Daily Current Affairs Quiz
16 & 17 March, 2025
International Affairs
1. India-France Defence Deals
Context:
Two major defence agreements with France, worth ~$11 billion, are awaiting final approval from the Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS). Deals include:
- 26 Rafale-M fighter jets for the Indian Navy.
- Three additional Scorpene-class submarines under Project-75.
Rafale-M Fighter Jet Deal
- Status
- All formalities and negotiations completed; pending CCS approval.
- Expected to be finalized in April 2025 during the French Defence Minister’s visit to India.
- Specifications
- 22 single-seater Rafale-M (carrier-compatible).
- 4 twin-seater Rafale trainers (not carrier-compatible).
- Purpose
- To bridge the fighter jet gap for aircraft carriers INS Vikramaditya and INS Vikrant.
- Temporary measure until indigenous Twin Engine Deck-Based Fighter (TEDBF) is ready.
- Delivery Timeline
- Begins four years after contract signing (estimated from 2029).
- Upcoming Evaluation
- The Indian Navy will assess Rafale-M performance on the French aircraft carrier Charles de Gaulle, which will participate in the Varuna naval exercise in Goa.
Scorpene-Class Submarine Deal
- Status
- Follow-up to the original six-Scorpene submarine deal between France’s Naval Group and India’s Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Ltd. (MDL).
- CCS approval awaited; likely conclusion in April 2025.
- Purpose
- Strengthen India’s submarine fleet amid regional security concerns.
Budget & Financial Considerations
- The Navy seeks to finalize both deals within this financial year (FY 2024-25) to include them in the current Budget.
- Given the government-to-government nature of the deal, allocated funds can be rolled over to the next fiscal year.
Additional Procurement & Future Plans
- India is also acquiring the MQ-9B drone from the U.S. for high-altitude, long-endurance surveillance.
- If the Scorpene deal is signed in April, deliveries are expected to begin by 2029.
2. Rodrigo Duterte’s Arrest
Context:
Former Philippine President Rodrigo Duterte was arrested on an International Criminal Court (ICC) warrant. A rare success for the ICC, as most warrants remain unexecuted without cooperation from national governments.
- Duterte’s arrest was facilitated by
- President Ferdinand Marcos Jr.’s administration, which executed the warrant.
- Political fallout with Vice-President Sara Duterte, his daughter, who is facing impeachment proceedings.
ICC’s Case Against Duterte
- Charges: “Crime against humanity of murder” due to his ‘war on drugs’, which involved state-backed killings.
- Timeframe of Investigation: 2011–2019 (before Duterte withdrew the Philippines from ICC membership).
- Legal Basis: The ICC ruled it has jurisdiction since crimes were committed when the Philippines was an ICC member.
Challenges Faced by the ICC
- Lack of Enforcement Power
- Relies on national governments to execute warrants.
- Many leaders evade arrest by avoiding ICC member states.
- Selective Justice Allegations
- Criticized for focusing on African warlords and conflict zone leaders.
- Warrants for Vladimir Putin and Benjamin Netanyahu remain unexecuted.
- Political Resistance
- The United States openly opposes the ICC and threatens punitive measures if it prosecutes U.S. nationals or allies.
The ICC’s Legal Precedents and Future Role
- The ICC has ruled that it can investigate crimes committed by nationals of non-state-parties if they occur in state-parties (e.g., Palestine ruling).
- A country’s non-ratification of the Rome Statute does not necessarily prevent the ICC from investigating or prosecuting individuals.
3. India-New Zealand Free Trade Agreement (FTA)
Context:
India and New Zealand first began negotiating the Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement (CECA) in April 2010.
Key Highlights:
- Talks stalled in February 2015 after 10 rounds of discussions.
- March 2025: The two nations officially resumed negotiations for a mutually beneficial Free Trade Agreement (FTA).
- Announcement followed a meeting between Commerce Minister Piyush Goyal and New Zealand Trade Minister Todd McClay.
- New Zealand PM Christopher Luxon is on a four-day visit to India.
Key Objectives of the FTA
- Enhance supply chain integration.
- Improve market access for businesses and consumers.
- Strengthen bilateral trade, which surpassed $1 billion during April 2024 – January 2025.
Challenges in Negotiations
a) Tariff Disparity
- New Zealand
- Low average tariff of 2.3%.
- More than 50% of imports already duty-free → Indian goods already have significant market access.
- India
- Higher average tariff of 17.8%.
- Would require substantial tariff cuts, making the FTA less attractive for India.
b) Dairy, Meat, and Wine Exports
- New Zealand’s demands
- Greater access to India’s dairy market (previously resisted by India).
- Lower tariffs on dairy, meat, and wine exports.
- India’s stance
- Strong protectionist approach to dairy due to the millions of farmers dependent on the sector.
- Currently, India’s dairy imports from New Zealand are minimal ($0.57 million).
- Might allow limited imports of value-added dairy products but not raw dairy.
c) Movement of Skilled Professionals & Services
- India’s demand
- Easier mobility for Indian skilled workers.
- Better access for IT and service sector companies in New Zealand.
- Potential U.S. Influence
- Pressure on India to open its dairy and agriculture sector could impact negotiations.
Next Steps
- Both countries must find common ground on tariffs, market access, and services.
- The success of the FTA will depend on balancing India’s domestic interests with trade benefits.
4. Baidu’s Ernie X1 AI
Context:
Baidu has launched Ernie X1, a reasoning-focused AI model, and upgraded its flagship foundation model to Ernie 4.5. The move comes as a response to DeepSeek’s rapid rise, which has disrupted the AI landscape with cost-effective, high-performing models.
Competitive Positioning Against DeepSeek & Global AI Leaders
- DeepSeek‘s Disruption: The startup has gained attention by offering models comparable to OpenAI’s but at a lower cost, shaking up the AI industry.
- Baidu’s Response
- Strengthening Reasoning Capabilities (daily dialogues, calculations, logical deductions).
- Open-Sourcing Ernie AI from June 30 to attract global developer adoption.
- Integrating AI models into its core search engine to reinforce its dominant business segment.
Benchmarking Against OpenAI
- Baidu claims Ernie 4.5 surpasses OpenAI’s GPT-4.5 in text generation, positioning itself as a strong domestic alternative.
- The AI boom contributed to a 26% rise in Baidu’s cloud revenue, showcasing a shift towards AI and cloud-driven growth.
Strategic Implications
- Open-Source AI as a Defensive Move
- Making Ernie AI open-source mirrors Alibaba’s Qwen and DeepSeek’s approach, signaling a shift from proprietary models to ecosystem-building.
- This move could broaden adoption among developers and enhance global competitiveness.
- China’s AI Race Heats Up
- Baidu faces stiff competition from ByteDance, Alibaba, and Moonshot AI, which have gained greater traction in AI adoption.
- China’s AI industry is evolving rapidly, with open-source models gaining developer preference over closed systems.
- Financial Reinvestment in AI
- A $2.1 billion takeover deal freed up $1.6 billion in capital, which Baidu plans to reinvest into AI and cloud infrastructure.
- This signals a long-term commitment to AI leadership despite challenges in advertising revenue.
Baidu is doubling down on AI innovation and open-source strategies to counter DeepSeek’s rise and maintain relevance in China’s AI landscape. While Ernie 4.5 claims superiority over OpenAI’s GPT-4.5, the key battleground will be adoption and developer engagement. The next phase of China’s AI race will likely be defined by cost efficiency, reasoning capabilities, and ecosystem strength.
5. NASA Astronauts’ Long-Awaited Return
Context:
NASA launched a new crew to the International Space Station (ISS) on Friday night to replace the two stranded astronauts. The relief team is expected to dock, ensuring a smooth transition.
- The new crew includes
- Anne McClain (NASA) and Nichole Ayers (NASA) – Both are military pilots.
- Takuya Onishi (Japan) and Kirill Peskov (Russia) – Both are former airline pilots.
The International Space Station (ISS)
The International Space Station (ISS) is a large space station that was assembled and is maintained in low Earth orbit by a collaboration of five space agencies and their contractors: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), ESA (Europe), JAXA (Japan), and CSA (Canada).
Do India Have Any Such Station in Space?
Bharatiya Antariksha Station is India’s planned modular space station that will work under the aegis of ISRO. Weighting around 52 tonnes, it would be stationed at a distance of 400 km above Earth. . Launch of the inaugural component aboard an LVM3 launch vehicle is planned for 2028, followed by launching the remaining components by 2035 on the Next Generation Launch Vehicle, Soorya.
- Launching Rocket
- LVM3, LVM3, Next Generation Launch Vehicle (NGLV)
Wilmore & Williams’ Unexpected Extended Stay
- Butch Wilmore and Sunita Williams, test pilots for Boeing’s Starliner capsule, were originally scheduled for a week-long mission but have been in space for nine months due to technical issues.
- Their return plan
- They will brief the replacement crew on ISS operations.
- They will depart next week, escorted by a SpaceX team that arrived last September.
- They will land off the Florida coast, weather permitting.
Boeing’s Starliner Capsule Issues
- Their extended mission was caused by helium leaks and thruster failures in Boeing’s Starliner capsule, leading to months of investigations by NASA and Boeing.
- The incident has raised concerns about the Starliner program, which was intended to be a competitor to SpaceX’s Crew Dragon.
National Affairs
1. Greenhouse Gas Emission Impact on Orbital Space of Earth
Context:
Increasing anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions will shrink the mesosphere and thermosphere of the Earth, reducing the safety carrying capacity of satellites from 50% to 66% by the year 2100.

Greenhouse Gas Emission
Greenhouse gas emissions are the release of gases like carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide into the atmosphere, which trap heat and contribute to the greenhouse effect, leading to global warming and climate change.
- What are Greenhouse Gases?
- Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are gases in the Earth’s atmosphere that trap heat and prevent it from escaping into space.
- This natural process, known as the greenhouse effect, is essential for maintaining a habitable planet, but increased emissions from human activities are causing the effect to intensify, leading to climate change.
- Major Greenhouse Gases
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2): The most abundant GHG, primarily from burning fossil fuels (coal, oil, and natural gas).
- Methane (CH4): A potent GHG, emitted from sources like livestock, landfills, and natural gas production.
- Nitrous Oxide (N2O): Emitted from agricultural activities, industrial processes, and burning fossil fuels.
- Fluorinated Gases: Synthetic gases used in refrigeration, industrial processes, and other applications.
- Sources of Greenhouse Gas Emissions
- Fossil Fuel Combustion: Burning coal, oil, and natural gas for energy production, transportation, and industry.
- Industrial Processes: Manufacturing, cement production, and other industrial activities.
- Agriculture: Livestock farming, fertilizer use, and rice cultivation.
- Deforestation: Removal of trees, which absorb CO2 from the atmosphere.
- Waste Management: Landfills and waste incineration.
Major Highlights of the Study
- In a high emission scenario (SSP5 8.5), the number of satellites that can be safely sustained in low Earth orbit (LEO) may decrease to as few as 25-40 million.
- Constriction of Earth’s upper atmosphere reduces the atmospheric drag, seemingly letting space debris linger longer in orbit, increasing the chance of collisions.
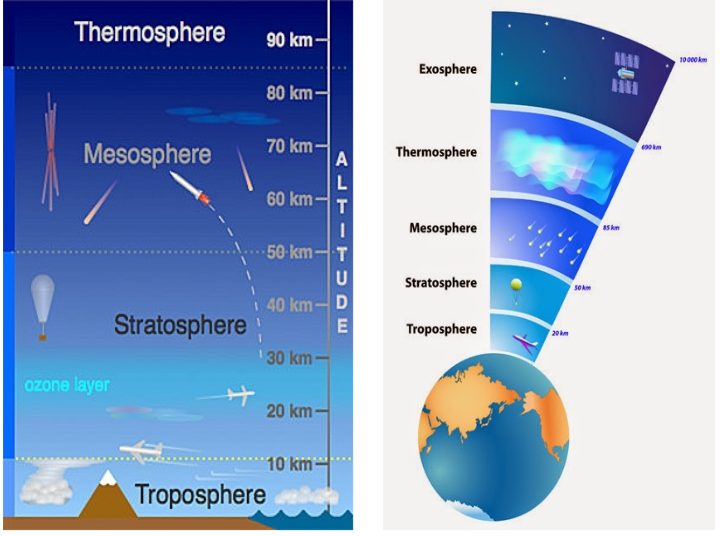
Modelling Insights
- The researchers from MIT Cambridge, led by Dr. William Parker, laid down atmospheric models to estimate the sustainable satellite limit under different emissions scenarios.
- The study compared contemporary circumstances with predicted ones in the light of greenhouse gas levels from the year 2000 baseline.
- It showed evidence of comparing the number of sat re entry rates declining significantly with increasing carbon dioxide emission statuses from moderate to high levels.
Implications and Recommendations
- Increasing debris in space will pose longer term threats to operations of satellites and exploration in space.
- Reducing those greenhouse gas emissions complicity goes beyond clime into the long term usability of Earth’s orbital space.
- Improved debris management strategies and international policies on satellite end of life decommissioning will be needed to address the challenges posed by a shrinking upper atmosphere.
2. Melioidosis in India
Overview of Melioidosis
- Cause
- Bacterial infection caused by Burkholderia pseudomallei, primarily acquired through inoculation, inhalation, or ingestion of contaminated soil and water.
- Global Burden
- Annually, 165,000 cases worldwide, with South Asia (including India) accounting for 44% of cases (The Lancet, 2016).
- Medical Complexity
- Can present as mild skin infection to severe sepsis (fatality rate up to 50% in septicemia).
- Difficult to diagnose due to prolonged bacterial incubation and similarity with Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
- Treatment requires extended antibiotic therapy: Intravenous phase followed by a 12-20 week eradication phase.
Odisha-Based Study on Environmental Impact
- Conducted by AIIMS Bhubaneswar (Microbiology Dept.) and IIT Bhubaneswar (Climate Sciences).
- Objective: To investigate how climate and environmental factors influence melioidosis transmission in Odisha.
- Methodology
- Nine-year study (2015-2023) tracking 144 cases.
- Analysed 3,024 days of meteorological data: rainfall, temperature, humidity, solar radiation.
- Created a state-wide risk map using 10 km grid sizes.
Key Findings
- Seasonal Pattern
- Peak infections during and after monsoon.
- Strong correlation with temperature, rainfall, cloud cover, and solar radiation.
- High-Risk Districts: Cuttack, Balasore, Khordha, and Jajpur—coinciding with densely populated regions.
- Other Contributing Factors
- Land-use changes and soil composition (not fully explored due to data limitations).
- Rapid urbanization and poor sanitation increasing human exposure to the bacteria.
- Climate change altering rainfall patterns, potentially expanding or shifting disease prevalence.
Implications for Public Health and Policy
- Need for Climate-Integrated Disease Surveillance
- Use weather and climate analytics in disease prediction models.
- Enhance public health planning and outbreak preparedness.
- Potential Beyond Melioidosis
- Study serves as a model for other climate-sensitive infectious diseases.
- Odisha’s research approach could be replicated in other vulnerable regions.
3. Treating Chikungunya using HIV/AIDS drug efavirenz
Efavirenz is a non-nucleoside inhibitor used for HIV/AIDS treatment.
- New Study
- Preliminary research suggests it could be repurposed for chikungunya treatment.
- Current Scenario
- No approved antiviral drugs exist for chikungunya, only a few have been tested in animal models.
Chikungunya in India
Chikungunya is a mosquito-borne viral disease characterized by fever and severe joint pain, transmitted by infected mosquitoes like Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus.
- Cause:Chikungunya is caused by a virus belonging to the alphavirus genus of the family Togaviridae.
- Re-emergence in 2006 after 20-30 years.
- 2006 Outbreak
- 14 million suspected cases, with 2,001 lab-confirmed cases.
- Decline until 2014, followed by a rise in cases from 2018 onwards.
Study Findings (IIT Roorkee Research)
- Conducted by Department of Biosciences and Bioengineering, IIT Roorkee.
- Published in: ACS Infectious Diseases.
A. In-vitro (Cell Line) Studies
- Tested on Vero cells and human hepatic cell lines (as chikungunya affects liver hepatocytes).
- Results:
- Efavirenz inhibited virus replication by 99% at low micromolar concentrations.
- Drug was effective up to 6-8 hours post-infection, acting in the early replication phase.
B. In-vivo (Mouse Model) Studies
- Efavirenz treatment significantly reduced viral load in chikungunya-infected mice.
- Unexpected Finding:
- Increased swelling in the limbs due to the drug’s pro-inflammatory action.
- Despite this, viral propagation was controlled.
C. Supporting Evidence from HIV Patients
- Anecdotal case of a 43-year-old HIV patient receiving efavirenz showed improvement in chikungunya symptoms.
- Improvement not solely attributed to efavirenz but aligns with anti-chikungunya activity observed in lab studies.
4. Potential and Future Steps
- Efavirenz shows strong promise due to:
- Good pharmacokinetics (effective drug absorption and metabolism).
- Proven safety and efficacy in HIV treatment.
- Demonstrated ability to suppress chikungunya virus replication.
- Next Steps:
- Clinical trials to assess efavirenz’s effectiveness and safety in humans for chikungunya treatment.
Source: TH
4. Madhav National Park Declared India’s 58th Tiger Reserve
Context:
Announced on March 9, 2024, by Environment Minister Bhupender Yadav. Madhav National Park (Madhya Pradesh) becomes India’s 58th tiger reserve. Madhya Pradesh now has 9 tiger reserves, the highest among all states.
Rationale Behind Tiger Reserves
- Tiger Population Decline
- Estimated 40,000 tigers in early 20th century.
- 1960s: Numbers dropped to 2,000–4,000 due to hunting, poaching, deforestation, and the fur trade.
- Conservation Measures
- 1969: Indian Board for Wild Life (IBWL) recommended a ban on wild cat skin exports.
- 1972: Tiger declared endangered in the Red Data Book by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
- 1973: Project Tiger launched with 9 reserves to protect the species.
Establishing a Tiger Reserve
- Project Tiger (Now NTCA, since 2006) mandates scientific reserve management:
- Core Zone: Strictly protected for tigers and prey.
- Buffer Zone: Managed for sustainable human activities.
- Tiger Conservation Plans (TCPs) include
- Habitat management for tigers, prey, and co-predators.
- Land-use planning to connect reserves via wildlife corridors.
- Community engagement and livelihood support for local populations.
- Approval Process
- State submits a proposal.
- National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) reviews and recommends it.
- State officially notifies the reserve.
Funding for Tiger Conservation
- Project Tiger funding model
- 60% Central Government, 40% State Government (for most states).
- 90% Central funding for Northeastern & Himalayan states.
- Utilization of Funds
- Anti-poaching efforts, habitat improvement, water conservation.
- Human-wildlife conflict mitigation.
- Relocation of villages from critical habitats.
- Rehabilitation of traditional hunting tribes.
- Independent monitoring & evaluation of reserves.
Importance of Madhav National Park
- Originally notified as a National Park in 1956 under the MP National Parks Act, 1955.
- Newly expanded area
- Core Zone: 355 sq km
- Buffer Zone: 4-6 sq km
- Recent Tiger Relocation (2023)
- Had no tigers before 2023.
- One male and two female tigers relocated.
- Population now increased to seven.
- Strategic Location
- Acts as a corridor between Ranthambore Tiger Reserve (Rajasthan) and Kuno National Park (MP).
- Potential competition between tigers and cheetahs for prey.
Madhya Pradesh as India’s Top Tiger State
- Home to 785 tigers, highest in India.
- Major reserves: Kanha, Bandhavgarh, Panna, Satpura, and Pench.
- Kuno-Madhav Forest Division:
- Historically neglected but gaining importance.
- Kuno National Park houses cheetahs imported from Namibia & South Africa.
- Potential future relocation of Asiatic lions from Gir (Gujarat).
- Government re-examining the co-existence of lions and cheetahs in Kuno.
India’s Tiger Conservation Status
- 2023 Tiger Census: Estimated 3,682 tigers.
- 30% of tigers live outside protected reserves, highlighting the need for better corridor connectivity.
Source: TH
5. Crisis in Public Health Education and Employment in India
Context:
The U.S. decision to withdraw from WHO and reduce US-AID funding has disrupted global aid and health services. India, which relies on only 1% of international aid for healthcare, remains largely unaffected at a system level.
Key Highlights:
- However, the public health development sector, which depends on global funding, faces severe strain.
- The biggest impact is on the public health job market, reducing opportunities for graduates in Master of Public Health (MPH) and similar programs.
Growth of Public Health Education in India
- Public health education in India has its roots in the colonial era, but for long, it remained embedded within medical training.
- The All India Institute of Hygiene and Public Health (1932) and later community medicine courses were early public health training efforts.
- Growth surged after 2005 with the National Rural Health Mission (NRHM), leading to an increase in MPH programs from 1 (in 2000) to over 100 today.
- Despite this expansion, government hiring plateaued, while graduates continued to increase, leading to an oversupply.
Challenges Facing Public Health Graduates
- Mismatch in supply & demand
- Entry-level public health jobs attract an overwhelming number of applicants for very few positions.
- Limited hiring in government and shrinking public health roles worsen the situation.
- Growing dominance of private sector
- Private healthcare systems prefer hospital/business management professionals over public health experts.
- Research and development opportunities rely heavily on foreign funding, which is declining.
- Concerns about education quality
- Many MPH programs lack standardisation, and faculty are often undertrained.
- No single regulatory body (like NMC or UGC) oversees MPH education.
- Intense competition among institutions leads to lower admission standards.
Possible Solutions
- Creating more public health jobs
- Governments should be the largest employers, as in developed countries.
- State-level public health cadres can create structured career paths.
- Strengthening regulation & standardisation
- A dedicated regulatory body should oversee curriculum and training quality.
- Integration of public health education with practical fieldwork is essential.
- Expanding public health institutions in underserved states
- Many states (e.g., Bihar, Assam, Jharkhand) lack sufficient MPH programs.
- Strengthening local public health ecosystems will ensure sustainable health development.
6. Tackling the Problem of Nutrition in India
Context:
While health was not a priority for Budget 2025, it seems that nutrition is. In the coming financial year, two Union government schemes will receive higher allocations — Saksham Anganwadi and Poshan 2.0.
Budget 2025 and Nutrition Focus
- While health was not a major priority, the government increased allocations for:
- Saksham Anganwadi
- Poshan 2.0
- However, will increased funding alone solve India’s nutrition challenge?
Broader Perspective on Nutrition
- Nutrition ≠ Just Food Insecurity
- Shaped by culture, caste, and gender dynamics.
- Policy focus is mainly on women and children, ignoring other groups like:
- Men, senior citizens, and non-reproductive-age women.
- Those affected by non-communicable diseases (NCDs) like diabetes and hypertension.
- Key Statistics (NFHS-5 Data)
- 36% of children under five are stunted.
- 57% of women (15-49 years) are anaemic.
- 24% of women and 23% of men are overweight or obese.
- 14% take diabetes medication.
Issues with Current Nutrition Programs
- Poshan 2.0 & Saksham Anganwadi
- Provide take-home rations, supplementary food, iron-folic acid tablets.
- Focused only on malnutrition hotspots (e.g., aspirational districts, NE India).
- Fails to address nutrition as a broader public health issue.
A Comprehensive Nutrition Agenda
A successful nutrition strategy must include:
- Expanding Focus Beyond Women and Children
- Nutrition for all population segments (elderly, men, those with NCDs).
- Localized and Culturally Relevant Solutions
- Promote local, nutrient-dense foods instead of sugar-laden, processed goods.
- Strengthening Local Implementation through HWCs
- Health and Wellness Centres (HWCs) should be the primary implementers.
- Expand their reach across both rural and urban areas.
- Dedicated nutrition staff needed at HWCs.
Factors for Successful Implementation
- Engaging Local Elites
- Research shows public ownership by local leaders boosts adoption (e.g., smallpox vaccine success in China).
- Linking Nutrition to Local Cuisines & Traditions
- Tailor interventions to regional dietary habits for better acceptance.
Moving Towards Holistic Well-being
- India must redefine health as well-being, not just the absence of illness.
- A locally owned, well-integrated nutrition agenda delivered by the primary healthcare system is the first step.
Source: TH
Multidimensional Poverty Index
7. Rising MGNREGA Demand
Context:
The steady rise in demand for rural jobs over six months suggests widening economic distress rather than temporary seasonal fluctuations. While seasonal factors contribute, the scale and consistency of the increase point to structural weaknesses in rural employment generation. The post-pandemic economic recovery appears uneven, with rural areas lagging behind despite earlier signs of consumption revival.
Link to Broader Economic Indicators
- GDP Growth Slowdown
- Q3 FY25 GDP growth at 6.2% is the slowest in nearly two years (excluding Q2).
- Requires an unrealistic 7.6% Q4 growth to meet the 6.5% full-year target.
- Indicates an economic deceleration, impacting rural employment.
- Manufacturing Weakness
- Consumption Trends
- Initial signs of rural demand recovery seem unsustainable, reinforcing the need for income support mechanisms like MGNREGA.
Structural & Policy Considerations
- Reliance on MGNREGA highlights gaps in job diversification
- Agricultural and allied sectors fail to absorb rural workforce efficiently.
- Limited rural industrialization & sluggish MSME growth contribute to job scarcity.
- Government spending post-elections (e.g., PMAY-G) may have temporarily increased work availability, but does not solve long-term employment issues.
- Need for Strategic Policy Shifts
- Expand rural skill development beyond MGNREGA’s unskilled labor model.
- Enhance rural non-farm employment through MSME and agro-based industries.
- Boost manufacturing sector competitiveness to create employment beyond rural safety nets.
The rising demand for MGNREGA reflects wider economic stress rather than seasonal fluctuations. Weak GDP growth, manufacturing slowdown, and job scarcity indicate deeper structural concerns. Policy interventions should move beyond short-term employment guarantees to focus on sustainable job creation and rural industrialization.
Banking/Finance
1. Why Mutual Funds Are Outpacing Bank Deposits?
Structural Shift in Investor Behavior
- Risk Appetite Evolution
- The preference for mutual funds over traditional fixed deposits signals a fundamental shift in investor mindset. Younger investors, particularly those in their 20s and 30s, are more willing to take risks for higher returns rather than prioritize capital safety.
- SIP Growth & Market Resilience
- Despite short-term volatility, Systematic Investment Plans (SIPs) continue to attract inflows as investors believe in long-term market growth. This trend highlights increasing financial literacy and confidence in equity markets.
Taxation Dynamics – A Critical Factor
- Impact of New Tax Regime
- The removal of 80C tax benefits for 5-year bank FDs has reduced their appeal, especially for tax-conscious investors.
- ELSS, traditionally a tax-saving MF category, has also lost some attractiveness, but this hasn’t deterred inflows into equity funds.
- Debt MFs vs. FDs: Debt mutual funds now offer a clear tax advantage, as taxes are paid only upon redemption, whereas FD interest is taxed annually with TDS deduction, eroding effective returns over time.
- Investor Behavior Shift
- This shift indicates that mutual funds are no longer seen only as tax-saving instruments but as wealth-generation tools, signaling a maturing investor base.
Product Innovation & Customization – The MF Advantage
- Mutual fund houses have created tailored products that cater to varied risk appetites, unlike the one-size-fits-all approach of bank deposits.
- Key Alternatives Eating into Bank Deposits:
- Arbitrage Funds & Equity Savings Schemes: Offering low-risk market participation with better post-tax returns than FDs.
- Balanced Advantage Funds: Allowing investors to dynamically switch between equity and debt based on market conditions, making them more flexible than FDs.
- Liquid & Ultra-Short-Term Funds: Emerging as a competitive alternative for short-term cash parking, offering higher liquidity and better yields.
The Digital & Distribution Edge
- Technology & Digital Platforms
- Fintech adoption has significantly improved mutual fund accessibility in smaller towns, driving retail participation.
- Instant KYC and paperless transactions have made it easier to invest in MFs than traditional FDs, reducing friction.
- Financial Awareness & Advisory Growth
- Investors now have better access to financial advice, leading to informed decision-making.
- The widespread awareness of market-linked returns and compounding benefits has fueled confidence in MFs.
Macro Factors & Liquidity Trends
- Slower Bank Deposit Growth
- Bank deposit growth slowed to 9.2%, while mutual funds grew 90%, indicating a liquidity shift from savings to investments.
- The slowdown in time deposits reflects a lower reliance on traditional saving instruments.
- Mutual Fund AUM Outpacing Deposits:
- MF industry AUM rose 24% YoY, compared to an 8% growth in total bank deposits, showing a structural change in capital allocation.
Future Outlook – Will the Trend Continue?
- If interest rates soften, bank FDs will become even less attractive, further pushing investors towards mutual funds.
- Equity market volatility remains a risk, but SIP discipline suggests investors are more resilient than before.
- New product innovation in MFs, such as AI-driven funds and hybrid strategies, will continue to attract flows.
- Financial literacy & digital penetration will drive deeper retail participation, sustaining MF dominance over FDs.
A Fundamental Shift in Investment Culture
The data suggests that mutual funds are no longer just an alternative to bank deposits—they are becoming the preferred choice for wealth accumulation. The interplay of changing risk appetite, tax efficiency, product innovation, and digital accessibility is reshaping India’s investment landscape. If these trends continue, we may see a long-term decline in bank deposit dominance, with mutual funds taking center stage in personal finance strategies.
Source: TH
2. RBI Assures Financial Stability of IndusInd Bank
Context:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) approved in clear terms that IndusInd Bank is well capitalized, and the financial position remains stable in light of certain quarters raising doubts.
Key Highlights:
- The bank’s share price fell after a discrepancy in its derivatives portfolio was discovered, with the disclosure expected to put 2.35% value at stake.
- The Central Bank insisted that the bank was under consideration by the RBI and insisted that remedial action must end in Q4FY25 with needed disclosures to all concerned stakeholders.
Financial Strength of IndusInd Bank
- Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR)
- 16.46% (as per Q3FY25 auditor reviewed results).
- Liquidity Coverage Ratio (LCR)
- 113% (as for March 9, 2025), surpassing the regulatory requirement of 100%.
- The bank has already engaged an external audit team to review its systems and assess the actual impact of the discrepancy.
RBI’s Appeal to Depositors
- The RBI urged depositors not to react to speculative reports, reiterating that IndusInd Bank’s financial health remains satisfactory.
- The regulator continues to closely monitor the situation to ensure stability and compliance.
3. Global Capability Centres (GCCs)
Context:
Neo banks (digital-only banks) and mid-sized banks are setting up Global Capability Centres (GCCs) in India. GCC expansion is the next big wave in India’s banking, financial services, and insurance (BFSI) sector. Market size of neo banks expected to grow from $19 billion in 2018 to $395 billion by 2026 (PwC).
Why Are Banks Setting Up GCCs in India?
Global Capability Centers (GCCs), also known as Global In-house Centers (GICs) or Captive Centers, are offshore or nearshore entities fully owned and operated by a parent company, providing a wide array of specialized services, ranging from IT and R&D to complex back-office functions.
- Cost advantages and access to top engineering talent.
- Lean workforce – Small banks operate with one-tenth or fewer employees than larger global banks.
- Resilience post-pandemic – High attrition (up to 70% at service providers) prompted banks to in-source operations.
- Technological advancements – GCCs focus on AI, cloud computing, blockchain, and digital banking.
Key Players Expanding in India
- US Banks: First Citizens Bank, PNC Financial, Fifth Third Bank.
- European Banks: Natixis, Credit Agricole, Santander (France), UniCredit (Italy).
- UK Banks: Revolut, Monzo.
Growth of BFSI GCCs in India
- 130 BFSI GCCs operating in India, employing 537,000+ people (EYWizmatic study).
- 22 GCCs operate with fewer than 500 employees, highlighting a tech-driven, agile approach.
- Top 10 banking GCCs employ 285,553 people.
- JP Morgan alone has 21,000 engineers working on AI, cloud computing, blockchain, and digital banking.
Future Outlook
- GCCs will continue to grow as banks look for cost savings, operational control, and tech innovation.
- Smaller, agile teams will play a significant global role in shaping digital banking.
- India will remain a strategic hub for BFSI technology and operations.
4. RBI’s Currency Management Modernization Project
Context:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is undertaking a project to modernize its currency management infrastructure, focusing on enhancing efficiency, security, and automation.
Key Features
- Advanced Storage & Handling: Upgraded facilities to manage the increasing volume of banknotes and coins.
- Automation & Efficiency: Implementation of warehouse automation and inventory management systems.
- Security Enhancements: Strengthening surveillance and security measures for currency handling.
- Centralized Command Center: Establishing a hub to coordinate nationwide currency management.
Why Now?
- Although the growth of Notes in Circulation (NIC) has moderated, cash usage is still expected to rise, necessitating infrastructure upgrades.
- The RBI seeks to reduce costs, improve security, and streamline operations, aligning with global best practices.
Global Benchmarking
Countries like the U.S., Japan, Germany, and Malaysia have undertaken similar initiatives to modernize their currency management systems.
Selection Process
- RBI received 11 Expressions of Interest (EoIs) and shortlisted six entities:
- Engineers India Limited (EIL)
- MECON
- Accenture Solutions
- Colliers International (India) Property Services
- PricewaterhouseCoopers
- The Boston Consulting Group (India)
- These firms will now move to the Request for Proposal (RFP) stage.
By modernizing its currency management, the RBI aims to enhance operational efficiency, security, and resilience, ensuring India’s readiness to meet future cash demands.
Source: BS
5. IndusInd Bank Leadership and RBI’s Role in CEO Appointments
Context:
On March 7, 2025, IndusInd Bank announced that the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) approved a one-year extension for MD & CEO Sumant Kathpalia until March 23, 2026. This decision followed a previous two-year extension, despite the bank’s request for three years. The RBI’s move signals concerns about Kathpalia’s leadership while avoiding sudden disruption.
The Derivatives Accounting Issue
Derivatives are financial contracts, set between two or more parties, that derive their value from an underlying asset, a group of assets, or a benchmark. A derivative can trade on an exchange or over the counter. Prices for derivatives derive from fluctuations in the prices of underlying assets.
- March 11, 2025: IndusInd Bank disclosed “discrepancies” in its derivatives accounting.
- Estimated impact: ₹1,600 crore, or 2.35% of net worth (as of Dec 2024).
- An external review is underway to verify the internal findings.
Market Reaction and RBI’s Response
- Stock market impact
- March 11: IndusInd Bank stock fell 3.86%.
- March 12: Historic crash of 27.6%, wiping out ₹18,000 crore in market value.
- March 15, 2025: RBI assured the public that:
- IndusInd Bank remains well-capitalized and financially stable.
- The bank must complete corrective actions within the current quarter.
- Depositors should not panic over speculative reports.
The Need for a Review of CEO Appointment Processes
- Current RBI approach
- CEO selections require RBI approval under Section 10B of the Banking Regulation Act.
- The board recommends candidates, but the RBI evaluates only the first choice.
- RBI has sometimes rejected all candidates, as seen in Tamilnad Mercantile Bank (2024).
- Challenges with the existing system
- Shortened tenures create uncertainty for investors and employees.
- If leadership is a concern, why not deny reappointment entirely?
- In global markets (e.g., JPMorgan Chase & Wells Fargo), boards have more control over CEO tenures.
Key Takeaways
- The RBI’s intervention in CEO appointments and tenure extensions needs a re-evaluation.
- Shortening CEO tenures without clarity on leadership concerns can create more market disruptions than necessary.
- India’s banking governance remains unique, but should RBI align its approach with international best practices?
6. Rupee Symbol Controversy
Political and Cultural Dimensions
- Symbolism vs. Unity
- Tamil Nadu’s decision to replace the rupee (
₹) symbol with a Tamil script equivalent sparked Centre-state tensions. - Union finance minister Nirmala Sitharaman viewed it as “regional chauvinism”, linking it to threats to national unity.
- The ruling DMK defended the move as a heritage assertion and part of Tamil linguistic pride, highlighting long-standing opposition to Hindi imposition.
- Tamil Nadu’s decision to replace the rupee (
- Political Context
- The controversy aligns with Tamil Nadu’s historical resistance to central linguistic policies.
- The episode fits within broader Centre-state power dynamics and regional identity politics.
- However, at its core, the debate is symbolic rather than economic, with no direct financial impact on the rupee itself.
Functional Importance of the Rupee Symbol (₹)
- The 2010 adoption of the
₹symbol was a strategic decision aimed at:- Global recognition: A distinct visual identity, similar to how Bitcoin (
₿) uses a recognizable glyph. - Cross-lingual familiarity: Designed from Devanagari ‘र’, but modified to resemble Latin ‘R’, appealing to English-speaking global markets.
- Psychological impact: The horizontal stroke enhances readability, making it instantly recognizable in financial transactions.
- Global recognition: A distinct visual identity, similar to how Bitcoin (
- Global Brand Power:
- Much like the dollar ($) and euro (€), brand strength matters in financial markets.
- Replacing the symbol weakens international consistency, creating potential confusion in global trade.
Economic and Technological Considerations for the Rupee
- Purchasing Power & Stability
- Regardless of symbol changes, the rupee’s real strength lies in its stability and purchasing power.
- Inflation control, currency reserves, and trade balances determine the rupee’s economic relevance, not its visual representation.
- Digital Evolution: The e-Rupee
- The RBI’s Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC), or e-Rupee, is the future of monetary transactions.
- Key benefits:
- Risk-free digital transactions (unlike private banks’ digital money).
- Efficient cross-border transfers with lower costs.
- Programmability, allowing controlled financial flows.
- As global finance moves toward digital currencies, India must ensure the rupee stays competitive in this transformation.
Geopolitical & Strategic Importance of the Rupee
- US Dollar Volatility & Currency Wars
- The US dollar’s global dominance may face challenges due to conflicting policies:
- The White House wants to maintain reserve currency status.
- Simultaneously, US economic policies may devalue the dollar to fix trade imbalances.
- This creates potential currency turbulence, making it crucial for India to strengthen and internationalize the rupee.
- The US dollar’s global dominance may face challenges due to conflicting policies:
- Future-proofing the Rupee
- India’s best response to potential global financial instability is to ensure the rupee remains stable, adaptable, and technologically advanced.
- The rupee’s long-term credibility depends on policy-driven resilience, not symbolic disputes.
Way Forward
- The political storm over the rupee symbol is largely symbolic, reflecting Centre-state frictions rather than economic imperatives.
- The
₹symbol has strong global recognition and aligns with modern branding principles. - Real challenges lie in currency stability, inflation control, and digital evolution (e-Rupee).
- India’s focus should be on strengthening the rupee’s global presence and adaptability, rather than debating symbolic heritage battles.
7. Banks’ Direct Integration with I4C
Context:
Large Indian banks and payments firms (e.g., Razorpay, Cashfree) are integrating with the Integrated Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C). Direct API integration will replace manual complaint processing, enabling instant alerts and automatic account freezing.
- Government Deadline
- Finance Ministry set January 31 as the deadline for integration.
- NPCI (National Payments Corporation of India) is already integrated for UPI transactions.
Rationale Behind the Move
- Rising Financial Fraud
- Only 10% of stolen funds were blocked in three years till 2022.
- In 2022, out of ₹2,294.8 crore reported stolen, only ₹57 lakh was recovered.
- Manual Processes Were Inefficient
- Banks previously relied on human intervention to process fraud complaints, causing delays and high manpower costs.
- Real-Time Fraud Mitigation
- API integration ensures instant action, preventing fraudsters from moving stolen funds.
- “Lien marking” (legal hold on disputed funds) is being integrated with banks’ Core Banking Systems (CBS).
Government & Regulatory Push
- Ministry of Electronics and IT (MeitY) confirmed banks are integrating with Citizen Financial Cyber Fraud Reporting & Management System (CFCFRMS).
- Collaboration with NPCI allows real-time responses to UPI fraud complaints.
- Efforts to track money trails across multiple mule accounts and prevent cross-border fund transfers via Nepal & Bangladesh.
Impact & Future Outlook
- Faster fraud response: Higher chances of recovering stolen money.
- Reduced operational burden on banks: Savings on manpower costs.
- More robust cybersecurity in digital payments: Increased consumer confidence.
- Potential expansion to wallets, NBFCs, and fintech players for broader fraud mitigation.
The direct integration of banks and fintech firms with I4C’s real-time fraud detection system marks a major step in India’s fight against financial fraud. While implementation challenges remain, this move could significantly improve fraud detection, recovery rates, and overall digital payment security.
Economy
1. RBI Rate Cut Prospects & Economic Implications
Key Economic Indicators Driving Rate Cut Expectations
- Retail Inflation Decline
- Consumer Price Index (CPI) inflation fell to 3.61% in February, down from 4.26% in January, slipping below the RBI’s 4% target for the first time in seven months.
- The steep drop in inflation provides the policy space for further rate cuts.
- Agricultural Output & Food Prices
- Rising farm output is expected to keep food prices stable, reinforcing the argument for monetary easing.
- Market Expectations & Policy Stance
- Most institutions predict a 25 bps rate cut in April, with some anticipating an additional 25 bps cut in June.
- The February repo rate cut (6.50% to 6.25%) was the first in five years, setting a dovish precedent for future rate reductions.
- Analysts, such as Nomura’s Sonal Varma, expect 75 bps total cuts by end-2025, implying further reductions in April, June, and August.
Financial Market Reactions & Monetary Policy Signals
- Interest Rate Derivatives Pricing in Cuts
- One-year OIS (Overnight Index Swap): Trading at 6.12%.
- Two-year OIS: Trading at 5.92%.
- The OIS market generally anticipates rate movements ahead of actual policy decisions, indicating market confidence in further cuts.
- Rupee Appreciation
- Rupee strengthened by 20 paise (87.01/$1), indicating positive sentiment following the expectation of rate cuts.
- Liquidity Infusion by RBI
- RBI has injected ₹1.5 lakh crore via Open Market Operations (OMO) and $20 billion through dollar-rupee swaps.
- This liquidity easing measure signals the central bank’s willingness to support lower borrowing costs.
Global Uncertainties & Potential Risks
- Some economists remain cautious about further rate action in June and beyond, citing:
- Global economic headwinds (trade tariffs, geopolitical risks).
- Currency fluctuations that may impact import costs and inflation.
- US Federal Reserve’s policy stance, which could affect capital flows and exchange rates.
Macroeconomic Implications of a Rate Cut
- Positive Impacts
- Lower borrowing costs: Encourages investment and consumer spending.
- Boosts liquidity: Supports credit growth and business expansion.
- Improves market sentiment: Strengthens rupee and financial market stability.
- Potential Risks
- Excessive easing could stoke inflationary pressures in the future.
- External shocks (currency volatility, global interest rate hikes) might limit RBI’s ability to sustain an extended rate cut cycle.
What Would be the Right Approach?
- The April rate cut (25 bps) is highly probable, with a June cut also in play, contingent on inflation trends and global stability.
- The financial markets are already pricing in a dovish RBI stance, reflecting strong expectations of continued monetary easing.
- RBI’s liquidity measures and intervention strategies suggest a commitment to reducing borrowing costs and supporting economic growth.
- Global uncertainties remain a wildcard, making further rate cuts beyond mid-2025 dependent on macroeconomic conditions.
Source: Economic Times
2. The Gold Rally
Drivers of the Gold Rally
- Safe-Haven Demand Due to Trump’s Economic Policies
- Investors are diversifying away from dollar exposure due to concerns over tariffs, trade policies, and economic uncertainty.
- Central banks, particularly in Asia, are buying gold to stabilize their reserves against US policy shifts.
- Macroeconomic Factors Supporting Gold’s Rise
- Stock market volatility is increasing demand for safe assets like gold.
- Rising inflation expectations make gold attractive as an inflation hedge.
- Easing interest rates (anticipated US Fed cuts) reduce the opportunity cost of holding non-yielding assets like gold.
- The US government’s borrowing program could impact global liquidity, indirectly benefiting gold.
Market Dynamics & Risks
- Sustained Institutional Demand vs. Weak Retail Sales:
- Strong institutional and central bank purchases continue to push prices higher.
- Retail demand is weakening, especially in Asia, due to:
- High gold prices, making jewellery less affordable.
- A stronger dollar, which increases local currency costs of gold imports.
- Off-season slump, further discouraging inventory buildup by jewellers.
- Speculative Risk to Gold Prices
- Large speculative long positions in the gold futures market could lead to a sudden price correction if unwound.
- However, fundamental drivers (central bank purchases, macro risks) are strong enough to mitigate a speculative downturn.
Impact on India’s Economy
- Gold Imports & Trade Deficit
- Gold import volumes are plateauing, offering temporary relief to India’s trade deficit.
- However, export uncertainty (due to slowing global demand and trade disruptions) may widen the deficit in the long run.
- Retail & Jewellery Sector Challenges
- High gold prices & a strong dollar are squeezing jewellery demand in India.
- The government has reduced import duties on jewellery to revive demand.
- More policy support may be needed, especially as festive-season gold buying approaches.
- RBI’s Gold Reserve Strategy
- The RBI remains cautious in its gold-buying approach, balancing between:
- Risk of revaluation losses if US Treasury yields rise.
- Gold’s role as a diversification tool against currency fluctuations.
- Unlike some Asian economies, India is not aggressively de-dollarizing trade, reducing the urgency for gold accumulation.
- The RBI remains cautious in its gold-buying approach, balancing between:
Way Forward
- The gold rally is likely to continue, supported by central bank buying, economic uncertainty, and US monetary easing.
- India’s jewellery sector is under pressure, requiring policy intervention to revive demand.
- The RBI’s gold-buying approach is cautious, reflecting a balanced reserve management strategy.
- The key risk is speculative unwinding, but strong fundamentals limit the likelihood of a major price correction.
Source: TET
Agriculture
1. Challenges of India’s Farmers Producer Organisations (FPOs)
Achievement of Target
- The government’s scheme to create 10,000 FPOs, launched in 2020 with a ₹6,865 crore allocation, has met its target.
- Including previously formed FPOs, the total count exceeds 44,400, with three million farmers involved, 40% of whom are women.
- However, many exist only on paper or struggle with commercial viability, raising concerns about the actual effectiveness of the scheme.
Economic and Structural Benefits of FPOs
- Improved Bargaining Power: Farmers gain better deals for inputs and marketing through bulk procurement and sales.
- Economies of Scale
- Shared resources (machinery, knowledge, inputs) reduce costs.
- Improved logistics, branding, and value addition help increase profitability.
- Legal Structure Advantage
- FPOs function as private companies rather than cooperatives, avoiding political interference that has plagued traditional cooperatives.
Key Challenges Hindering FPO Growth
- Financial Constraints
- FPOs struggle to secure credit as financial institutions perceive them as high-risk due to poor asset bases.
- Limited ability to raise equity due to the small financial capacity of members (mostly small or landless farmers).
- Lack of Professional Management
- Insufficient funds prevent FPOs from hiring skilled professionals for marketing, accounting, and strategy development.
- Operational Risks & Sustainability Issues
- FPOs lack risk mitigation measures to handle financial and production losses.
- Many struggle with scalability due to poor business models and limited value addition.
Policy Recommendations for Sustainable Growth
- Develop Robust Business Models
- Focus on value addition, branding, and processing to improve profitability.
- Capacity Building & Leadership Training
- Enhance managerial, technical, and administrative skills among FPO leaders.
- Integration of Digital & Modern Technologies
- Digital tools for quality control, marketing, and production efficiency can improve long-term viability.
- Continued Support Beyond the 10,000 FPO Milestone
- Expansion of the financial assistance program to ensure the sustainability of FPOs.
While India has successfully created 10,000 FPOs on paper, their long-term success depends on financial sustainability, professional management, and value-driven business models. A continued focus on technological integration, skill development, and market linkages will be crucial for ensuring that these farmer collectives thrive beyond mere numerical targets.
2. Parliamentary Panel’s Recommendations on Crop Insurance & Residue Management
Key Recommendations on PMFBY (Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana)
- Coverage Expansion
- Include damages caused by stray animals in crop loss coverage under PMFBY.
- Rationale: Farmers face frequent crop destruction from stray animals, leading to financial losses.
- Free Compulsory Crop Insurance for Small Farmers
- Coverage for farmers with land holdings of up to 2 hectares (similar to PMJAY health insurance model).
- Expected Benefits:
- Strengthens financial stability of smallholder farmers.
- Encourages investment in farming practices.
- Reduces risk of falling into debt traps due to crop failures.
- Operational Challenges in PMFBY
- Delays in fund release from states.
- Inadequate compensation against crop losses.
- The panel urged the government to resolve these issues for improved effectiveness.
Proposal to Curb Crop Residue Burning
- Financial Incentives for Farmers
- ₹100 per quintal of paddy to be provided as compensation for collection and disposal of crop residue.
- Payment via Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT), ensuring transparency and efficiency.
- Additional to Minimum Support Price (MSP).
- Alternative Crop Residue Management
- Conversion to bioenergy, composting, and other productive uses instead of burning.
- Need for policy interventions, farmer education, and technological innovations to support adoption.
- Long-term Strategy
- Pilot study on alternative residue management costs and benefits before scaling financial incentives.
Potential Impact of Recommendations
- Farmer Welfare
- Expanded insurance coverage reduces financial risks for small farmers.
- Compensation for crop residue collection provides economic relief and incentivizes sustainable farming.
- Environmental Benefits
- Reduced air pollution from stubble burning, especially in North India.
- Promotion of eco-friendly residue management techniques.
- Economic & Policy Considerations
- Higher fiscal burden on the government due to increased PMFBY coverage and direct incentives.
- Need for efficient policy execution to ensure timely fund disbursement.
The committee’s recommendations focus on expanding crop insurance, ensuring financial security for small farmers, and tackling the environmental hazards of stubble burning. While implementation challenges exist, these measures could significantly enhance agricultural sustainability and farmer resilience in India.
Source: BL
Facts To Remember
1. Mumbai Indians regains title, Delhi falters yet again
Two years after winning the inaugural edition of the Women’s Premier League, Mumbai Indians added another title to its cabinet with a heart-stopping eight-run win at the Brabourne Stadium.
2. Odia poet Ramakanta Rath dies at 90; President, Prime Minister express condolences
Renowned Odia poet and former bureaucrat Ramakanta Rath died at his residence in the Kharvel Nagar area here on Sunday, family sources said. He was 90.
3. Shi and An win All England crowns for the second time
Top seed Shi Yuqi beat Chinese Taipei’s Lee Chia Hao in straight games to win the All England Open title for a second time in Birmingham.
4. Leo — The Untold Story officially launched
A new book on Chennai Super Kings, Leo — The Untold Story, authored by senior advocate and former TNCA vice-president P.S. Raman, was officially launched in the presence of former CSK skipper M.S. Dhoni at a star-studded event.
5. Pradhan Mantri Aawas Yojana-Gramin (PMAY-G) scheme
A preliminary survey by the Odisha government has found that 44,743 rural households lack land, posing a major hurdle in providing houses under the Pradhan Mantri Aawas Yojana-Gramin (PMAY-G) scheme.
6. PM Modi commends RBI for being selected for Digital Transformation Award 2025
Prime Minister Narendra Modi today commended the Reserve Bank of India for being selected for the Digital Transformation Award 2025 by Central Banking, London, UK.
7. Wholesale price inflation rises to 2.38% in February
The Wholesale Price Index (WPI) inflation slightly increased to 2.38 per cent last month.
8. Former Union Minister Dr Debendra Pradhan passes away
Senior BJP leader and former Union Minister Dr Debendra Pradhan passed away this morning at the age of 84 in New Delhi.
9. Justice Joymalya Bagchi takes oath as Supreme Court judge
Chief Justice of India Sanjiv Khanna today administered the oath of office to Justice Joymalya Bagchi, a judge of the Calcutta High Court, as a Supreme Court judge.
10. India’s first-ever comprehensive river dolphin survey estimated presence of 6,327 river dolphins across the country
India’s first-ever comprehensive river dolphin survey has estimated the presence of 6,327 river dolphins across the country, with Assam recording 635 individuals in its five rivers.
11. Stuart Young to sworn in as new Prime Minister of Trinidad and Tobago today
Stuart Young, will sworn in as the new Prime Minister of Trinidad and Tobago, during a ceremony at the President’s House in St. Ann’s today.
12. Three day ASEAN Gaming Summit to begin in Philippines today
The three-day ASEAN Gaming Summit is set to begin at the Shangri-La the Fort in Manila, Philippines today.
13. Stranded astronauts Sunita Williams, Butch Wilmore on ISS return to Earth on Tuesday: Nasa
Two US astronauts stuck for more than nine months on the International Space Station will return to Earth tomorrow night.
14. Norway’s Statkraft Looks to Sell India Assets for $2 billion
Norwegian utility Statkraft hired EY to facilitate the sale of its Indian hydropower and solar power assets at an expected valuation of $2 billion, said people in the know. A formal launch of the sale process could start in 2-3 weeks and could see interest from global renewable power companies and investment funds, the people said.
















