
INS Surat
INS Surat is the fourth ship in the Visakhapatnam-class stealth guided-missile destroyers of the Indian Navy, the last of the entire line built under Project 15, which includes the Delhi-class and Kolkata-class destroyers. Initially named after Porbandar, it was later named as Surat. Other warships of this class include INS Visakhapatnam, INS Mormugao, and INS Imphal.
INS Nilgiri
INS Nilgiri is the lead ship of the Nilgiri-class stealth guided missile frigates being built by Mazagon Shipyard Dock Limited for the Indian Navy.
The Nilgiri-class frigates, which are also referred to as the Project-17 Alpha frigates or P-17A, are stealth guided-missile frigates built by Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders and Garden Reach Shipbuilders & Engineers for the Indian Navy.
The INS Vagsheer
The INS Vagsheer (s-26) is a French Naval Group-designed diesel-electric attack submarine from the Indian Navy, capable of eluding enemy radar, area-surveillance, intelligence gathering, and using precision-guided weapons, 18 torpedoes, and tube-launched anti-ship missiles.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q.1 Which one of the following is the best description of ‘INS Astradharini’, that was in the news recently? (2016)
(a) Amphibious warfare ship
(b) Nuclear-powered submarine
(c) Torpedo launch and recovery vessel
(d) Nuclear-powered aircraft carrier
Ans: (c)
Q.2 Consider the following in respect of Indian Ocean Naval Symposium (IONS): (2017)
- Inaugural IONS was held in India in 2015 under the chairmanship of the Indian Navy.
- IONS is a voluntary initiative that seeks to increase maritime co-operation among navies of the littoral states of the Indian Ocean Region.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
3. Labour Legislation
Context:
The Union labour ministry is aiming to “standardise and harmonise” the rules made by state governments, except West Bengal, under the four new labour codes, which may pave the way for implementing the labour legislation.
Labor Legislation
Labor legislation is a set of laws that protect the rights of workers and establish a balance between employees and employers. It also aims to create a healthy and safe working environment, and to provide a legal framework for people to find jobs.
Labour Laws in India
4. The Dharavi Redevelopment Project
The Dharavi Redevelopment Project is an initiative of large-scale urban renewal, aimed at changing one of the biggest and most densely populated slums in the world. It is located in Mumbai, India. The challenges are overcrowding, inadequate infrastructure, and poor living conditions in this area. The project promotes inclusive development.
- Aim
- Overcrowding, lack of infrastructural support to the residents, and poor living conditions will be dealt with while promoting inclusive development.
- Dharavi
- Dharavi is located close to the international airport of Mumbai with a built area of approximately 590-acre.
- Urban Hub
- The project will revamp Dharavi as a complete urban hub with modern infrastructure, housing, and amenities.
- Role of Adani Group
- The project will be led by Navbharat Mega Developers Pvt Ltd (NMDPL), a joint venture of Adani Group and the Government of Maharashtra.
- The government will execute this project through Dharavi Redevelopment Authority (DRP) and Slum Rehabilitation Authority (SRA).
- Features
- Housing for slum dwellers, land development, and economic and social impacts will be underlined in this project.
- Challenges
- Land acquisition and execution delays from regulatory, financial, and political hurdles.
5. Wind Energy
Context:
In an effort to help Indian Railways achieve net zero carbon emissions by 2030, the Ministry of Railways is considering leveraging wind energy by installing wind turbines along railway tracks, according to sources.
Indian Railways Wind Energy Scheme
- Objective
- Indian Railways must conduct a preliminary feasibility study about installing wind turbines along railway tracks to achieve zero net carbon emission by 2030.
- Current Developments
- 487MW of solar, 103 MW of wind turbines has already installed.
- Wind turbines placed along transport infrastructures are known to be innovative sources of renewable energy generation around the world.
Wind Turbines
Wind turbines are a source of renewable energy that converts wind into electricity. Wind turbines are a source of clean energy because they do not burn fuel or pollute the air.
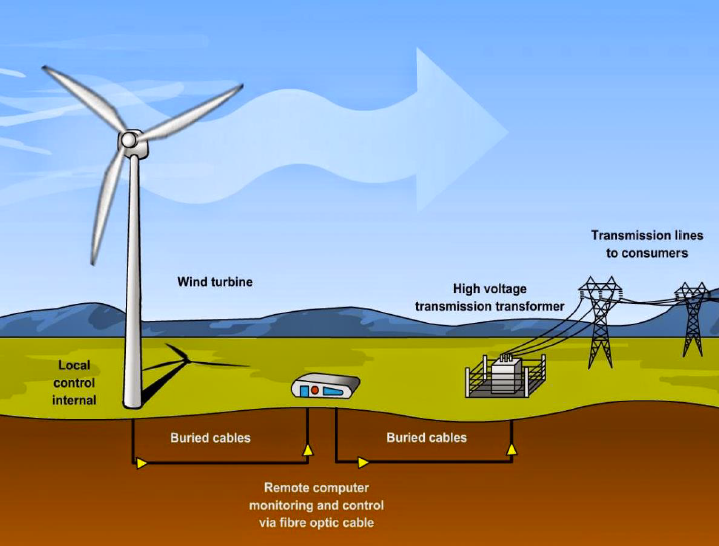
- How do wind turbines work?
- Wind turbines use the force of wind to spin a rotor, which is connected to a generator.
- The rotor blades operate similar to the wings of an airplane, whereby air pressure is different on the opposite sides of the blade.
- The difference in air pressure will result in creating lift and drag forces, which the lift forces are stronger than the drag forces causing the rotor to spin.
- Spinning rotor power will drive a generator, hence generating electricity
- Advantages of wind turbines
- Wind is a vast inexhaustible resource.
- Wind turbines can be used in powering homes and businesses.
- Wind turbines can reduce carbon dioxide emissions.
- Factors affecting the performance of wind turbines
- The size of the turbine and the length of its blades
- The speed of the wind
- The seasonal or annual rhythm of the wind
The Indian Renewable Energy Development Agency Limited (IREDA)
The Indian Renewable Energy Development Agency Limited (IREDA) is an Indian public sector enterprise, which provides financial assistance and other services to projects related to renewable sources of energy and energy efficiency/conservation.
- Founded
- 1987
- Chairman
- Pradip Kumar Das
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q.With reference to the Indian Renewable Energy Development Agency Limited (IREDA), which of the following statements is/are correct? (2015)
- It is a Public Limited Government Company.
- It is a Non-Banking Financial Company.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (c)
6. Prime Minister Internship Scheme
Context:
The Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) is releasing the second tranche of the Prime Minister Internship Scheme in February 2025.
Prime Minister Internship Scheme
- The scheme plans to offer 1 crore of internship schemes to young people over the next five years.
- Ministry
- Ministry of Corporate Affairs, Government of India
- Features
- Application will be paid ₹4,500 as stipend by the government, and an additional amount of ₹500 by the companies under Corporate Social Responsibility that consists of one year.
- A one-time grant of ₹6,000 will be given at the time of joining, and insurance cover under PM Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana and PM Suraksha Bima Yojana.
- Eligibility Criteria
- Age: 21- 24 years.
- Education
- At least Class 10th; graduates from premier institutions (IITs, IIMs) and professional qualifications (CA) are excluded.
- Employment Status
- Must not be in full-time employment.
- Income Restriction
- Family income should not exceed ₹8 lakh in a year; families of government employees are not eligible.
- Benefits of the Scheme
- Provides working skills in a practical environment.
- It will provide the youths with monetary support.
7. IMD Initiatives for Weather Forecasting
Zero-Error Forecasting
- Aims to achieve zero-error forecasts by 2047.
- Has an aim to have an accuracy of 90% for five-day forecasts, 80% and 70% for seven and ten-day forecasts respectively, in the severe weather event predictions.
Severe Weather Preparedness
- The early and accurate warning is targeted for zero fatality due to severe weather.
- Severe weather will be detected 100% at the village and household level through the improved radars, satellites, and remote-sensing systems.
Key Initiatives Launched
- Vision Document “Har Har Mausam, Har Ghar Mausam” with improved forecasting and disaster management
- Mission Mausam for Next Generation Weather Technology
- Global Contributions
- India’s Flash Flood Guidance System supports countries like Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh, and Sri Lanka.
India Meteorological Department
It is the national meteorological service of India.
- What does IMD do?
- IMD is the primary government agency for all meteorological matters in India
- IMD provides weather observations, forecasts, and warnings
- When was IMD established?
- IMD was established in 15 January 1875.
- Where is IMD headquartered?
- IMD’s headquarters are located in Mausam Bhawan, Lodhi Road, New Delhi.
- Who is the head of IMD?
- The Director General of Meteorology is the head of IMD
- Ministry
- Ministry of Earth Sciences
8. National Turmeric Board
Context:
Union Minister of Commerce & Industry, Shri Piyush Goyal, inaugurated the National Turmeric Board in New Delhi. Shri Palle Ganga Reddy was announced as the first Chairperson of the Board. The Board’s headquarters is established in Nizamabad.
Composition of the National Turmeric Board
- Includes representatives from Ministry of AYUSH, Department of Pharmaceuticals, Department of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare, and Department of Commerce.
- Representatives from exporters and turmeric producers’ organizations will be part of the Board.
- State representatives from major turmeric-growing states such as Maharashtra, Telangana, and Meghalaya (known for Lakadong Turmeric) will join, with rotational representation.
Objectives and Focus Areas
- Enhance welfare and income of turmeric farmers across 20 states including Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Madhya Pradesh, and Meghalaya.
- Boost turmeric production, with special emphasis on Andhra Pradesh and Telangana’s growth potential.
- Promote research and development (R&D) of new turmeric products and value addition.
- Create awareness about turmeric’s essential and medicinal properties.
- Improve turmeric yield, logistics, and supply chain efficiency to expand into new markets.
- Ensure quality and safety standards for turmeric cultivation and exports.
Turmeric Production and Export Statistics
- In 2023-24, turmeric was cultivated on 3.05 lakh hectares in India, producing 10.74 lakh tonnes.
- India contributes over 70% of global turmeric production and holds more than 62% share of the global turmeric trade.
- India grows 30 different varieties of turmeric.
- Exports of turmeric and related products reached 1.62 lakh tonnes, valued at USD 226.5 million in 2023-24.
Strategic Importance of the National Turmeric Board
- Acts as a coordinating body across government departments for turmeric sector growth and development.
- Focuses on expanding turmeric trade globally, leveraging health and wellness benefits of turmeric.
- Supports farmers by improving production quality, marketing, and export potential.
- Aims to strengthen India’s leadership as the largest producer, consumer, and exporter of turmeric.
9. Atal Innovation Mission
Context:
GOI’s Atal Innovation Mission argue that results so far have been excellent, including incubating apps like DigiYatra.
The Atal Innovation Mission (AIM)
The Atal Innovation Mission (AIM) is a government of India initiative to promote innovation and entrepreneurship. It was launched in 2016 by the National Institution for Transforming India (NITI Aayog)
- About
- Launched by NITI Aayog in 2016, AIM promotes innovation and entrepreneurship by fostering a problem-solving mindset in students and strengthening the entrepreneurial ecosystem in universities and research institutions.
- Key Programs under AIM
- Atal Tinkering Labs (ATLs): In schools, to inculcate innovation among students in grades 6-12 using tools such as 3D printing.
- Atal Incubation Centres (AICs): Business incubators for startups with mentorship, funding, and technical support.
- Atal Community Innovation Centres (ACICs): For the underserved regions, to innovate in Tier 2/3 cities, tribal areas, etc.
- Atal New India Challenges (ANIC): Technology-based innovations for national challenges, funding, and mentorship.
- Mentor India: Engages 6,200+ mentors across sectors to guide entrepreneurs and innovators under AIM’s programs.
Recent Update
The Union Cabinet has sanctioned the continuation of Atal Innovation Mission (AIM) under NITI Aayog (National Institution for Transforming India) with an increased budget of Rs. 2,750 crore, marking the launch of AIM 2.0 to strengthen India’s innovation ecosystem until 2028.
- What is the AIM 2.0?
- AIM 2.0: Building on AIM success, such as Atal Tinkering Labs (ATLs) and Atal Incubation Centers (AICs), AIM 2.0 seeks to scale and pilot new initiatives.
- Aims
- It aims to expand and deepen India’s innovation and entrepreneurship ecosystem.
- India Ranks
- India ranks 39th on the Global Innovation Index and is home to the world’s third-largest start-up ecosystem.
Key Programs Under AIM 2.0
- Language Inclusive Program of Innovation (LIPI)
- Vernacular innovation centers in 22 scheduled languages for non-English-speaking innovators.
- Frontier Program
- Creating 2500 new ATLs in underserved regions such as Jammu and Kashmir, North Eastern states, and Aspirational Districts.
- Programs Targeting Improving Ecosystem
- Trains professionals (managers, teachers, trainers) for the innovation ecosystem.
- Enhance India’s Innovation Ecosystem
- Enhance India’s innovation ecosystem worldwide through collaborations with developed countries, Global Tinkering Olympiad, and collaboration with United Nations World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) and G20.
- Programmes for Enhanced Quality of Output
- The Industrial Accelerator Programme intends to scale up advanced startups by establishing 10 accelerators in critical sectors through Public-Private Partnerships (PPP).
- The Atal Sectoral Innovation Launchpads (ASIL)
- The Atal Sectoral Innovation Launchpads (ASIL) program will establish 10 iDEX-like platforms across central ministries to integrate and procure from startups in key industry sectors.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Atal Innovation Mission is set up under the (2019)
(a) Department of Science and Technology
(b) Ministry of Labour and Employment
(c) NITI Aayog
(d) Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship
Ans: (c)
Banking/Finance
1. Currency Volatility
Context:
RBI will retain its policy of currency market intervention to check excessive volatility as part of its overall strategy for macro-economic management, amid reports indicating a more “flexible approach”.
The RBI is adhering to the policy of entering the currency market for controlling the extreme volatility in currency.
Currency Volatility
Currency volatility refers to the fluctuation of the value of a currency over time. It is also termed foreign exchange (forex) volatility. The fluctuation and deviation in the values of a currency over others results in trade and investment and brings about instability to the economy of a country.
- How is currency volatility measured?
- Standard deviation
- The standard deviation of a currency’s change in exchange rate over a given period is a measure of its volatility.
- Dispersion of exchange rate changes
- Volatility is measured as the dispersion of exchange rate changes around the mean.
- Standard deviation
- What causes currency volatility?
- Geopolitical factors
- Wars, riots, uprisings, and other civil unrest can cause volatility.
- Trade wars
- Trade wars between countries can cause volatility due to the large number of transactions involved.
- Economic Factors
- Inflation rate, interest rate, and balance of payments lead to the deviation in the rate of exchange
- Monetary policy
- The interest rates are regulated by the central banks to tackle the inflation rate and slow-down of the economic activity
- Geopolitical factors
- What are the effects of currency volatility?
- Economic growth
- Exchange rate volatility can be a source of both opportunities and challenges for an economy of a country
- Companies with inadequate hedging programs
- Companies with inadequate hedging programs may feel the impact of volatility on their performance.
- Cross-border trading
- One who takes advantage of currency volatility involves consumers participating in cross-border trade.
- Opportune time for profit
- Actually, there’s more opportunity of making a profit from volatile currency exchange if you put your strategy appropriately.
- Economic growth
2. Sebi Proposes Demat Shares for Corporate Restructuring
Context:
Sebi is proposing to issue all shares in demat mode in case a company splits or consolidates the face value of its shares. The regulator is also proposing to issue demat shares in case of corporate restructuring.
Definition of SEBI’s Proposal and Keywords
- The Securities and Exchange Board of India is the regulatory authority for securities and capital markets in India.
- Shares
- Definition: Units of ownership in a company that investors buy to own a share in the business.
- Background: SEBI has recommended that shares should be issued in the demat mode only for some specific corporate actions.
- Demat Mode
- Definition: Dematerialized mode, where shares are available in record form only, electronically and not in physical certificate form.
- Benefits: It saves from losses because of theft, fraud, or destruction of the physical certificates.
- Division of Shares
- Definition: The division of already existing shares into smaller units, in order to enhance the share liquidity.
- Background: As per the guidelines of SEBI, it is mandatory for shares that occur as a result of splits should be issued in demat mode only.
- Consolidation of Shares
- Meaning: Combining more than one smaller share to reduce the total outstanding shares by one large share.
- Context: SEBI also proposes that consolidation shares must be only in demat mode.
- Corporate Restructuring
- Meaning: Structures significantly changed, especially to infuse efficiency or profitability by means of mergers or de-mergers.
- Context: According to SEBI, physical certificates to be issued only in demat.
- Physical certificates
- Meaning: It is the traditional paper-based proof of share ownership.
- Drawbacks: Exposed to loss, theft, damage, and forgery.
- History: SEBI plans to abolish the paper certificates completely.
- Suspense Escrow Account
- Definition: The provisional demat account which companies open in order to keep shares for those investors who haven’t opened demat accounts as yet.
- Objective: This kind of system guarantees that ownership records are kept until the investors open their demat accounts.
- Consultation Paper
- Meaning: A paper by SEBI that invites public comments on proposed regulations or amendments.
- Timeline: The public can comment on this proposal till February 4, 2025.
- LODR Regulations
- Meaning: Listing Obligations and Disclosure Requirements, 2015, which deals with the disclosures and operations of listed entities.
- Proposed Changes: Demat-only securities issuance for split, consolidation, or restructuring actions.
- Fraud Prevention
- Meaning: Elimination of forgery and unauthorized transfers of shares.
- Advantage: Demat shares have clean records of ownership and avoid lawsuits.
- Delivery Receipt
- This is delivery proof of notices that are signed among shareholders and lack a corresponding original signature.
- Proposal for elimination: SEBI recommends eliminating this feature to ease some processes.
- Dematerialisation
- Meaning: Conversion of physical share certificates into electronic records.
- Objective: To avoid further issuance of new physical certificates and to be entirely electronic securities.
- Minor Difference in Signatures among Shareholders
- This is any minor variation made on shareholders’ signatures of different documents. Companies must deliver notice to its investors, in addition to recording proof of the delivery.
3. The Geotagging Initiative
Context:
The Union Ministry of Finance (FinMin) is planning to direct banks to implement geotagging for all Business Correspondents (BCs) in order to enhance accountability and facilitate better monitoring of their activities.
The Geotagging Initiative
The geotagging initiative in banking is the process of adding geographical coordinates to banking touchpoints to improve accountability and monitor activities. It can ensure that services are delivered efficiently to the intended beneficiaries.
- What is geotagging?
- Geo-tagging is the process of adding geographical coordinates to media based on the location of electronic devices.
- Geo-tags can be applied to photos, videos, websites, text messages, and QR codes.
- Geo-tagging data typically contains latitude and longitude coordinates, but can also contain altitude, bearing, distance, accuracy data, and place names.
- How is geotagging used in banking?
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has used geotagging to map and manage its banking units, including branches, ATMs, administrative offices, and electronic kiosks.
- The Union Ministry of Finance (FinMin) is planning to ask banks to implement geotagging for all Business Correspondents (BCs).
- Advantages of geotagging in banking
- Geotagging will result in an increased accountability and oversight of the activity.
- Geotagging helps ensure services reach the point efficiently and effectively.
- Geotagging facilitates the development of digital payment infrastructure.
Business Correspondents (BCs)
Business Correspondents (BCs) are bank representatives who provide banking services to customers at locations other than a bank branch or ATM. They are also known as retail agents.
- What do BCs do?
- Open bank accounts, Process loan applications, Deposit and withdraw money, Provide financial advice, and Help with government payments.
4. Wholesale Price Inflation
Context:
Wholesale price inflation accelerated in Dec due to an increase in prices of some manufactured products and non food items.
Wholesale price inflation is a measure of how much prices of goods sold in bulk have increased over time. It’s calculated using the Wholesale Price Index (WPI)
Wholesale Price Index (WPI) & Consumer Price Index (CPI)
5. BharatPe is Targeting an Initial Public Offering (IPO)
Context:
Fintech firm BharatPe is targeting an initial public offering (IPO) in the next 18 to 24 months with the company expecting profitability at an earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and ammotisation level for FY25, chief executive officer (CEO) Nalin Negi said.
EBITDA
EBITDA or Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization, is a financial metric. Companies use it extensively to compute their business’ performance in terms of finances. Furthermore, it offers a distinct idea to the investors and lenders about the profitability and of a company.
6. International Financial Services Centres Authority (Ifsca)
Context:
Arecent proposal by the International Financial Services Centres Authority (Ifsca) to set up special purpose vehicles (SPVs) for coinvestment will enable investors in GIFT City to choose their preferred portfolio companies, bring ease of business, and enhance transparency.
The International Financial Services Centres Authority (IFSCA) is a regulatory body established by the Government of India to oversee and develop financial services in India’s International Financial Services Centres (IFSCs), with the primary focus on promoting and regulating cross-border financial activities. The IFSCA was set up in April 2020 through the enactment of the International Financial Services Centres Authority Act, 2019.
- Chairperson:
- Shri K. Rajaraman
- Ministry:
- Ministry of Finance
- Headquarter:
- GIFT City, Gandhinagar, Gujarat, India
Economy
1. Effects of Trade Deficit on India’s Economy
Context:
China sold goods and services worth $3.6tn to other countries in 2024, bought stuff worth $2.6tn, and finished with a trade surplus of almost $1tn an all-time record even after adjusting for inflation.
A trade deficit occurs when the value of any country’s imports exceeds the value of its exports which creates a negative balance of trade.
Effects of Increased Trade Deficit to India’s Economy
- Negative Impacts
- Depletion of Forex Reserves: Over-import reduces foreign exchange, thus affecting domestic currency.
- Prolonged Trade Deficit Increases Current Account Deficit: This can escalate the current account deficit, damaging credit ratings and making borrowing even costlier.
- Strategic Implications: Trade deficits in critical sectors or essential items could raise strategic security concerns at the national level.
- Positive Impacts
- Increased Access to Goods: Trade deficit provides access to a greater range of goods than are available at home.
- Domestic Investment: Capital goods import driven deficit might increase domestic investment and industrial growth.
Reasons for India’s Higher Trade Deficit
- Import dependence
- Import dependence on crude oil and pharmaceutical ingredients, which India cannot be independent of
- Changing Patterns of Consumption
- Increasing demand for luxury goods and consumer durables that would increase imports.
- Structural Factors
- Slow growth in manufacturing output, higher cost of logistics, and infrastructure bottlenecks all contribute to this trade imbalance.
- Domestic Policies
- Inverse duty structure, export bans and other similar issues add to the trade imbalance.
- Other Factors
- Sub-optimal utilization of FTAs and the non-tariff barriers used by developed nations.
Trade Deficit
Agriculture
1. AgriTech
Context:
Vritti will launch sophisticated analytical tools that will help farmers understand market rates in a more detailed manner and track their financial performance. A credit control module will be launched to enable commission agents to manage outstanding debts and assess the creditworthiness of buyers.
Key Features:
- Tracking and Analytics
- The software tracks auction sales, delivery dates, and proceeds, providing analytics to assess profit or loss on each consignment.
- Mobile, Cloud, and Payment Integration
- The software also integrates with a mobile, cloud, barcode, UPI payment system, RTGS payment gateway, for higher speed transactions.
- eNAM (Electronic National Agricultural Market )
- Vritti is to be integrated with an eNAM (Electronic National Agricultural Market ) for better exposure of market and hence, online auctioning.
- Future Prospects
- The platform will integrate IoT, drone technology, and blockchain as such technologies increase usage in agriculture.
Government Schemes on Technology and Innovation in Agriculture
- Schemes
- This involves technology and innovation schemes like National e-Governance Plan in Agriculture (NeGPA), Sub Mission on Agriculture Mechanization (SMAM), Rastriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY), Promotion of Agriculture Mechanization for in-situ Management of Crop Residue, National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA), and Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchai Yojana (PMKSY).
- AgriStack
- Develops a high-level Task Force that finalizes a report on India Digital Ecosystem of Agriculture (IDEA), that outlines the architecture of Digital AgriStack, including a unique ID for farmers and standards for interoperability between data streams in the Agristack.
- Makes in India
- Makes in India innovation in farming technology, encourages start-ups in agriculture and establishes 50 Agri Business Incubators.
- Subsidies
- Under different schemes, subsidies are offered to promote the adoption of new varieties/technologies.
- Training and Skills Upgradation
- The program provides training, demonstrations, exhibitions, and skill development programs for farmers, farm women, and rural youth.
- Drone Technology for Pesticides
- Releases SOPs for the use of drones in pesticide and nutrient application.
Facts To Remember
1. Pawar invites PM to inaugurate Marathi lit event
- NCP-SP chief Sharad Pawar has invited PM Modi to inaugurate a prominent Marathi literary event, a gesture that is being seen as a gratitude to the Centre for granting classical language status to Marathi.
2. RBI redistributes portfolios as Patra retires as dy guv
- RBI has redistributed portfolios among its deputy governors following the retirement of Michael Patra
3. Over 100 feared dead, 500 trapped in SAfrica mine
- Rescuers sent a cagelike structure down into one of South Africa´s deepest gold mines on Tuesday to bring out survivors among hundreds of miners who were working illegally in an abandoned shaft and have been trapped for months.
4. Hamas accepts draft deal for Gaza ceasefire, hostage release
- Hamas has accepted a draft agreement for a ceasefire in the Gaza Strip and the release of dozens of hostages, two officials involved in the talks said.
5. Major Asian markets end in negative
Four out of five major Asian indices ended in negative today.
6. Rupee appreciated by 27 paise against US dollar
In the Forex market, the rupee today appreciated by 27 paise to settle at 86 rupees and 36 paise against the US dollar.
7. India Women’s team to face Iran in Kho Kho WC 2025
The Indian Women’s Kho Kho team is set to face Iran in the Kho Kho World Cup 2025 this evening at the Indira Gandhi Indoor Stadium.
8. Highlighting ‘Make in India’ initiative, India Pavilion opens at Heimtextil 2025
Textile Minister, Giriraj Singh highlighted the ‘Make in India’ initiative as a proven strategy driving India’s emergence as a competitive manufacturing hub.
9. Country’s coal imports drop by over 3% in April-October 2024
Coal imports in the country dropped by over three per cent from April to October last year from over 154 million tonnes to over 149 million tonnes during the same period in the previous year.
10. Women’s Cricket: India aims for ODI series whitewash against Ireland in final match
In Women’s Cricket, India will look to whitewash Ireland in the three-match ODI series in the final match today at Rajkot, in Gujarat.
















