Daily Current Affairs Quiz
11 June, 2025
National Affairs
1. State of the World Population 2025 Report
Source: United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA) & The Hindu
Context:
India’s population is estimated to have reached 146.39 crore by April, says a new UN demographic report, which adds that the country’s total fertility rate (TFR) has declined to 1.9, falling below the replacement level of 2.1.

Key Highlights:
- Global Population Trends:
- World population reached 8.2 billion in 2025.
- While population growth is slowing, significant disparities persist between high-income and low-income countries.
- Fertility Crisis Reframed:
- The real concern is unmet fertility goals—not overpopulation or underpopulation.
- Many individuals are unable to achieve desired family size due to lack of access to reproductive choices.
- Reproductive Rights and Agency:
- Focus on autonomy in reproductive decisions—when, how many, and whether to have children.
- Emphasizes access to contraception, healthcare, and education as foundational rights.
- Demographic Dividend Window:
- Over 60% of global population is aged 15–64, presenting a historic productivity opportunity.
- Potential for economic growth, especially in LMICs, if supported by education and job creation.
- Ageing Population Challenge:
- Rapid rise in the 65+ age group globally.
- Urgent need for healthcare systems, pension reforms, and social safety nets to support the elderly.
- Youth Bulge in LMICs:
- Countries like India, Nigeria have a high concentration of youth, posing both challenges and opportunities.
- Investing in skill development, health, and employment is crucial to harness this potential.
- Gender Gaps in Fertility and Healthcare:
- Women’s education, autonomy, and access to services directly influence fertility patterns.
- Persistent inequalities in contraception, maternal care, and family planning.
India’s Position
India’s Current Population Status (2025):
- Estimated population: 146.39 crore (April 2025)
- India is now the world’s most populous nation, overtaking China (141.61 crore)
Fertility Trends:
- Total Fertility Rate (TFR): Declined to 1.9, below the replacement level of 2.1
- TFR in 2021 (SRS data): 2.0 – replacement level “attained” nationally
- Replacement level TFR: Average number of children per woman required to maintain population level
- The report emphasizes reproductive agency – ensuring individuals have informed and free choices in reproductive matters
Population Growth Projection:
- India’s population expected to peak at 170 crore in the next ~40 years
- Post-peak, a gradual decline is anticipated due to sustained low fertility
Youth and Working-Age Demographics:
- 0–14 years: 24%
- 10–19 years: 17%
- 10–24 years: 26%
- Working age (15–64 years): 68% – reflects demographic dividend opportunity
Elderly Population and Life Expectancy:
- Aged 65+: 7% of total population in 2025
- Expected to rise significantly in future decades
- Life expectancy at birth (2025):
- Men: 71 years
- Women: 74 years
Census and Official Estimates:
- Last Census conducted in 2011
- The delayed 2021 Census now scheduled for completion by March 2027
- India’s internal population projection (2019): 141.10 crore by 2025
2. NABARD’s Rural Economic Conditions and Sentiments Survey (RECSS)
Context:
NABARD’s Rural Economic Conditions and Sentiments Survey (RECSS), conducted in May 2025 across 600 villages and 6,000 households, reveals a record-high rural income optimism, backed by positive employment sentiment, steady consumption patterns, and an above-normal monsoon forecast. This is the fifth round of the bi-monthly survey that began in September 2024.
Key Highlights:
Income Expectations at Historic High
- 73.6% of rural households expect their incomes to rise in the next 12 months — the highest ever recorded in RECSS.
- The proportion of respondents expecting income to fall dropped to 6.7% (lowest on record).
- Optimism is fueled by favorable monsoon predictions and improved farm income outlook.
One-Year Income Outlook Trends
| Survey Round | Income Increase | Income Decline | No Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sep 2024 | 70.2% | 7.3% | 22.5% |
| Nov 2024 | 71.3% | 7.8% | 20.9% |
| Jan 2025 | 71.2% | 7.4% | 21.4% |
| Mar 2025 | 72.2% | 7.5% | 20.3% |
| May 2025 | 73.6% | 6.7% | 19.7% |
Household Income – Past 12-Month Comparison
- 37.4% reported income growth (vs. 34.8% in March).
- 21.4% saw income decline; 41.3% reported no change.
Employment Sentiment Improves Sharply
- 53.5% expect better job opportunities in July–September 2025.
- Only 8% foresee deterioration in employment.
- Net positive sentiment: +45.4%, strongest since survey inception.
Consumption Remains Strong
- 79.1% of rural households reported increased spending (down slightly from 79.9% in March).
- Net consumption sentiment: +74.6%, indicating sustained rural demand.
Savings Sentiment Still Weak
- Only 18.8% households increased savings in May.
- 28.7% reported a decline in savings.
- Net savings sentiment remains negative at -9.9%, though slightly better than -11.9% in March.
- Savings sentiment has been in the red for five consecutive rounds.
Real Wages Outlook – FY26 (India Ratings)
- Real wage growth projected at 6.5%, marginally down from 7% in FY25.
- Supported by steady agricultural output.
- Risks include monsoon disruption, weather shocks, and global trade/geopolitical tensions.
3. Portal SAHAV Launched in Third United Nations Ocean Conference (UNOC3)
Context:
At the Third United Nations Ocean Conference (UNOC3) held in Nice, France, India called for urgent global collaboration on marine conservation and ocean governance. Union Minister Dr. Jitendra Singh led the Indian delegation, reaffirming India’s commitment to SDG-14 (Life Below Water).
Launch of SAHAV Digital Ocean Data Portal
- India introduced SAHAV, a real-time digital portal that:
- Facilitates open access to oceanic data
- Promotes transparent, evidence-driven ocean governance
- Aims to support climate forecasting, marine resource tracking, and disaster early warnings
Key Highlights:
- Call for Global Pact & Legal Frameworks:
- India advocated for a Global Ocean Pact and speedy ratification of the BBNJ Agreement (Biodiversity Beyond National Jurisdiction).
- Supported the creation of a legally binding Global Plastics Treaty to combat marine pollution.
- Deep Ocean Mission and Samudrayaan:
- Progress on ‘Samudrayaan’, India’s first manned deep-sea submersible, targeting ocean exploration up to 6,000 meters by 2026.
- Represents a leap in India’s marine scientific capabilities.
- Marine Conservation & Biodiversity:
- Expansion of Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) to 6.6% of India’s EEZ.
- Restoration of 10,000+ hectares of mangroves and launch of shoreline management plans using nature-based solutions.
- Marine Pollution & Plastic Cleanup:
- ‘Swachh Sagar, Surakshit Sagar’ campaign cleaned coastline and removed tonnes of plastic waste.
- Draft Marine Litter Policy prepared; India committed to supporting global plastics treaty negotiations.
- Blue Economy Investment & Fisheries Modernization:
- Highlighted progress under Sagarmala and Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY):
- Climate Resilience and Paris Commitments:
- Integrated ocean-based climate actions into India’s NDCs under the Paris Agreement.
- Promoted marine spatial planning through India-Norway collaboration.
4. Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
Context:
Indian venture capital funding is undergoing a structural shift from pure-play SaaS (Software-as-a-Service) companies to AI-native startups, as investors prioritize scalability, automation, and deep tech innovation.
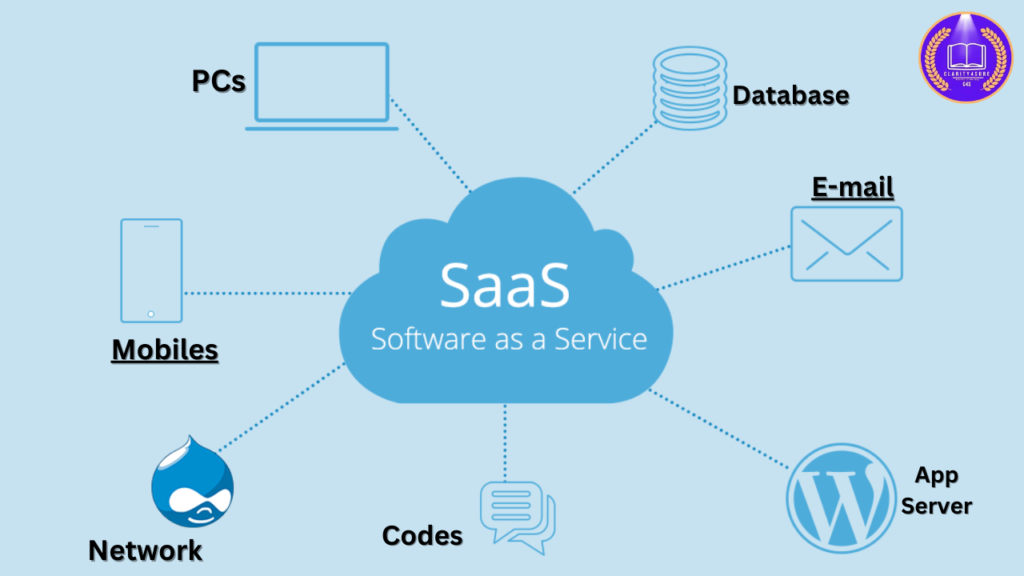
What is Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)?
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) is a cloud-based software delivery model where applications are hosted by a service provider and made available to users via a web browser. Unlike traditional on-premises software, SaaS does not require installation, maintenance, or hardware infrastructure, as everything is managed by the vendor.
How SaaS Works ?
- Application Hosting –
- SaaS providers host applications on remote cloud servers.
- Internet Access –
- Users access the application via a web browser or dedicated app.
- Subscription Model –
- SaaS software is typically offered on a subscription basis (monthly/annually).
- Automatic Updates –
- The provider manages software updates, security patches, and maintenance.
- Scalability –
- Users can scale services up or down based on their business needs.
Benefits of SaaS
Cost Efficiency
- No need for expensive hardware or software licenses.
- Subscription-based pricing allows businesses to pay for what they use.
- Reduced IT maintenance costs, as providers handle updates and support.
Accessibility & Remote Work
- SaaS applications can be accessed from any device with an internet connection.
- Ideal for remote teams and businesses with multiple locations.
Automatic Updates & Maintenance
- Service providers manage all software updates and security patches.
- No need for manual installation or system downtime for upgrades.
Scalability & Flexibility
- Businesses can easily upgrade/downgrade their SaaS plans as per demand.
- Supports business growth without additional infrastructure costs.
Security & Compliance
- Leading SaaS providers implement high-end encryption, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and compliance certifications (GDPR, HIPAA, SOC 2, etc.) to ensure data security.
- Regular data backups prevent loss of critical information.
Seamless Integration
- SaaS applications often support API integrations with other software (e.g., CRM, ERP, accounting tools).
- Businesses can connect SaaS solutions with their existing workflows.
5. Jan Man Survey Launched on NaMo App
Context:
To commemorate 11 years of Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s leadership, the NaMo App launched a large-scale citizen engagement survey titled ‘Jan Man Survey’, aimed at gathering public opinion on governance, security, and development.
Key Highlights:
- About the Jan Man Survey:
- Launched via: NaMo App (June 2025)
- Objective: To collect real-time feedback from citizens on the performance of the government and future priorities.
- Survey Focus Areas:
- Governance and administration
- National security
- Cultural pride and heritage
- Youth empowerment and development
- Significance & Impact:
- Promotes participatory governance and direct democracy
- Strengthens digital civic engagement
- Encourages transparency and accountability through citizen-driven feedback mechanisms
- Digital Governance Tools:
- Utilizes the NaMo App as a tech-enabled feedback platform
- Integrates data insights into policy communication and perception management
6. Thailand’s National Bird Siamese Fireback
Context:
In a rare ecological occurrence, the Siamese Fireback (Lophura diardi)—Thailand’s national bird—was sighted for the first time in India, in the forests of Ranikhet, Uttarakhand, by a local bird enthusiast.
Key Highlights:
- About the Siamese Fireback:
- Scientific Name: Lophura diardi
- IUCN Status: Least Concern (IUCN), but witnessing moderate population decline due to habitat loss and poaching
- National Symbol: Official bird of Thailand
- Native Geographic Range:
- Commonly found in:
- Thailand
- Laos
- Cambodia
- Vietnam
- Commonly found in:
Banking/Finance
1. Finance Minister on Unclaimed Assets
Context:
Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman chaired the 29th meeting of the Financial Stability and Development Council (FSDC) in Mumbai on June 11, 2025, where she emphasized reducing unclaimed assets and ensuring seamless refund to rightful owners. The meeting also reviewed macro-financial stability, regulatory reforms, and investment strategies.
Key Highlights:
Focus on Unclaimed Assets
- FM urged regulators to reduce unclaimed financial assets, including:
- Bank deposits
- Unclaimed dividends and shares
- Post office savings
- Insurance and pension funds
- Directed district-level special camps to facilitate refunds in coordination with:
- RBI, SEBI, IRDAI, PFRDA, Ministry of Corporate Affairs, banks, and other financial institutions.
What is Unclaimed Assets?
Unclaimed assets refer to financial assets (money, shares, mutual funds, etc.) that have been left unclaimed or inactive by their owner for an extended period. These assets can become unclaimed due to various reasons, including death of the account holder, a change of address, or simply forgetting about them.
- Examples:
- Unclaimed assets can include forgotten bank accounts, uncashed checks, dormant stocks, and other financial assets.
- Reasons for Unclaimed Assets:
- Death of the account holder.
- Change of address without updating financial institutions.
- Lack of awareness about the assets.
- Incomplete documentation.
- Government Involvement:
- After a specified period, unclaimed assets are typically turned over to the government or state treasury.
- Claiming the Assets:
- The rightful owner or beneficiary can file a claim to retrieve the unclaimed assets.
- Digitalization and Unclaimed Assets:
- There are ongoing efforts to improve the process of identifying and retrieving unclaimed assets, including through digital platforms like Digilocker.
2. SEBI Probes Jane Street for Algorithmic Manipulation
Context:
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has launched an investigation into the activities of Jane Street, a global proprietary trading firm, for potential manipulation of benchmark indices through algorithmic trades in India’s Nifty 50 and banking indices. The probe spans the last three years and follows complaints from rival firms over unusual trading patterns and supernormal profits.
What Is Jane Street?
- A global quantitative trading firm founded in 2000 in New York.
- Operates across ETFs, equities, bonds, and derivatives.
Why Is SEBI Investigating Jane Street?
- Allegations of algorithmic manipulation using high-frequency trading (HFT).
- Specific trades flagged by NSE in January 2025 involved rapid buy-sell reversals at extreme prices, possibly impacting price discovery.
- The probe is part of SEBI’s larger effort to protect retail investors, who have suffered heavy losses in F&O markets.
What is Algorithmic Manipulation?
Algorithmic Manipulation refers to the intentional use of algorithmic trading systems—such as automated, high-frequency, or black-box algorithms. This includes generating false or misleading signals about supply, demand, or price of securities, often to mislead other market participants for unfair gain.
Key Elements:
- Intentional misuse of automated trading logic.
- Distortion of market prices, order book dynamics, or trading volumes.
- Can involve spoofing, layering, quote stuffing, or momentum ignition.
- Violates principles of market integrity and transparency.
India’s Current Legal Framework:
- SEBI (Prohibition of Insider Trading) Regulations, 2015:
- Focuses on preventing misuse of Unpublished Price Sensitive Information (UPSI).
- Enacted for traditional manual trading; lacks specificity for algorithmic contexts.
- Insufficient to track automated insider trading without AI-enabled enforcement tools.
- Key Gaps Identified:
- Absence of mandatory algorithm disclosure and audit norms.
- No clear definition or legal interpretation of “algorithmic intent”.
- Limited tech-based surveillance and reliance on post-facto compliance reviews.
BS
3. Alternative Investment Funds (AIFs)
Context:
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has extended the deadline for winding up expired Venture Capital Funds (VCFs) by one year, allowing more time for liquidation. However, it has mandated migration to the Alternative Investment Fund (AIF) framework by 19 July 2025, with one additional year granted for full liquidation after migration.
What Are Alternative Investment Funds (AIFs)?
Alternative Investment Funds (AIFs) are privately pooled investment vehicles that raise funds from investors to invest in non-traditional assets such as private equity, venture capital, hedge funds, infrastructure, and social impact ventures. These differ from conventional instruments like stocks and mutual funds and are governed under the SEBI (Alternative Investment Funds) Regulations, 2012.
Legal Structure:
AIFs in India can be formed as:
- Trusts
- Limited Liability Partnerships (LLPs)
- Companies
- Other permissible entities
Types of AIFs in India
Category I: Growth-Oriented and Impact Investments
Focus: Promote innovation, start-ups, SMEs, and social impact.
- Venture Capital Funds (VCFs): Finance high-growth start-ups; high risk, high return.
- Angel Funds: Early-stage funding with ₹25 lakh minimum per investor.
- Infrastructure Funds: Invest in sectors like transport, energy, and urban development.
- Social Venture Funds: Support impact-driven ventures in health, education, etc.
Category II: Private and Debt-Oriented Funds
Focus: Invest in private equity and debt without leverage.
- Private Equity (PE) Funds: Back unlisted firms with long lock-in periods.
- Debt Funds: Invest in unlisted debt securities with strong governance.
- Fund of Funds (FoFs): Invest in units of other AIFs for diversified exposure.
Category III: High-Risk, Market-Linked Strategies
Focus: Aggressive strategies, including leverage and arbitrage.
- PIPE Funds: Buy publicly traded shares at discounted prices.
- Hedge Funds: Invest in domestic/global markets using derivatives and leverage; high fee structure (typically 2% management + 20% performance fee).
Investor Eligibility and Requirements:
- Who Can Invest: Resident Indians, NRIs, foreign nationals.
- Minimum Investment: ₹1 crore (₹25 lakh for fund managers, employees, directors).
- Lock-in Period: Minimum 3 years.
- Investor Cap: Max 1,000 investors per scheme (49 for Angel Funds).
Key Benefits of AIFs:
- High Return Potential: Access to strategic and alternative investment models.
- Lower Volatility: Less sensitivity to public market movements.
- Diversification: Broader exposure beyond traditional equities and debt instruments.
- Tailored Investment Strategies: Better alignment with specific financial goals of HNIs.
4. SEBI Issues Recovery Notice to OPG Securities in NSE Co-Location Case
Context:
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has initiated recovery proceedings against OPG Securities and its directors for failing to pay penalties linked to the NSE co-location case, involving unfair trading access.
- Background:
- The penalty was originally imposed in April 2024
- It relates to unfair access to NSE’s secondary market servers via the co-location facility
- OPG Securities allegedly gained preferential access, violating fair market norms
NSE Co-Location Case
The NSE co-location case involves allegations that the National Stock Exchange of India (NSE) granted preferential access to certain stockbrokers through its co-location facility, giving them an unfair speed advantage in executing trades. This case has raised serious concerns about market integrity, transparency, and regulatory oversight in India’s capital markets.
Key Aspects of the NSE Co-Location Case
Co-Location Facility:
- The NSE allows brokers to place their trading servers in close proximity to the exchange’s main servers.
- This proximity reduces latency (delay in data transmission), enabling faster trade execution.
Secondary Server Access:
- Some brokers allegedly gained unfair and repeated access to NSE’s Secondary Point of Presence (POP) servers, which were less crowded and had faster data transmission.
- This resulted in preferential treatment and a latency advantage over other brokers.
Tick-by-Tick (TBT) Data Feed:
- The TBT feed provides real-time order book data to market participants.
- The allegations state that certain brokers were able to log in first and receive TBT data ahead of others, helping them anticipate market trends and front-run trades.
Unfair Market Advantage:
- By accessing faster and earlier market data, these brokers could execute trades with higher speed and accuracy.
- This compromised the level playing field, potentially harming retail investors and fair market participants.
Regulatory and Legal Actions:
- SEBI investigated the case and found violations of fair access norms.
- Penalties were imposed on NSE, certain brokers like OPG Securities, and individual officials.
- In 2024, SEBI dropped charges against NSE and its ex-officials citing lack of evidence, but maintained penalties on brokers.
- The Securities Appellate Tribunal (SAT) and the Supreme Court are still hearing appeals related to this matter.
5. SEBI’s Social Bonds, Sustainability Bonds, and Sustainability-Linked Bonds (SLBs) Framework
Context:
On June 5, 2025, the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) introduced a comprehensive operational framework for ESG debt securities. This applies to Social Bonds, Sustainability Bonds, and Sustainability-Linked Bonds (SLBs), excluding green bonds (which are already covered under a separate regulation).
Objective:
To ensure transparency, credibility, and accountability in ESG-labelled debt instruments and to curb “purpose-washing” (misuse of ESG labels without genuine impact).
Key Highlights:
- Applicable Instruments:
- Social Bonds: Targeting social projects (e.g., healthcare, education, food security)
- Sustainability Bonds: Blend of environmental and social goals
- Sustainability-Linked Bonds (SLBs): Linked to performance-based ESG targets
- Effective Date:
- Framework applicable from June 5, 2025, for all fresh issuances of these instruments
- Disclosures & Reporting:
- Offer Document Must Include:
- ESG objectives, project categories, eligibility criteria
- Intended use of proceeds and project evaluation mechanisms
- Post-Issuance Disclosures:
- Annual reporting on fund utilization and ESG impact
- For SLBs, status of achievement of sustainability KPIs
- Offer Document Must Include:
- Third-Party Review Mandatory:
- Issuers must appoint an external reviewer or certifier
- Certifications must align with international frameworks like:
- ICMA Principles
- EU Green Bond Standards
- ASEAN Social/Sustainability Bond Standards
- Climate Bonds Initiative
- Penalties for Non-Compliance:
- SLBs failing to meet stated ESG targets may trigger:
- Higher coupon payments or
- Other financial penalties
- SLBs failing to meet stated ESG targets may trigger:
- Purpose:
- To align India’s ESG debt market with global standards
- To attract sustainable finance into socially beneficial and verifiable ESG projects
- To ensure investor protection through verified impact reporting
Significance:
- Brings standardization and governance in ESG bond issuances
- Prevents green/social washing by ensuring clear frameworks and accountability
- Boosts investor confidence and aligns India’s market with global ESG trends
- Supports India’s sustainable development goals and climate finance commitments
6. AU Small Finance Bank Partners with IFC to Integrate Climate Risk into Core Banking Operations (June 2025)
Context:
AU Small Finance Bank (AU SFB) has entered into a strategic partnership with the International Finance Corporation (IFC) to embed climate risk into its core banking systems. This initiative enhances the bank’s alignment with global climate resilience standards and the Reserve Bank of India’s evolving climate-related financial guidelines.
Objective:
To build climate risk resilience into AU SFB’s governance, risk management, strategy, and ESG disclosures—boosting long-term sustainability and compliance with frameworks like TCFD and NGFS.
Key Features of the Climate Risk Program:
- Physical Risk Assessment:
- Evaluates the vulnerability of AU SFB’s loan portfolio to climate-induced natural disasters (floods, droughts, extreme weather).
- Uses IPCC scenarios through the year 2100.
- Transition Risk Assessment:
- Analyzes financial exposure to policy, market, and technology shifts in India’s transition to a low-carbon economy.
- Follows Network for Greening the Financial System (NGFS) transition risk scenarios.
- Financed Emissions Calculation:
- Measures Scope 3, Category 15 emissions (financed emissions) across:
- Corporate loans
- SME finance
- Real estate
- Sovereign bonds
- Uses PCAF (Partnership for Carbon Accounting Financials) methodology
- Covers FY 2024–25 and FY 2025–26.
- Measures Scope 3, Category 15 emissions (financed emissions) across:
Significance:
- Embeds climate risk into AU SFB’s risk framework and business strategy
- Aligns with RBI’s sustainable finance agenda
- Supports long-term climate-resilient banking practices in India
- Strengthens climate disclosure and ESG reporting standards in Indian banking
About AU Small Finance Bank (AU SFB):
- Founded: 1996
- MD & CEO: Sanjay Agarwal
About International Finance Corporation (IFC):
- Formation: July 20, 1956
- Headquarters: Washington, D.C., USA
- MD: Makhtar Diop
- Membership: 186 countries
7. RBI Annual Report Flags India’s FDI Paradox
Context:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI), in its Annual Report 2024–25, highlighted a paradox in India’s foreign direct investment (FDI) landscape. While gross FDI inflows rose by 13.7%, net FDI sharply dropped to just $0.4 billion, compared to $44 billion in FY 2020–21, driven by high disinvestments and repatriation.
What is FDI?
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) is investment by foreign entities in India’s productive sectors (equity, joint ventures, greenfield, etc.), aimed at:
- Capital inflow for infrastructure and startups
- Technology transfer and skill enhancement
- Job creation
- Support to balance of payments (BoP)
Key Findings – RBI Annual Report 2024–25:
- Gross vs Net Disparity:
- Gross inflows: Up 13.7% in FY25
- Net FDI: Down to $0.4 billion (from $44 billion in FY21) due to sharp rise in disinvestments
- FDI Composition Concerns:
- High disinvestment rate: Now 63.5% of gross FDI
- Major sources: Singapore (15%), Mauritius (~10%) – reflecting round-tripping and tax haven usage
- Fall in manufacturing FDI share: Down to 12% from previous peaks
- Long-Term Trends:
- Average annual FDI growth (FY21–FY25): Just 0.3%
- Outward FDI (OFDI): Rose to $29.2 billion, tripling in 5 years
- Rising private equity and venture capital flows focused on exits rather than production
- Sectoral and Geographic Issues:
- Withdrawal from productive sectors: Manufacturing, computer services see declining FDI
- Drop in FDI from innovation hubs like the US, Germany, and UK
- Discrepancy between RBI and UNCTAD FDI figures: RBI estimates up to 60% higher
Structural Challenges in India’s FDI Framework:
- Over-reliance on financial flows vs. greenfield investments
- Policy uncertainty and tax complications
- Limited reforms in labour, land acquisition, and judicial ease
- Weak monitoring of FDI’s real economic impact
Policy Recommendations – The Way Forward:
- Ensure Policy Consistency:
- Clear, stable FDI rules to attract long-term investors
- Prioritize Quality over Quantity:
- Target manufacturing, green energy, and R&D-driven investments
- Domestic Reforms Alignment:
- Improve ease of doing business, simplify labour and land laws
- Tax Treaty Rationalization:
- Prevent round-tripping through financial centres like Mauritius
- Robust Monitoring Mechanism:
- Evaluate sector-wise FDI impact, employment creation, and value addition
8. Zero-Coupon Bonds
Context:
Zero-Coupon Bonds (ZCBs), or deep-discount bonds, are fixed-income instruments issued at a discount and redeemed at face value. Popular among HNIs and family offices for their tax efficiency and lump-sum maturity payout, ZCBs saw high demand in late 2024. However, recent monetary and market developments have weakened investor interest.
What Is a Zero-Coupon Bond?
A Zero-Coupon Bond (ZCB) is a type of debt security that does not pay periodic interest (coupons). Instead, it is sold at a deep discount and redeemed at full face value (par value) upon maturity. The investor’s return is the difference between the purchase price and maturity value.
Also known as: Accrual Bond
Key Features of Zero-Coupon Bonds:
- No periodic interest payments (coupons)
- Issued at a discount, repaid at full face value at maturity
- Return = Par Value – Purchase Price
- Subject to interest rate risk if sold before maturity
- Longer maturity = deeper discount = more price volatility
Who Issues ZCBs?
- Government entities
- Corporations
- Financial institutions (which may strip coupons and repackage bonds)
How Zero-Coupon Bonds Work:
- Investor buys a ZCB at a low price (e.g., ₹6,855)
- At maturity, the investor receives full face value (e.g., ₹20,000)
- The implied yield (e.g., 5.5%) is compounded semiannually
- No interim payments; interest is “imputed” or “phantom” interest
Pricing Formula:

Where:
- M = Maturity Value (Face Value)
- r = Required Interest Rate (Yield)
- n = Years to Maturity
Taxation of Zero-Coupon Bonds:
- Imputed interest is taxable annually, even though no cash is received until maturity
- Taxed as ordinary income, not capital gains
- Known as “phantom interest”
- Ways to avoid tax:
- Buy municipal zero-coupon bonds (often tax-exempt)
- Hold in tax-deferred or tax-exempt accounts (e.g., retirement funds)
- Invest in tax-exempt corporate ZCBs
Advantages of ZCBs:
- Predictable lump-sum payout at maturity
- No reinvestment risk (unlike coupon-bearing bonds)
- Useful for long-term goals (e.g., education, retirement)
- Higher price sensitivity provides opportunities in falling interest rate scenarios
Disadvantages:
- No interim income
- Higher duration and price volatility
- Taxation on imputed interest
- Limited liquidity in secondary markets
Zero-Coupon Bond vs. Regular Bond:
| Feature | Zero-Coupon Bond | Regular (Coupon) Bond |
|---|---|---|
| Interest Payment | None (imputed, not paid) | Paid periodically (semiannual/annual) |
| Purchase Price | Deep discount to face value | Close to face value |
| Return | At maturity (par – purchase price) | Coupons + principal at maturity |
| Price Volatility | Higher | Lower |
| Tax on Interest | On imputed interest annually | On actual coupons received |
Economy
1. World Bank Retains India’s FY26 GDP Growth
Context:
The World Bank, in its Global Economic Prospects Report (June 2025), retained India’s FY26 GDP growth forecast at 6.3%, while projecting a gradual decline in the public debt-to-GDP ratio due to higher tax revenues and lower current expenditures.
Key Highlights:
India’s Growth Outlook:
- FY26 GDP growth forecast: Retained at 6.3%.
- Despite global headwinds, India is set to maintain the fastest growth among large global economies.
- Growth moderation in FY25 attributed to slower industrial output, but rebound expected from FY27 onwards, averaging 6.6% annually.
- Services sector and export recovery are seen as key drivers of medium-term growth.
Fiscal Outlook and Debt Management:
- The World Bank noted India’s shift from a fiscal deficit target to a debt-to-GDP anchor.
- The government targets bringing debt-to-GDP down to 50% by FY31, allowing for a ±1% deviation.
- Fiscal consolidation will be aided by:
- Higher tax revenues
- Falling current expenditures
Regional & Global Trends:
- India’s import demand will support trade across the South Asia region.
- Global growth in 2025 is projected at 2.3%, the weakest in 17 years excluding recessions.
- Trade tensions, policy uncertainty, and geopolitical risks pose downside risks.
- The report encourages developing countries to:
- Diversify trade
- Enter regional trade agreements
- Pursue strategic investment partnerships
Agriculture
1. India Launches ₹300 Cr Clean Plant Projects to Boost Horticulture
Context:
Union Agriculture Minister Shivraj Singh Chouhan, at the conclusion of India’s first International Agri Hackathon held in Pune, announced the launch of nine ‘Clean Plant’ projects across India. The initiative is aimed at supplying disease-free planting materials and boosting India’s horticulture competitiveness.
Key Announcements:
- Clean Plant Projects:
- Total Projects: 9 nationwide
- Maharashtra: 3 major centres at a cost of ₹300 crore
- Pune: Clean planting material for grapes
- Nagpur: Focus on oranges
- Solapur: Focus on pomegranates
- Objective: To produce 8 crore healthy seedlings annually through modern nurseries
- Funding Support for Nurseries:
- Large nurseries: ₹3 crore assistance
- Medium nurseries: ₹1.5 crore assistance
- Global Collaboration:
- International partners: Israel and Netherlands
- Role: Support modern horticulture technologies and practices
Key Policy Initiatives:
- Lab to Land Mission:
- 16,000 agricultural scientists to engage directly with farmers
- Focus: Transfer of seed technologies, disease solutions, yield optimization
- Youth & Startups:
- Emphasis on agri-entrepreneurship among the youth
- Promotion of agri-tech innovation in AI, mechanization, soil health, post-harvest tech, and pest control
- Viksit Krishi Sankalp Abhiyan 2025:
- Ongoing outreach campaign for farmer welfare and innovation diffusion
- Focus areas: Combat fake fertilizers, promote modern techniques, and improve market linkages
PIB
Facts To Remember
1. World Bank retains India growth forecast
The World Banks Global Economic Prospectss Report on Tuesday said that growing tax revenues and declining current expendituress are projected to contribute toa graduall decline in Indias public debttoGDP ratio and fiscal consolidation.
2. Pooran retires from international cricket
West Indies cricketer Nicholas Pooran, aged 29, has retired from international cricket as of June 11, 2025.
3. RBI Discontinues Daily VRR Auctions Amid Rs 3 Lakh Crore Liquidity Surplus
The Reserve Bank of India has discontinued daily Variable Rate Repo (VRR) auctions starting today, in view of a liquidity surplus in the banking system, currently estimated at around 2.75 to 3 lakh crore rupees.
4. PM Modi Reaffirms Commitment to Welfare-Driven Growth as Social Security Coverage Hits 64.3%
Prime Minister Narendra Modi today reaffirmed the government’s unwavering dedication to welfare-driven development, ensuring that various pro-people schemes reach maximum number of citizens
5. India’s social security coverage jumps to 64.3%, ranks 2nd globally: ILO
India’s social security coverage has increased from 19 per cent in 2015 to 64.3 per cent in 2025. According to the latest data from the International Labour Organisation’s ILOSTAT, the coverage reflects a 45 percentage point surge over the past decade.
6. A decade of transformation: Seva, Sushasan, & Garib Kalyan driving ease of living
India has undergone a decade of remarkable transformation, driven by the principles of Seva, Sushasan, and Garib Kalyan. Akashvani News brings you a special feature on the Government’s efforts over the last 11 years across key sectors.
7. Government sets target of 3 lakh crore rupees defence production by 2029
Defence Minister Rajnath Singh said that the government has set a target of 3 lakh crore rupees for defence production by 2029. Addressing an event on the topic ‘National Security & Terrorism’, organised in Dehradun, Uttarakhand, Mr Rajnath Singh added that the country’s exports in the sector will reach 50,000 crore by that time.
















